Asymptomatic, CT Angiography-Detected CAD Linked to 8-Fold Higher Heart Attack Risk
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 29 Mar 2023 |
The biological process of coronary atherosclerosis is responsible for the onset of myocardial infarction, which together comprise the clinical syndrome known as "ischemic heart disease." Subclinical coronary atherosclerosis precedes ischemic heart disease and may develop at a young age, many years prior to the onset of clinical disease. For over five decades, obstructive coronary artery disease has been considered a significant risk factor, characterized by a luminal coronary stenosis of 50% or more. In recent years, however, the extent of atherosclerosis in the coronary tree, as well as specific morphologic characteristics of the atherosclerotic plaque, have been recognized as crucial risk factors.
A study conducted by researchers from the University of Copenhagen (Copenhagen, Denmark) on a cohort of over 9,000 individuals has found that subclinical, obstructive coronary atherosclerosis is linked to more than an eight-fold increased risk of myocardial infarction in asymptomatic middle-aged individuals without any known cardiovascular disease. The study's researchers examined 9,533 asymptomatic individuals aged 40 years or older with no previous history of cardiovascular disease to identify subclinical coronary atherosclerosis characteristics associated with myocardial infarction development. Computed tomography angiography (CTA) was used to diagnose obstructive coronary atherosclerosis in the participants.
The study revealed that 54% of individuals did not have any subclinical coronary atherosclerosis, while 46% did. Of those diagnosed with subclinical coronary atherosclerosis, 36% had non-obstructive disease and 10% had obstructive disease. Additionally, among those diagnosed with the condition, 61% of males and 36% of females had subclinical coronary atherosclerosis. The researchers concluded that identifying luminal obstructive or extensive subclinical coronary atherosclerosis could offer valuable risk assessment in patients without suspected or known ischemic heart disease who are undergoing cardiac CT and/or electrocardiogram-gated chest CT for other clinical reasons.
The team believes that their research presents an opportunity to study the contemporary natural history of coronary artery disease without any intervention, where both patients and clinicians are unaware of the scan results. The research also provides crucial insights into the rate of events and prevalence of asymptomatic coronary artery disease, which can help healthcare professionals develop targeted preventative therapies and implement effective public health prevention strategies by screening individuals with an underlying risk of coronary artery disease.
Related Links:
University of Copenhagen
Latest General/Advanced Imaging News
- AI Predicts Cardiac Risk and Mortality from Routine Chest CT Scans
- Radiation Therapy Computed Tomography Solution Boosts Imaging Accuracy
- PET Scans Reveal Hidden Inflammation in Multiple Sclerosis Patients
- Artificial Intelligence Evaluates Cardiovascular Risk from CT Scans
- New AI Method Captures Uncertainty in Medical Images
- CT Coronary Angiography Reduces Need for Invasive Tests to Diagnose Coronary Artery Disease
- Novel Blood Test Could Reduce Need for PET Imaging of Patients with Alzheimer’s
- CT-Based Deep Learning Algorithm Accurately Differentiates Benign From Malignant Vertebral Fractures
- Minimally Invasive Procedure Could Help Patients Avoid Thyroid Surgery
- Self-Driving Mobile C-Arm Reduces Imaging Time during Surgery
- AR Application Turns Medical Scans Into Holograms for Assistance in Surgical Planning
- Imaging Technology Provides Ground-Breaking New Approach for Diagnosing and Treating Bowel Cancer
- CT Coronary Calcium Scoring Predicts Heart Attacks and Strokes
- AI Model Detects 90% of Lymphatic Cancer Cases from PET and CT Images
- Breakthrough Technology Revolutionizes Breast Imaging
- State-Of-The-Art System Enhances Accuracy of Image-Guided Diagnostic and Interventional Procedures
