AI Tools Increase Low-Dose CT Lung Nodule Specificity
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 02 Feb 2021 |

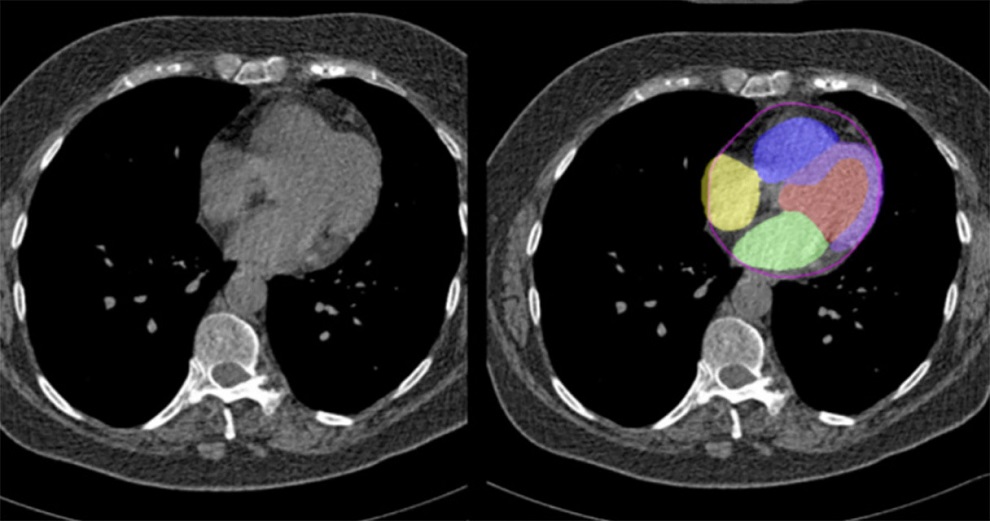
Image: AI identification of lung nodule matches or bests that of trained radiologists (Photo courtesy of iStock)
Combining artificial intelligence (AI) and lung imaging reporting and data system (Lung-RADS) scores can increase CT scan specificity without reducing sensitivity, according to a new study.
Researchers at the University of Saskatchewan (Saskatoon, Canada) conducted a study that performed secondary analysis of a known data set using an AI model developed by Google in 2019, and Lung-RADS classifications from six radiologists. They then compared them to assess a representative cohort of 3,197 baseline low-dose CT screening patients. To ensure the AI algorithm matched the 91% sensitivity level achieved by the providers, the researchers determined a 0.27 AI risk-score threshold, based on a 0-to-1 scale.
The results showed that the AI-informed management strategy achieved sensitivity and specificity of 91% and 96%, respectively, while the average sensitivity and specificity of the six radiologists using only Lung-RADS was 91% and 61%, respectively. Based on the AI management strategy, 0.2% of category 1 or 2 Lung-RADS classifications were upgraded to category 3, and 30% of category 3 or higher classifications were downgraded to category 2. The minimum net cost savings, based on 2019 U.S. Medicare physician fee schedule, was USD 72 per patient screened. The study was published on January 19, 2021, in Journal of the American College of Radiology.
“Using an AI risk score combined with Lung-RADS at baseline lung cancer screening may result in fewer follow-up investigations and substantial cost savings. Specificity could rise by more than fifty percent,” concluded lead author Scott Adams, MD, and colleagues. “Additional research for other AI thresholds could also beneficial, especially for Lung-RADS category 4 nodules. Ultimately, additional investigations could lead to AI algorithms being used in a similar way to what has been suggested for screening mammography.”
Lung-RADS is a quality assurance tool designed to standardize lung cancer screening CT reporting and management recommendations, reduce confusion in lung cancer screening CT interpretations, and facilitate outcome monitoring. It is modeled on the success of the Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS), with the primary goal of minimizing variation in the management of CT-detected lung nodules so that screening can be implemented effectively in radiology practices.
