Novel Tele-Robotic Cardiovascular Ultrasound Imaging Trial Planned Between New York and Chicago
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 18 May 2015 |
A new clinical trial between the Mount Sinai hospital Icahn School of Medicine (ISMMS; New York, NY, USA) and the Chicago-based Rush University Medical Center (Chicago, IL, USA) will test the feasibility of carrying out tele-robotic, long-distance ultrasound examinations over the Internet.
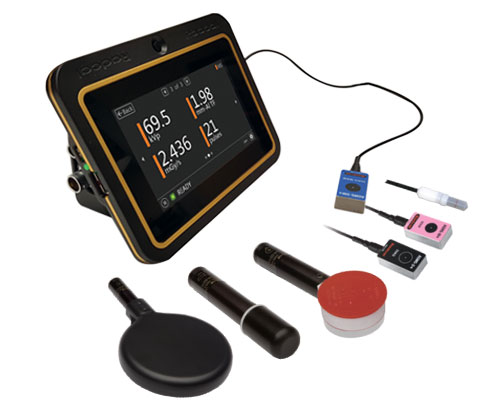
The study, a research collaboration between cardiovascular imaging specialists at the two locations, and will test the feasibility and efficiency of physicians in New York City remotely performing ultrasound examinations on patients in Chicago, over the internet. The study has enrolled 100 patients, over the age of 60, and involves the use of a small, robotic arm fitted with an ultrasound device, and connected to the Internet.
The Tele-Robotic Ultrasound for Distance Imaging (TRUDI) technology was developed by Dr. Jeff Soble, MD and Sarah Doherty TeleHealthRobotics (Chicago, IL, USA). The robotic arm is controlled remotely by a cardiovascular specialist at Mount Sinai, who can complete a carotid artery scan in four minutes. The patients will also each undergo a manual ultrasound exam locally, in the Rush Medical Center.
The aim of the research team is to test whether remote, tele-robotic ultrasound exams of the carotid artery in the neck, intended to find thickening of the carotid intima-media and carotid atherosclerotic plaque, can be as efficient as traditional manual ultrasound exams. Both conditions are risk factors for heart attack, stroke, and other cardiovascular events.
Rami Doukky, MD, MSc, principal investigator of the study at Rush Medical, said, “Imaging technology is evolving at a rapid pace. If this tele-health breakthrough proves feasible and successful it may open the door for more accessible screening, prevention, and diagnostic capabilities for patients who may be at high-risk for cardiovascular diseases.”
Related Links:
Mount Sinai hospital Icahn School of Medicine
Rush University Medical Center
TeleHealthRobotics
The study, a research collaboration between cardiovascular imaging specialists at the two locations, and will test the feasibility and efficiency of physicians in New York City remotely performing ultrasound examinations on patients in Chicago, over the internet. The study has enrolled 100 patients, over the age of 60, and involves the use of a small, robotic arm fitted with an ultrasound device, and connected to the Internet.
The Tele-Robotic Ultrasound for Distance Imaging (TRUDI) technology was developed by Dr. Jeff Soble, MD and Sarah Doherty TeleHealthRobotics (Chicago, IL, USA). The robotic arm is controlled remotely by a cardiovascular specialist at Mount Sinai, who can complete a carotid artery scan in four minutes. The patients will also each undergo a manual ultrasound exam locally, in the Rush Medical Center.
The aim of the research team is to test whether remote, tele-robotic ultrasound exams of the carotid artery in the neck, intended to find thickening of the carotid intima-media and carotid atherosclerotic plaque, can be as efficient as traditional manual ultrasound exams. Both conditions are risk factors for heart attack, stroke, and other cardiovascular events.
Rami Doukky, MD, MSc, principal investigator of the study at Rush Medical, said, “Imaging technology is evolving at a rapid pace. If this tele-health breakthrough proves feasible and successful it may open the door for more accessible screening, prevention, and diagnostic capabilities for patients who may be at high-risk for cardiovascular diseases.”