Channels
Radiography
view channel
Novel Breast Imaging System Proves As Effective As Mammography
Breast cancer remains the most frequently diagnosed cancer among women. It is projected that one in eight women will be diagnosed with breast cancer during her lifetime, and one in 42 women who turn 50... Read more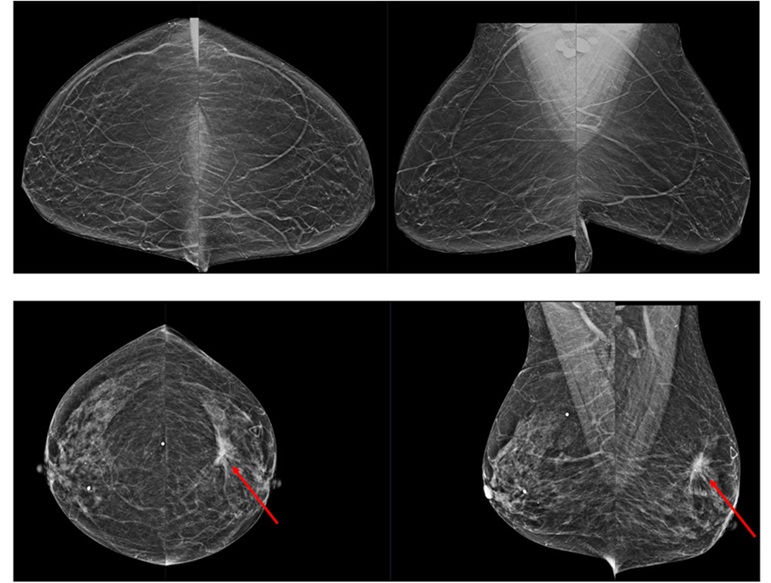
AI Assistance Improves Breast-Cancer Screening by Reducing False Positives
Radiologists typically detect one case of cancer for every 200 mammograms reviewed. However, these evaluations often result in false positives, leading to unnecessary patient recalls for additional testing,... Read moreMRI
view channel
Low-Cost Whole-Body MRI Device Combined with AI Generates High-Quality Results
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) has significantly transformed healthcare, providing a noninvasive, radiation-free method for detailed imaging. It is especially promising for the future of medical diagnosis... Read more
World's First Whole-Body Ultra-High Field MRI Officially Comes To Market
The world's first whole-body ultra-high field (UHF) MRI has officially come to market, marking a remarkable advancement in diagnostic radiology. United Imaging (Shanghai, China) has secured clearance from the U.... Read moreUltrasound
view channel.jpg)
Diagnostic System Automatically Analyzes TTE Images to Identify Congenital Heart Disease
Congenital heart disease (CHD) is one of the most prevalent congenital anomalies worldwide, presenting substantial health and financial challenges for affected patients. Early detection and treatment of... Read more
Super-Resolution Imaging Technique Could Improve Evaluation of Cardiac Conditions
The heart depends on efficient blood circulation to pump blood throughout the body, delivering oxygen to tissues and removing carbon dioxide and waste. Yet, when heart vessels are damaged, it can disrupt... Read more
First AI-Powered POC Ultrasound Diagnostic Solution Helps Prioritize Cases Based On Severity
Ultrasound scans are essential for identifying and diagnosing various medical conditions, but often, patients must wait weeks or months for results due to a shortage of qualified medical professionals... Read moreNuclear Medicine
view channelNew PET Agent Rapidly and Accurately Visualizes Lesions in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma Patients
Clear cell renal cell cancer (ccRCC) represents 70-80% of renal cell carcinoma cases. While localized disease can be effectively treated with surgery and ablative therapies, one-third of patients either... Read more
New Imaging Technique Monitors Inflammation Disorders without Radiation Exposure
Imaging inflammation using traditional radiological techniques presents significant challenges, including radiation exposure, poor image quality, high costs, and invasive procedures. Now, new contrast... Read more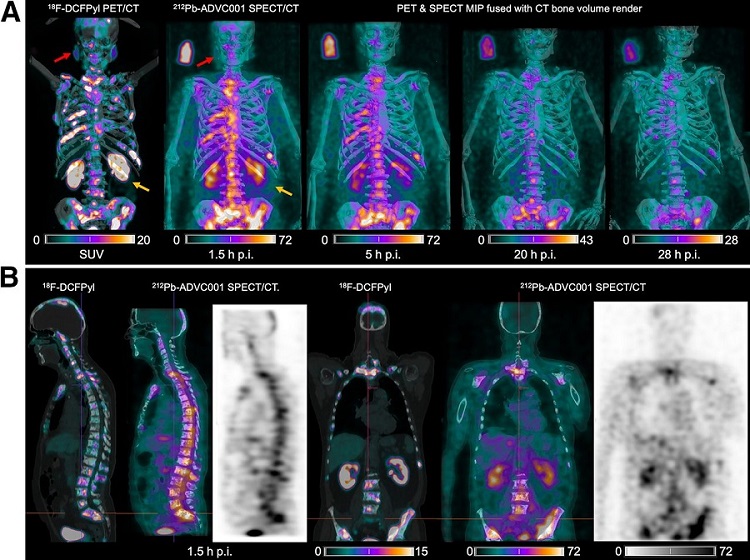
New SPECT/CT Technique Could Change Imaging Practices and Increase Patient Access
The development of lead-212 (212Pb)-PSMA–based targeted alpha therapy (TAT) is garnering significant interest in treating patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. The imaging of 212Pb,... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more
Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in medical diagnostics market is expanding with early disease detection being one of its key applications and image recognition becoming a compelling consumer proposition... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
Hologic Acquires UK-Based Breast Surgical Guidance Company Endomagnetics Ltd.
Hologic, Inc. (Marlborough, MA, USA) has entered into a definitive agreement to acquire Endomagnetics Ltd. (Cambridge, UK), a privately held developer of breast cancer surgery technologies, for approximately... Read more
Bayer and Google Partner on New AI Product for Radiologists
Medical imaging data comprises around 90% of all healthcare data, and it is a highly complex and rich clinical data modality and serves as a vital tool for diagnosing patients. Each year, billions of medical... Read more