Researchers Develop AI Algorithm to Predict Immunotherapy Response
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 12 Sep 2018 |
A team of French researchers have designed an algorithm and developed it to analyze Computed Tomography (CT) scan images, establishing for the first time that artificial intelligence (AI) can process medical images to extract biological and clinical information. The researchers have created a so-called radiomic signature, which defines the level of lymphocyte infiltration of a tumor and provides a predictive score for the efficacy of immunotherapy in the patient.
In the near future, this could make it possible for physicians to use imaging to identify biological phenomena in a tumor located anywhere in the body without performing a biopsy.
Currently, there are no markers, which can accurately identify patients who will respond to anti-PD-1/PD-L1 immunotherapy in a situation where only 15 to 30% of patients do respond to such treatment. The more immunologically richer the tumor environment (presence of lymphocytes), the higher is the chances of immunotherapy being effective. Hence, the researchers tried to characterize this environment using imaging and correlate this with the patients’ clinical response. In their study, the radiomic signature was captured, developed and validated genomically, histologically and clinically in 500 patients with solid tumors (all sites) from four independent cohorts.
The researchers first used a machine learning-based approach to teach the algorithm how to use relevant information extracted from CT scans of patients participating in an earlier study, which also held tumor genome data. Thus, based solely on images, the algorithm learned to predict what the genome might have revealed about the tumor immune infiltrate, in particular with respect to the presence of cytotoxic T-lymphocytes (CD8) in the tumor, thus establishing a radiomic signature.
The researchers tested and validated this signature in other cohorts, including that of TCGA (The Cancer Genome Atlas), thus demonstrating that imaging could predict a biological phenomenon, providing an estimation of the degree of immune infiltration of a tumor. Further, in order to test the signature’s applicability in a real situation and correlate it to the efficacy of immunotherapy, it was evaluated using CT scans performed before the start of treatment in patients participating in five phase I trials of anti-PD-1/PD-L1 immunotherapy. The researchers found that the patients in whom immunotherapy was effective at three and six months had higher radiomic scores as did those with better overall survival.
In their next clinical study, the researchers will assess the signature both retrospectively and prospectively, using a larger number of patients and stratifying them based on cancer type in order to refine the signature. They will also use more sophisticated automatic learning and AI algorithms to predict patient response to immunotherapy, while integrating data from imaging, molecular biology and tissue analysis. The researchers aim to identify those patients who are most likely to respond to treatment, thereby improving the efficacy/cost ratio of treatment.
In the near future, this could make it possible for physicians to use imaging to identify biological phenomena in a tumor located anywhere in the body without performing a biopsy.
Currently, there are no markers, which can accurately identify patients who will respond to anti-PD-1/PD-L1 immunotherapy in a situation where only 15 to 30% of patients do respond to such treatment. The more immunologically richer the tumor environment (presence of lymphocytes), the higher is the chances of immunotherapy being effective. Hence, the researchers tried to characterize this environment using imaging and correlate this with the patients’ clinical response. In their study, the radiomic signature was captured, developed and validated genomically, histologically and clinically in 500 patients with solid tumors (all sites) from four independent cohorts.
The researchers first used a machine learning-based approach to teach the algorithm how to use relevant information extracted from CT scans of patients participating in an earlier study, which also held tumor genome data. Thus, based solely on images, the algorithm learned to predict what the genome might have revealed about the tumor immune infiltrate, in particular with respect to the presence of cytotoxic T-lymphocytes (CD8) in the tumor, thus establishing a radiomic signature.
The researchers tested and validated this signature in other cohorts, including that of TCGA (The Cancer Genome Atlas), thus demonstrating that imaging could predict a biological phenomenon, providing an estimation of the degree of immune infiltration of a tumor. Further, in order to test the signature’s applicability in a real situation and correlate it to the efficacy of immunotherapy, it was evaluated using CT scans performed before the start of treatment in patients participating in five phase I trials of anti-PD-1/PD-L1 immunotherapy. The researchers found that the patients in whom immunotherapy was effective at three and six months had higher radiomic scores as did those with better overall survival.
In their next clinical study, the researchers will assess the signature both retrospectively and prospectively, using a larger number of patients and stratifying them based on cancer type in order to refine the signature. They will also use more sophisticated automatic learning and AI algorithms to predict patient response to immunotherapy, while integrating data from imaging, molecular biology and tissue analysis. The researchers aim to identify those patients who are most likely to respond to treatment, thereby improving the efficacy/cost ratio of treatment.