Related Links:
University of Saskatchewan
Researchers at the University of Saskatchewan (Saskatoon, Canada) conducted a study that performed secondary analysis of a known data set using an AI model developed by Google in 2019, and Lung-RADS classifications from six radiologists. They then compared them to assess a representative cohort of 3,197 baseline low-dose CT screening patients. To ensure the AI algorithm matched the 91% sensitivity level achieved by the providers, the researchers determined a 0.27 AI risk-score threshold, based on a 0-to-1 scale.
The results showed that the AI-informed management strategy achieved sensitivity and specificity of 91% and 96%, respectively, while the average sensitivity and specificity of the six radiologists using only Lung-RADS was 91% and 61%, respectively. Based on the AI management strategy, 0.2% of category 1 or 2 Lung-RADS classifications were upgraded to category 3, and 30% of category 3 or higher classifications were downgraded to category 2. The minimum net cost savings, based on 2019 U.S. Medicare physician fee schedule, was USD 72 per patient screened. The study was published on January 19, 2021, in Journal of the American College of Radiology.
“Using an AI risk score combined with Lung-RADS at baseline lung cancer screening may result in fewer follow-up investigations and substantial cost savings. Specificity could rise by more than fifty percent,” concluded lead author Scott Adams, MD, and colleagues. “Additional research for other AI thresholds could also beneficial, especially for Lung-RADS category 4 nodules. Ultimately, additional investigations could lead to AI algorithms being used in a similar way to what has been suggested for screening mammography.”
Lung-RADS is a quality assurance tool designed to standardize lung cancer screening CT reporting and management recommendations, reduce confusion in lung cancer screening CT interpretations, and facilitate outcome monitoring. It is modeled on the success of the Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS), with the primary goal of minimizing variation in the management of CT-detected lung nodules so that screening can be implemented effectively in radiology practices.
Related Links:
University of Saskatchewan
Latest Radiography News
- Novel Breast Imaging System Proves As Effective As Mammography
- AI Assistance Improves Breast-Cancer Screening by Reducing False Positives
- AI Could Boost Clinical Adoption of Chest DDR
- 3D Mammography Almost Halves Breast Cancer Incidence between Two Screening Tests
