PET/MRI Machine Learning Model Eliminates Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy in Most Breast Cancer Patients
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 21 Nov 2022 |
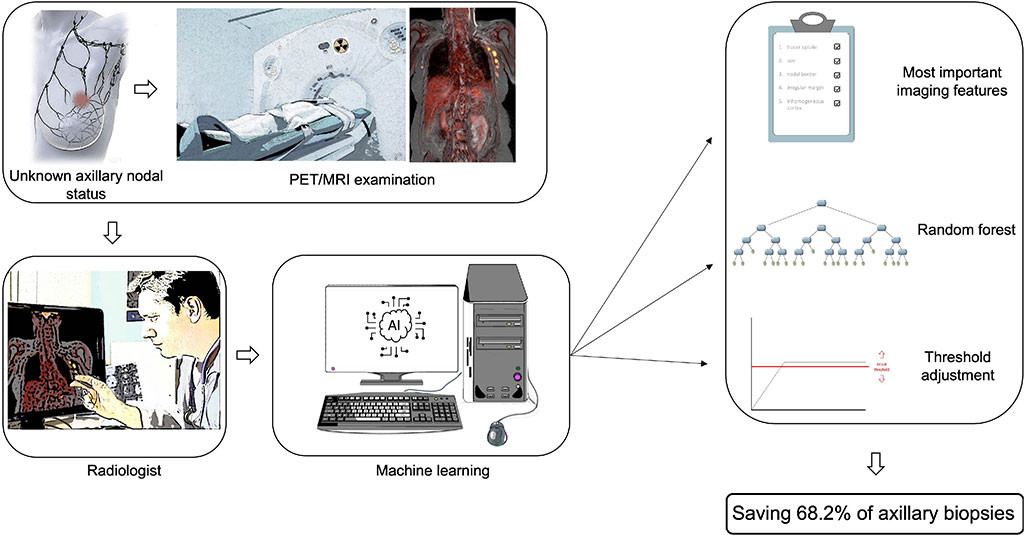
The presence of lymph node metastases in breast cancer patients plays a crucial role in treatment planning, especially regarding the extent of surgery and radiation. Therefore, it is of high clinical relevance to distinguish patients with lymph node metastases from patients without lymph node metastases. Now, nearly 70% of breast cancer patients could find out if their cancer has spread to their lymph nodes without having to undergo an invasive sentinel node biopsy. New research shows that with the help of machine learning (a type of artificial intelligence), axillary lymph node metastasis can be reliably ruled out based on imaging with PET/MRI.
In the study, researchers at the Institute for Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology at the University Hospital Düsseldorf (Düsseldorf, Germany) sought to determine whether machine learning prediction models could determine lymph node status in PET/MRI examinations as accurately as an experienced radiologist could. A total of 303 primary breast cancer patients from three medical centers were recruited for the study and were divided into a training group sample and a testing group sample.
All patients underwent MRI and dedicated whole-body 18F-FDG PET/MRI. The imaging datasets were evaluated for axillary lymph node metastases based on structural and functional features. Machine learning models were developed based on the MRI and PET/MRI training group sample and were then applied to the testing group sample. The diagnostic accuracy of MRI was 87.5% for both radiologists and the machine learning algorithm. For PET/MRI, the accuracy was 89.3% for radiologists and 91.2% for machine learning. After adjusting the machine learning model for PET/MRI, a sensitivity of 96.2% and a specificity of 68.2% was achieved.
“Sixty percent of patients do not have lymph node metastases at initial diagnosis of breast cancer,” said study author Janna Morawitz, MD, radiology resident at the Institute for Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology at the University Hospital Düsseldorf. “As such, it would be desirable to be able to prove negative lymph node status by imaging with a high degree of certainty to spare these patients the invasive procedure of biopsy or surgery.”