Related Links:
Mount Sinai hospital Icahn School of Medicine
Rush University Medical Center
TeleHealthRobotics
Latest Ultrasound News
- First AI-Powered POC Ultrasound Diagnostic Solution Helps Prioritize Cases Based On Severity

- Largest Model Trained On Echocardiography Images Assesses Heart Structure and Function
- Groundbreaking Technology Enables Precise, Automatic Measurement of Peripheral Blood Vessels
- Deep Learning Advances Super-Resolution Ultrasound Imaging
- Novel Ultrasound-Launched Targeted Nanoparticle Eliminates Biofilm and Bacterial Infection
- AI-Guided Ultrasound System Enables Rapid Assessments of DVT
- Focused Ultrasound Technique Gets Quality Assurance Protocol
- AI-Guided Handheld Ultrasound System Helps Capture Diagnostic-Quality Cardiac Images
- Non-Invasive Ultrasound Imaging Device Diagnoses Risk of Chronic Kidney Disease
- Wearable Ultrasound Platform Paves Way for 24/7 Blood Pressure Monitoring On the Wrist
- Diagnostic Ultrasound Enhancing Agent to Improve Image Quality in Pediatric Heart Patients
- AI Detects COVID-19 in Lung Ultrasound Images
- New Ultrasound Technology to Revolutionize Respiratory Disease Diagnoses
- Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound Highly Useful For Interventions
- Ultrasensitive Broadband Transparent Ultrasound Transducer Enhances Medical Diagnosis
- Artificial Intelligence Detects Heart Defects in Newborns from Ultrasound Images
Channels
Radiography
view channel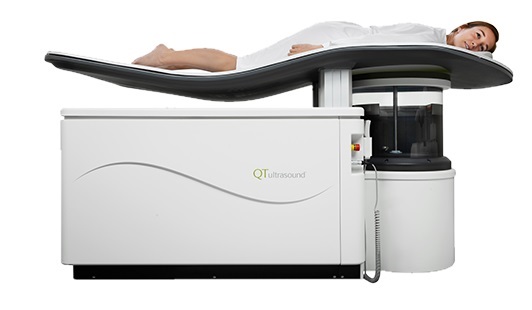
Novel Breast Imaging System Proves As Effective As Mammography
Breast cancer remains the most frequently diagnosed cancer among women. It is projected that one in eight women will be diagnosed with breast cancer during her lifetime, and one in 42 women who turn 50... Read more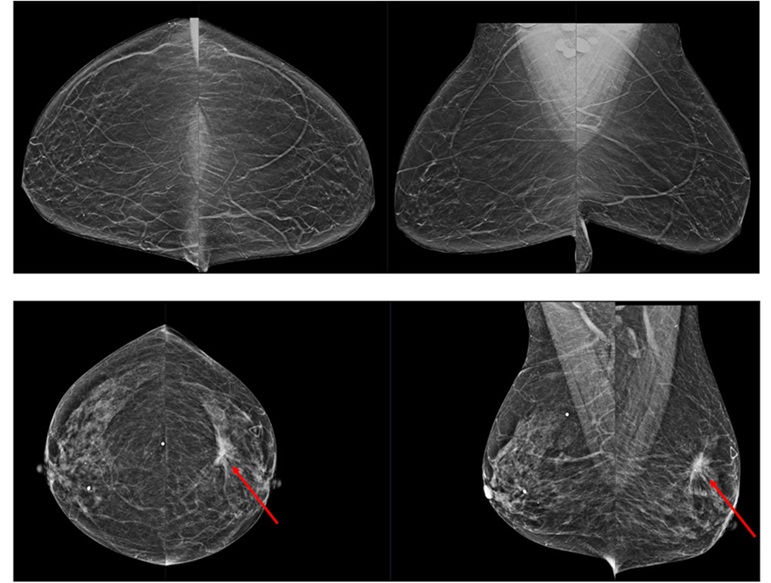
AI Assistance Improves Breast-Cancer Screening by Reducing False Positives
Radiologists typically detect one case of cancer for every 200 mammograms reviewed. However, these evaluations often result in false positives, leading to unnecessary patient recalls for additional testing,... Read moreMRI
view channel
World's First Whole-Body Ultra-High Field MRI Officially Comes To Market
The world's first whole-body ultra-high field (UHF) MRI has officially come to market, marking a remarkable advancement in diagnostic radiology. United Imaging (Shanghai, China) has secured clearance from the U.... Read more
World's First Sensor Detects Errors in MRI Scans Using Laser Light and Gas
MRI scanners are daily tools for doctors and healthcare professionals, providing unparalleled 3D imaging of the brain, vital organs, and soft tissues, far surpassing other imaging technologies in quality.... Read more
Diamond Dust Could Offer New Contrast Agent Option for Future MRI Scans
Gadolinium, a heavy metal used for over three decades as a contrast agent in medical imaging, enhances the clarity of MRI scans by highlighting affected areas. Despite its utility, gadolinium not only... Read more.jpg)