Latest Imaging IT News
- New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
- Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
- AI-Based Mammography Triage Software Helps Dramatically Improve Interpretation Process
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) Program Accurately Predicts Lung Cancer Risk from CT Images
- Image Management Platform Streamlines Treatment Plans
- AI-Based Technology for Ultrasound Image Analysis Receives FDA Approval
- AI Technology for Detecting Breast Cancer Receives CE Mark Approval
- Digital Pathology Software Improves Workflow Efficiency
- Patient-Centric Portal Facilitates Direct Imaging Access
- New Workstation Supports Customer-Driven Imaging Workflow
Channels
Radiography
view channel
Routine Mammograms Could Predict Future Cardiovascular Disease in Women
Mammograms are widely used to screen for breast cancer, but they may also contain overlooked clues about cardiovascular health. Calcium deposits in the arteries of the breast signal stiffening blood vessels,... Read more
AI Detects Early Signs of Aging from Chest X-Rays
Chronological age does not always reflect how fast the body is truly aging, and current biological age tests often rely on DNA-based markers that may miss early organ-level decline. Detecting subtle, age-related... Read moreMRI
view channel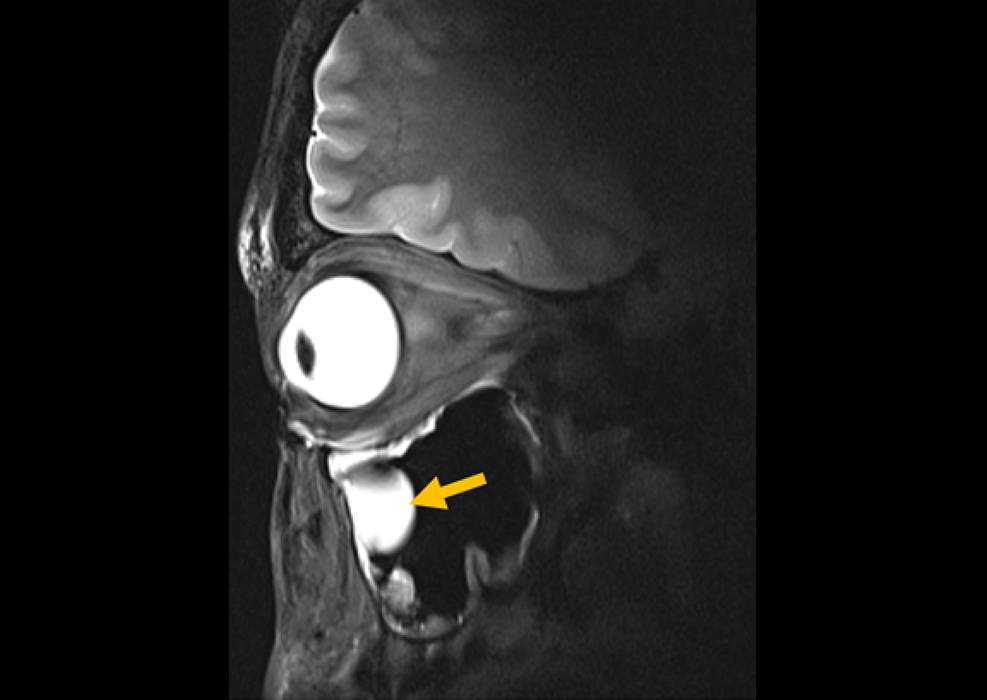
New Material Boosts MRI Image Quality
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a cornerstone of modern diagnostics, yet certain deep or anatomically complex tissues, including delicate structures of the eye and orbit, remain difficult to visualize clearly.... Read more
AI Model Reads and Diagnoses Brain MRI in Seconds
Brain MRI scans are critical for diagnosing strokes, hemorrhages, and other neurological disorders, but interpreting them can take hours or even days due to growing demand and limited specialist availability.... Read moreMRI Scan Breakthrough to Help Avoid Risky Invasive Tests for Heart Patients
Heart failure patients often require right heart catheterization to assess how severely their heart is struggling to pump blood, a procedure that involves inserting a tube into the heart to measure blood... Read more
MRI Scans Reveal Signature Patterns of Brain Activity to Predict Recovery from TBI
Recovery after traumatic brain injury (TBI) varies widely, with some patients regaining full function while others are left with lasting disabilities. Prognosis is especially difficult to assess in patients... Read moreUltrasound
view channel
AI Model Accurately Detects Placenta Accreta in Pregnancy Before Delivery
Placenta accreta spectrum (PAS) is a life-threatening pregnancy complication in which the placenta abnormally attaches to the uterine wall. The condition is a leading cause of maternal mortality and morbidity... Read more
Portable Ultrasound Sensor to Enable Earlier Breast Cancer Detection
Breast cancer screening relies heavily on annual mammograms, but aggressive tumors can develop between scans, accounting for up to 30 percent of cases. These interval cancers are often diagnosed later,... Read more
Portable Imaging Scanner to Diagnose Lymphatic Disease in Real Time
Lymphatic disorders affect hundreds of millions of people worldwide and are linked to conditions ranging from limb swelling and organ dysfunction to birth defects and cancer-related complications.... Read more
Imaging Technique Generates Simultaneous 3D Color Images of Soft-Tissue Structure and Vasculature
Medical imaging tools often force clinicians to choose between speed, structural detail, and functional insight. Ultrasound is fast and affordable but typically limited to two-dimensional anatomy, while... Read moreNuclear Medicine
view channel
Radiopharmaceutical Molecule Marker to Improve Choice of Bladder Cancer Therapies
Targeted cancer therapies only work when tumor cells express the specific molecular structures they are designed to attack. In urothelial carcinoma, a common form of bladder cancer, the cell surface protein... Read more
Cancer “Flashlight” Shows Who Can Benefit from Targeted Treatments
Targeted cancer therapies can be highly effective, but only when a patient’s tumor expresses the specific protein the treatment is designed to attack. Determining this usually requires biopsies or advanced... Read moreGeneral/Advanced Imaging
view channel
AI Tool Offers Prognosis for Patients with Head and Neck Cancer
Oropharyngeal cancer is a form of head and neck cancer that can spread through lymph nodes, significantly affecting survival and treatment decisions. Current therapies often involve combinations of surgery,... Read more
New 3D Imaging System Addresses MRI, CT and Ultrasound Limitations
Medical imaging is central to diagnosing and managing injuries, cancer, infections, and chronic diseases, yet existing tools each come with trade-offs. Ultrasound, X-ray, CT, and MRI can be costly, time-consuming,... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more



