Related Links:
University Hospital Düsseldorf
Latest MRI News
- Low-Cost Whole-Body MRI Device Combined with AI Generates High-Quality Results
- World's First Whole-Body Ultra-High Field MRI Officially Comes To Market
- World's First Sensor Detects Errors in MRI Scans Using Laser Light and Gas
- Diamond Dust Could Offer New Contrast Agent Option for Future MRI Scans
- Combining MRI with PSA Testing Improves Clinical Outcomes for Prostate Cancer Patients
- PET/MRI Improves Diagnostic Accuracy for Prostate Cancer Patients
- Next Generation MR-Guided Focused Ultrasound Ushers In Future of Incisionless Neurosurgery
- Two-Part MRI Scan Detects Prostate Cancer More Quickly without Compromising Diagnostic Quality
- World’s Most Powerful MRI Machine Images Living Brain with Unrivaled Clarity
- New Whole-Body Imaging Technology Makes It Possible to View Inflammation on MRI Scan
- Combining Prostate MRI with Blood Test Can Avoid Unnecessary Prostate Biopsies
- New Treatment Combines MRI and Ultrasound to Control Prostate Cancer without Serious Side Effects
- MRI Improves Diagnosis and Treatment of Prostate Cancer
- Combined PET-MRI Scan Improves Treatment for Early Breast Cancer Patients
- 4D MRI Could Improve Clinical Assessment of Heart Blood Flow Abnormalities
- MRI-Guided Focused Ultrasound Therapy Shows Promise in Treating Prostate Cancer
Channels
Radiography
view channel
Novel Breast Imaging System Proves As Effective As Mammography
Breast cancer remains the most frequently diagnosed cancer among women. It is projected that one in eight women will be diagnosed with breast cancer during her lifetime, and one in 42 women who turn 50... Read more
AI Assistance Improves Breast-Cancer Screening by Reducing False Positives
Radiologists typically detect one case of cancer for every 200 mammograms reviewed. However, these evaluations often result in false positives, leading to unnecessary patient recalls for additional testing,... Read moreUltrasound
view channel
Super-Resolution Imaging Technique Could Improve Evaluation of Cardiac Conditions
The heart depends on efficient blood circulation to pump blood throughout the body, delivering oxygen to tissues and removing carbon dioxide and waste. Yet, when heart vessels are damaged, it can disrupt... Read more
First AI-Powered POC Ultrasound Diagnostic Solution Helps Prioritize Cases Based On Severity
Ultrasound scans are essential for identifying and diagnosing various medical conditions, but often, patients must wait weeks or months for results due to a shortage of qualified medical professionals... Read more
Largest Model Trained On Echocardiography Images Assesses Heart Structure and Function
Foundation models represent an exciting frontier in generative artificial intelligence (AI), yet many lack the specialized medical data needed to make them applicable in healthcare settings.... Read more.jpg)
Groundbreaking Technology Enables Precise, Automatic Measurement of Peripheral Blood Vessels
The current standard of care of using angiographic information is often inadequate for accurately assessing vessel size in the estimated 20 million people in the U.S. who suffer from peripheral vascular disease.... Read moreNuclear Medicine
view channelNew PET Agent Rapidly and Accurately Visualizes Lesions in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma Patients
Clear cell renal cell cancer (ccRCC) represents 70-80% of renal cell carcinoma cases. While localized disease can be effectively treated with surgery and ablative therapies, one-third of patients either... Read more
New Imaging Technique Monitors Inflammation Disorders without Radiation Exposure
Imaging inflammation using traditional radiological techniques presents significant challenges, including radiation exposure, poor image quality, high costs, and invasive procedures. Now, new contrast... Read more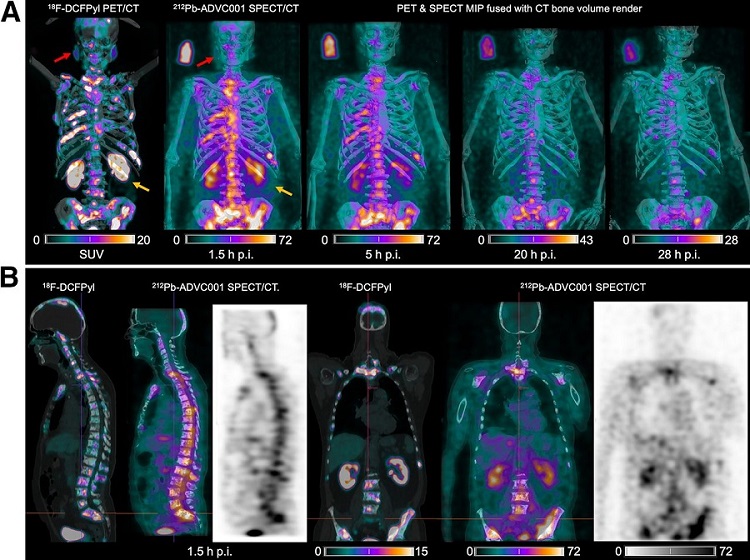
New SPECT/CT Technique Could Change Imaging Practices and Increase Patient Access
The development of lead-212 (212Pb)-PSMA–based targeted alpha therapy (TAT) is garnering significant interest in treating patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. The imaging of 212Pb,... Read moreGeneral/Advanced Imaging
view channel
Radiation Therapy Computed Tomography Solution Boosts Imaging Accuracy
One of the most significant challenges in oncology care is disease complexity in terms of the variety of cancer types and the individualized presentation of each patient. This complexity necessitates a... Read more
PET Scans Reveal Hidden Inflammation in Multiple Sclerosis Patients
A key challenge for clinicians treating patients with multiple sclerosis (MS) is that after a certain amount of time, they continue to worsen even though their MRIs show no change. A new study has now... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more
Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in medical diagnostics market is expanding with early disease detection being one of its key applications and image recognition becoming a compelling consumer proposition... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
Hologic Acquires UK-Based Breast Surgical Guidance Company Endomagnetics Ltd.
Hologic, Inc. (Marlborough, MA, USA) has entered into a definitive agreement to acquire Endomagnetics Ltd. (Cambridge, UK), a privately held developer of breast cancer surgery technologies, for approximately... Read more
Bayer and Google Partner on New AI Product for Radiologists
Medical imaging data comprises around 90% of all healthcare data, and it is a highly complex and rich clinical data modality and serves as a vital tool for diagnosing patients. Each year, billions of medical... Read more