First-Of-Its-Kind Tool Analyzes MRI Scans to Measure Brain Aging
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 25 Feb 2025 |
Biological age differs from chronological age, as two individuals of the same age may have distinct biological ages based on the functionality of their bodies and how the tissues appear at a cellular level. Faster brain aging is strongly linked to an increased risk of cognitive decline. Common biological age measures often rely on blood samples to assess epigenetic aging and DNA methylation, which affects gene function in cells. However, using blood samples to gauge biological age is ineffective for determining brain age. The blood-brain barrier prevents blood cells from entering the brain, meaning that blood samples cannot directly reflect aging processes such as DNA methylation in the brain. On the other hand, obtaining a sample directly from the brain is highly invasive, making it impractical to measure DNA methylation and other aging indicators from living human brain cells. Now, researchers have developed a new artificial intelligence (AI) model capable of non-invasively measuring the speed of brain aging, providing an invaluable tool for understanding and addressing cognitive decline and dementia. This innovative model analyzes magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans to track brain changes.
Earlier research at the USC Leonard Davis School of Gerontology (Los Angeles, CA, USA) revealed the potential of MRI scans to estimate brain biological age without invasive methods. In earlier studies, AI was used to compare a patient’s brain structure with data from MRI scans of thousands of individuals, assessing various ages and cognitive health outcomes. However, the previous model had limitations, as it relied on a single MRI scan to estimate brain age. Although it could indicate whether a patient’s brain was older than their chronological age, it could not determine when the accelerated aging occurred or whether the brain aging process was speeding up.
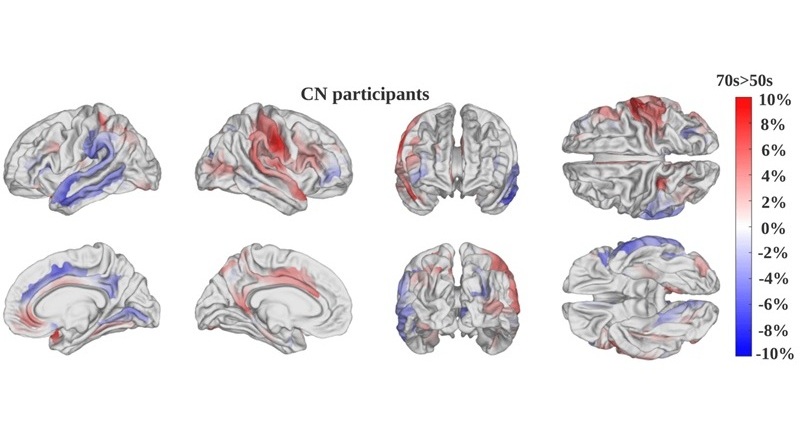
The researchers have developed a new three-dimensional convolutional neural network (3D-CNN) that offers a more accurate method to measure brain aging over time. Trained and validated on more than 3,000 MRI scans from cognitively normal adults, the model's predictive ability was detailed in a study published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. Unlike traditional methods that rely on one-time scans, this new longitudinal approach compares baseline and follow-up MRI scans of the same person. This allows for a more precise identification of neuroanatomic changes associated with faster or slower brain aging. The 3D-CNN also produces “saliency maps,” which highlight the specific brain regions that most significantly influence aging speed.
When applied to 104 cognitively healthy adults and 140 Alzheimer’s disease patients, the model’s assessment of brain aging speed showed a close correlation with changes in cognitive function tests at both time points. The researchers suggest that this model could be instrumental in better understanding the trajectories of both healthy aging and neurodegenerative diseases. Moreover, its predictive capabilities could help identify the most effective treatments tailored to individual characteristics. The new model was also able to differentiate the rates of aging in various brain regions, providing insight into how genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors may influence brain pathology.
The study also noted differences in brain aging between the sexes, which may help explain why men and women face different risks for neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer’s. The researchers are particularly excited about the potential of this new model to identify individuals experiencing accelerated brain aging before they exhibit any cognitive symptoms. With the introduction of new Alzheimer’s treatments, their effectiveness has been less than expected, possibly because patients have not begun treatment until significant brain pathology has already developed.
“This is a novel measurement that could change the way we track brain health both in the research lab and in the clinic,” said Andrei Irimia, associate professor of gerontology, biomedical engineering, quantitative & computational biology and neuroscience at the USC Leonard Davis School of Gerontology. “Knowing how fast one’s brain is aging can be powerful.”