Combining MRI with PSA Testing Improves Clinical Outcomes for Prostate Cancer Patients
Prostate cancer is a leading health concern globally, consistently being one of the most common types of cancer among men and a major cause of cancer-related deaths. In the United States, it is the most... Read moreNuclear Medicine
view channel
New Imaging Technique Monitors Inflammation Disorders without Radiation Exposure
Imaging inflammation using traditional radiological techniques presents significant challenges, including radiation exposure, poor image quality, high costs, and invasive procedures. Now, new contrast... Read more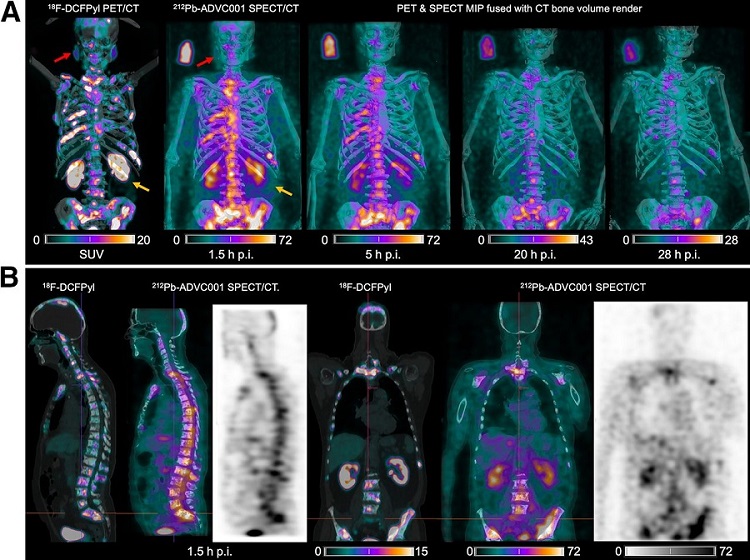
New SPECT/CT Technique Could Change Imaging Practices and Increase Patient Access
The development of lead-212 (212Pb)-PSMA–based targeted alpha therapy (TAT) is garnering significant interest in treating patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. The imaging of 212Pb,... Read moreNew Radiotheranostic System Detects and Treats Ovarian Cancer Noninvasively
Ovarian cancer is the most lethal gynecological cancer, with less than a 30% five-year survival rate for those diagnosed in late stages. Despite surgery and platinum-based chemotherapy being the standard... Read more
AI System Automatically and Reliably Detects Cardiac Amyloidosis Using Scintigraphy Imaging
Cardiac amyloidosis, a condition characterized by the buildup of abnormal protein deposits (amyloids) in the heart muscle, severely affects heart function and can lead to heart failure or death without... Read moreGeneral/Advanced Imaging
view channel
Radiation Therapy Computed Tomography Solution Boosts Imaging Accuracy
One of the most significant challenges in oncology care is disease complexity in terms of the variety of cancer types and the individualized presentation of each patient. This complexity necessitates a... Read more
PET Scans Reveal Hidden Inflammation in Multiple Sclerosis Patients
A key challenge for clinicians treating patients with multiple sclerosis (MS) is that after a certain amount of time, they continue to worsen even though their MRIs show no change. A new study has now... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more
Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in medical diagnostics market is expanding with early disease detection being one of its key applications and image recognition becoming a compelling consumer proposition... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
Hologic Acquires UK-Based Breast Surgical Guidance Company Endomagnetics Ltd.
Hologic, Inc. (Marlborough, MA, USA) has entered into a definitive agreement to acquire Endomagnetics Ltd. (Cambridge, UK), a privately held developer of breast cancer surgery technologies, for approximately... Read more
Bayer and Google Partner on New AI Product for Radiologists
Medical imaging data comprises around 90% of all healthcare data, and it is a highly complex and rich clinical data modality and serves as a vital tool for diagnosing patients. Each year, billions of medical... Read more