AI Predicts Cardiac Risk and Mortality from Routine Chest CT Scans
Posted on 15 May 2024
Heart disease remains the leading cause of death and is largely preventable, yet many individuals are unaware of their risk until it becomes severe. Early detection through screening can reveal heart issues, identifying individuals who may need further examination or potential intervention. While traditional screening methods often measure blood indicators like cholesterol and triglyceride levels, computed tomography (CT) scans can offer a wealth of real-time data about heart health. However, acquiring detailed, quantitative cardiac images usually requires specialized equipment and dyes, making cardiac CT scans costly and not widely used. On the other hand, routine chest CT scans are commonly performed for various reasons, such as checking for lung infections or cancer. Now, a new study has found that these routine CT scans can potentially be used as a screening tool for heart disease.
A collaborative team at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center (Los Angeles, CA, US) is leveraging artificial intelligence (AI) to analyze standard chest CT scans to predict mortality risks. Their research has pinpointed several cardiac indicators within these scans that correlate with a higher risk of death, laying the groundwork for more effective cardiac screenings. The AI system examines images from thousands of patients to automatically extract prognostic features from routine chest CTs—features originally not targeted by these scans. These indicators are then aggregated and analyzed to predict the likelihood of cardiac-related mortality.
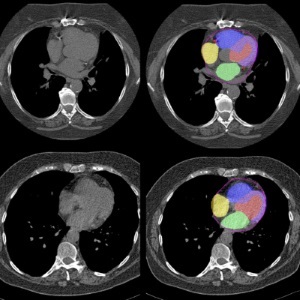
Traditionally, cardiac risk is assessed by radiologists identifying abnormalities in imaging. The innovative AI approach has significantly enhanced risk classification beyond this conventional standard. Integrating this AI technology into existing clinical workflows has proved to be simple and has already been implemented at Cedars-Sinai for research purposes. This AI tool is now used to routinely assess CT scans for cardiac prognostic factors. Radiologists typically focused on cancer detections, might not look for cardiac issues such as arterial calcification or chamber enlargement. The AI can assist them by screening these images in the background, identifying patients who may need further cardiac evaluation and potentially early treatment.
“There is a lot of important information that is hiding in chest CT scans,” explained senior study author Piotr Slomka, Ph.D., a professor at Cedars-Sinai. “By using AI to unearth and analyze key prognostic signals in these scans, we could perform opportunistic cardiac screening and potentially prompt treatments or lifestyle changes, which could ultimately save lives.”
Related Links:
Cedars-Sinai Medical Center