Related Links:
USC Leonard Davis School of Gerontology
Latest MRI News
- Ultra-Powerful MRI Scans Enable Life-Changing Surgery in Treatment-Resistant Epileptic Patients
- AI-Powered MRI Technology Improves Parkinson’s Diagnoses
- Biparametric MRI Combined with AI Enhances Detection of Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer
- First-Of-Its-Kind AI-Driven Brain Imaging Platform to Better Guide Stroke Treatment Options
- New Model Improves Comparison of MRIs Taken at Different Institutions
- Groundbreaking New Scanner Sees 'Previously Undetectable' Cancer Spread
- AI-Enhanced MRI Images Make Cancerous Breast Tissue Glow
- AI Model Automatically Segments MRI Images
- New Research Supports Routine Brain MRI Screening in Asymptomatic Late-Stage Breast Cancer Patients
- Revolutionary Portable Device Performs Rapid MRI-Based Stroke Imaging at Patient's Bedside
- AI Predicts After-Effects of Brain Tumor Surgery from MRI Scans
- MRI-First Strategy for Prostate Cancer Detection Proven Safe
- First-Of-Its-Kind 10' x 48' Mobile MRI Scanner Transforms User and Patient Experience
- New Model Makes MRI More Accurate and Reliable
- New Scan Method Shows Effects of Treatment on Lung Function in Real Time
- Simple Scan Could Identify Patients at Risk for Serious Heart Problems
Channels
Radiography
view channel
AI-Powered Imaging Technique Shows Promise in Evaluating Patients for PCI
Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), also known as coronary angioplasty, is a minimally invasive procedure where small metal tubes called stents are inserted into partially blocked coronary arteries... Read more
Higher Chest X-Ray Usage Catches Lung Cancer Earlier and Improves Survival
Lung cancer continues to be the leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide. While advanced technologies like CT scanners play a crucial role in detecting lung cancer, more accessible and affordable... Read moreUltrasound
view channel
Tiny Magnetic Robot Takes 3D Scans from Deep Within Body
Colorectal cancer ranks as one of the leading causes of cancer-related mortality worldwide. However, when detected early, it is highly treatable. Now, a new minimally invasive technique could significantly... Read more
High Resolution Ultrasound Speeds Up Prostate Cancer Diagnosis
Each year, approximately one million prostate cancer biopsies are conducted across Europe, with similar numbers in the USA and around 100,000 in Canada. Most of these biopsies are performed using MRI images... Read more
World's First Wireless, Handheld, Whole-Body Ultrasound with Single PZT Transducer Makes Imaging More Accessible
Ultrasound devices play a vital role in the medical field, routinely used to examine the body's internal tissues and structures. While advancements have steadily improved ultrasound image quality and processing... Read moreNuclear Medicine
view channel
Novel PET Imaging Approach Offers Never-Before-Seen View of Neuroinflammation
COX-2, an enzyme that plays a key role in brain inflammation, can be significantly upregulated by inflammatory stimuli and neuroexcitation. Researchers suggest that COX-2 density in the brain could serve... Read more
Novel Radiotracer Identifies Biomarker for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC), which represents 15-20% of all breast cancer cases, is one of the most aggressive subtypes, with a five-year survival rate of about 40%. Due to its significant heterogeneity... Read moreGeneral/Advanced Imaging
view channel
AI Model Significantly Enhances Low-Dose CT Capabilities
Lung cancer remains one of the most challenging diseases, making early diagnosis vital for effective treatment. Fortunately, advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) are revolutionizing lung cancer... Read more
Ultra-Low Dose CT Aids Pneumonia Diagnosis in Immunocompromised Patients
Lung infections can be life-threatening for patients with weakened immune systems, making timely diagnosis crucial. While CT scans are considered the gold standard for detecting pneumonia, repeated scans... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more
Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in medical diagnostics market is expanding with early disease detection being one of its key applications and image recognition becoming a compelling consumer proposition... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
GE HealthCare and NVIDIA Collaboration to Reimagine Diagnostic Imaging
GE HealthCare (Chicago, IL, USA) has entered into a collaboration with NVIDIA (Santa Clara, CA, USA), expanding the existing relationship between the two companies to focus on pioneering innovation in... Read more
Patient-Specific 3D-Printed Phantoms Transform CT Imaging
New research has highlighted how anatomically precise, patient-specific 3D-printed phantoms are proving to be scalable, cost-effective, and efficient tools in the development of new CT scan algorithms... Read more
Siemens and Sectra Collaborate on Enhancing Radiology Workflows
Siemens Healthineers (Forchheim, Germany) and Sectra (Linköping, Sweden) have entered into a collaboration aimed at enhancing radiologists' diagnostic capabilities and, in turn, improving patient care... Read more