- AI Model Predicts 5-Year Breast Cancer Risk from Mammograms
- Deep Learning Framework Detects Fractures in X-Ray Images With 99% Accuracy
- Direct AI-Based Medical X-Ray Imaging System a Paradigm-Shift from Conventional DR and CT
- Chest X-Ray AI Solution Automatically Identifies, Categorizes and Highlights Suspicious Areas
- AI Diagnoses Wrist Fractures As Well As Radiologists
- Annual Mammography Beginning At 40 Cuts Breast Cancer Mortality By 42%
- 3D Human GPS Powered By Light Paves Way for Radiation-Free Minimally-Invasive Surgery
- Novel AI Technology to Revolutionize Cancer Detection in Dense Breasts
- AI Solution Provides Radiologists with 'Second Pair' Of Eyes to Detect Breast Cancers
- AI Helps General Radiologists Achieve Specialist-Level Performance in Interpreting Mammograms
- Novel Imaging Technique Could Transform Breast Cancer Detection
- Computer Program Combines AI and Heat-Imaging Technology for Early Breast Cancer Detection
Channels
MRI
view channel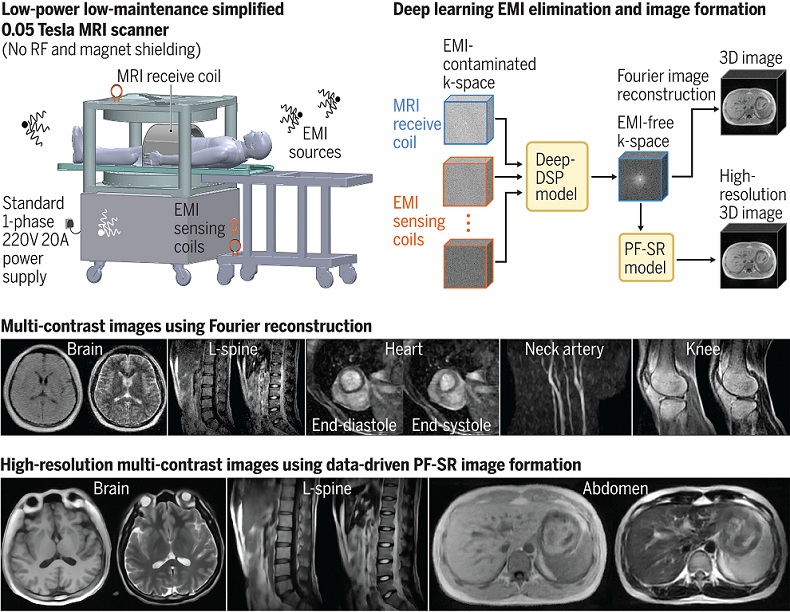
Low-Cost Whole-Body MRI Device Combined with AI Generates High-Quality Results
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) has significantly transformed healthcare, providing a noninvasive, radiation-free method for detailed imaging. It is especially promising for the future of medical diagnosis... Read more
World's First Whole-Body Ultra-High Field MRI Officially Comes To Market
The world's first whole-body ultra-high field (UHF) MRI has officially come to market, marking a remarkable advancement in diagnostic radiology. United Imaging (Shanghai, China) has secured clearance from the U.... Read moreUltrasound
view channel.jpg)
Diagnostic System Automatically Analyzes TTE Images to Identify Congenital Heart Disease
Congenital heart disease (CHD) is one of the most prevalent congenital anomalies worldwide, presenting substantial health and financial challenges for affected patients. Early detection and treatment of... Read more
Super-Resolution Imaging Technique Could Improve Evaluation of Cardiac Conditions
The heart depends on efficient blood circulation to pump blood throughout the body, delivering oxygen to tissues and removing carbon dioxide and waste. Yet, when heart vessels are damaged, it can disrupt... Read more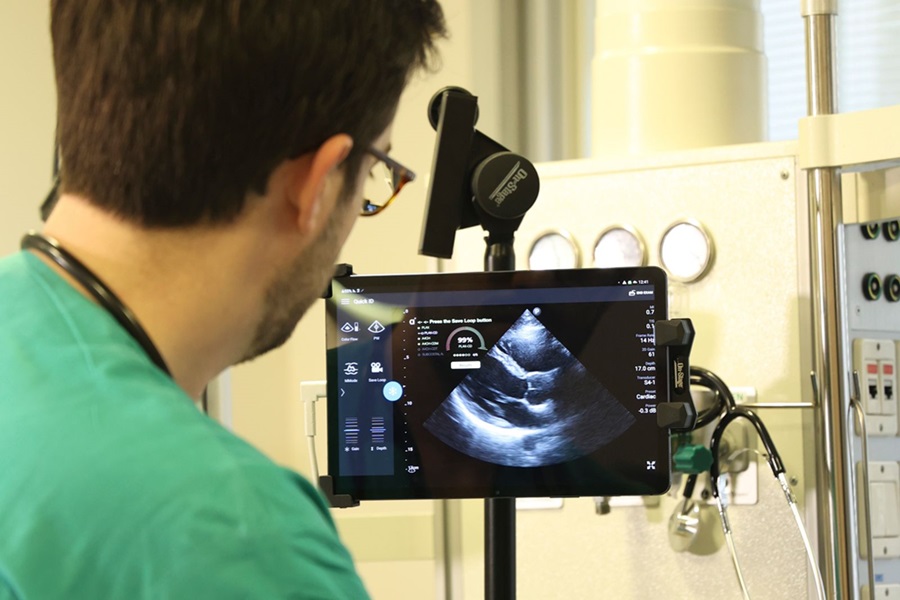
First AI-Powered POC Ultrasound Diagnostic Solution Helps Prioritize Cases Based On Severity
Ultrasound scans are essential for identifying and diagnosing various medical conditions, but often, patients must wait weeks or months for results due to a shortage of qualified medical professionals... Read moreNuclear Medicine
view channelNew PET Agent Rapidly and Accurately Visualizes Lesions in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma Patients
Clear cell renal cell cancer (ccRCC) represents 70-80% of renal cell carcinoma cases. While localized disease can be effectively treated with surgery and ablative therapies, one-third of patients either... Read more
New Imaging Technique Monitors Inflammation Disorders without Radiation Exposure
Imaging inflammation using traditional radiological techniques presents significant challenges, including radiation exposure, poor image quality, high costs, and invasive procedures. Now, new contrast... Read more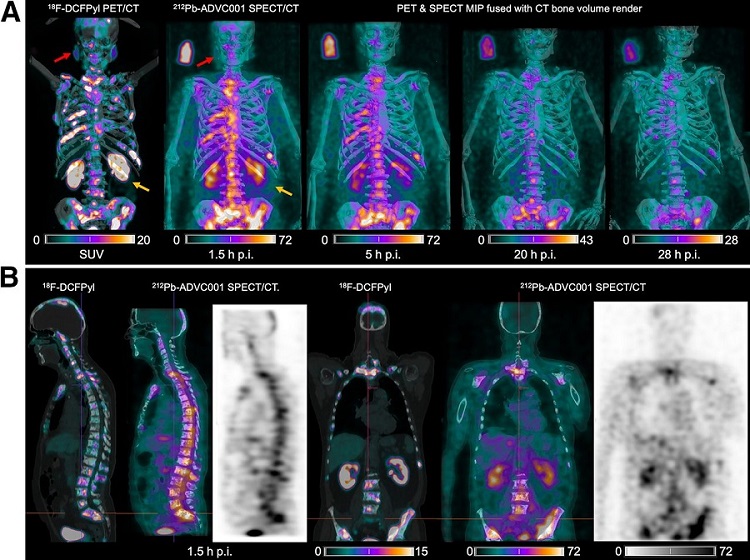
New SPECT/CT Technique Could Change Imaging Practices and Increase Patient Access
The development of lead-212 (212Pb)-PSMA–based targeted alpha therapy (TAT) is garnering significant interest in treating patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. The imaging of 212Pb,... Read moreGeneral/Advanced Imaging
view channel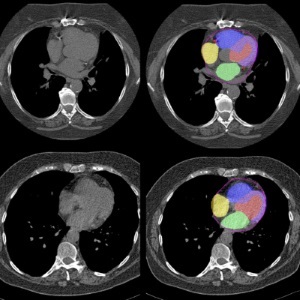
AI Predicts Cardiac Risk and Mortality from Routine Chest CT Scans
Heart disease remains the leading cause of death and is largely preventable, yet many individuals are unaware of their risk until it becomes severe. Early detection through screening can reveal heart issues,... Read more
Radiation Therapy Computed Tomography Solution Boosts Imaging Accuracy
One of the most significant challenges in oncology care is disease complexity in terms of the variety of cancer types and the individualized presentation of each patient. This complexity necessitates a... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more
Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in medical diagnostics market is expanding with early disease detection being one of its key applications and image recognition becoming a compelling consumer proposition... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
Hologic Acquires UK-Based Breast Surgical Guidance Company Endomagnetics Ltd.
Hologic, Inc. (Marlborough, MA, USA) has entered into a definitive agreement to acquire Endomagnetics Ltd. (Cambridge, UK), a privately held developer of breast cancer surgery technologies, for approximately... Read more
Bayer and Google Partner on New AI Product for Radiologists
Medical imaging data comprises around 90% of all healthcare data, and it is a highly complex and rich clinical data modality and serves as a vital tool for diagnosing patients. Each year, billions of medical... Read more