New Contrast Agent for Ultrasound Imaging Ensures Affordable and Safer Medical Diagnostics
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 22 Jan 2025 |
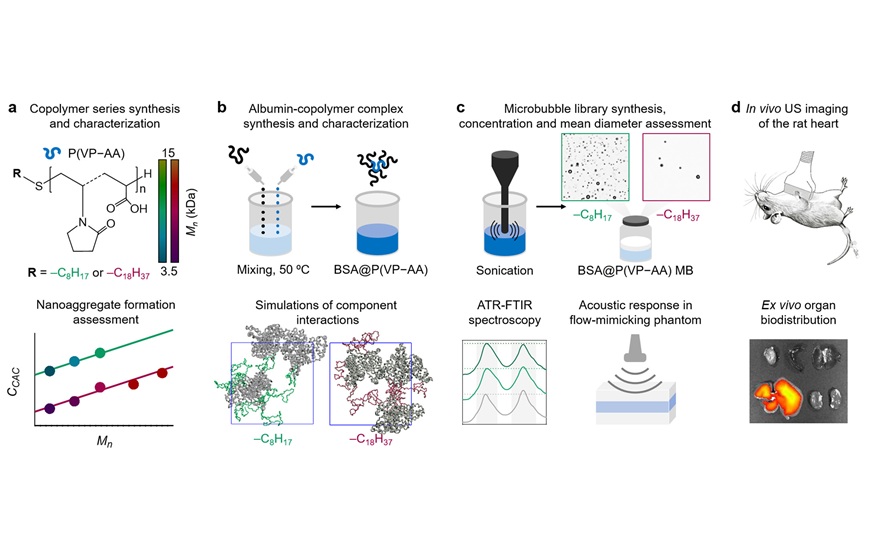
Ultrasound imaging is an affordable and non-invasive diagnostic method that uses widely available equipment. However, its results are often not highly accurate, and the image quality is heavily dependent on the operator's skill. In contrast, techniques like MRI and CT scans are not always accessible due to their high cost, lack of available equipment, and potential harm caused by the contrast agents used in these methods. These contrast agents are toxic, and CT scans expose patients to high radiation doses. On the other hand, ultrasound imaging with contrast agents can significantly improve the quality of images for internal organs, such as the heart, liver, and brain. This enhanced ultrasound technique could be useful for diagnosing a wide array of diseases in the cardiovascular, liver, kidney, and female reproductive systems. Ultrasound contrast agents are often microbubbles made from proteins, lipids, or polymers. Proteins enhance image quality, while lipids and polymers provide stability, extending the time available for diagnostics. Despite these benefits, further improvements in their performance are still needed.
Researchers at Skolkovo Institute of Science and Technology (Skoltech, Moscow, Russia) have developed and tested protein-polymer microbubbles for medical ultrasound imaging. When injected intravenously, these microbubbles serve as contrast agents, improving image quality. Tested in rats, the new microbubbles stayed in the bloodstream longer than the currently available alternatives, giving doctors more time to complete the examination. This enhanced contrast could make ultrasound a viable alternative to MRI and CT scans, which are more expensive and potentially harmful. The researchers created the first "hybrid" microbubble formulation by combining a protein called albumin with a copolymer.
This formulation resulted in 100 different microbubble types for ultrasound imaging, from which the most effective contrast agent was chosen and tested on a rat’s beating heart. The selection process involved multiple steps: evaluating microbubble size, concentration, and acoustic response in organ phantoms and animals. Compared to a protein-based agent without the added copolymer, the hybrid microbubbles showed significant improvements in both image contrast and the time they remained in the bloodstream, which was one and a half to two times longer.
To create the new contrast agent, the team combined bovine serum albumin—a commonly used protein in pharmacology, including in microbubble production—with biocompatible polymers. They tested 100 different combinations, varying the type of polymer and the polymer's proportion in the mixture from 2% to nearly 50%. The challenge was to find the right balance between microbubble stability, concentration, and ultrasound response. Formulations that did not produce stable microbubbles were discarded, and the remaining candidates were tested on a blood vessel phantom to measure bubble size, concentration, and acoustic response. This process led to the identification of the most promising formulation, which was then compared with pure albumin microbubbles and a saline injection in animal trials.
In these tests, the contrast agent was injected into a rat’s tail vein, followed by an ultrasound exam of its heart. The results, published in Biomaterials Advances, revealed that while the image without contrast showed few details, and the image with the protein contrast only displayed the ventricles, the hybrid agent provided a clear view of the entire four-chamber heart. Moreover, the effect lasted up to 7 minutes, compared to just 3 minutes with standard agents. The researchers believe the new agent’s high contrast could make it a valuable tool for diagnosing infertility in women and studying blood vessels in the brain, although further work is needed to fully explore its potential.
Latest Ultrasound News
- AI-Powered Lung Ultrasound Outperforms Human Experts in Tuberculosis Diagnosis
- AI Identifies Heart Valve Disease from Common Imaging Test
- Novel Imaging Method Enables Early Diagnosis and Treatment Monitoring of Type 2 Diabetes
- Ultrasound-Based Microscopy Technique to Help Diagnose Small Vessel Diseases
- Smart Ultrasound-Activated Immune Cells Destroy Cancer Cells for Extended Periods
- Tiny Magnetic Robot Takes 3D Scans from Deep Within Body
- High Resolution Ultrasound Speeds Up Prostate Cancer Diagnosis
- World's First Wireless, Handheld, Whole-Body Ultrasound with Single PZT Transducer Makes Imaging More Accessible
- Artificial Intelligence Detects Undiagnosed Liver Disease from Echocardiograms
- Ultrasound Imaging Non-Invasively Tracks Tumor Response to Radiation and Immunotherapy
- AI Improves Detection of Congenital Heart Defects on Routine Prenatal Ultrasounds
- AI Diagnoses Lung Diseases from Ultrasound Videos with 96.57% Accuracy
- Ultrasound-Directed Microbubbles Boost Immune Response Against Tumors
- POC Ultrasound Enhances Early Pregnancy Care and Cuts Emergency Visits
- AI-Based Models Outperform Human Experts at Identifying Ovarian Cancer in Ultrasound Images
- Automated Breast Ultrasound Provides Alternative to Mammography in Low-Resource Settings
Channels
Radiography
view channel
World's Largest Class Single Crystal Diamond Radiation Detector Opens New Possibilities for Diagnostic Imaging
Diamonds possess ideal physical properties for radiation detection, such as exceptional thermal and chemical stability along with a quick response time. Made of carbon with an atomic number of six, diamonds... Read more
AI-Powered Imaging Technique Shows Promise in Evaluating Patients for PCI
Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), also known as coronary angioplasty, is a minimally invasive procedure where small metal tubes called stents are inserted into partially blocked coronary arteries... Read moreMRI
view channel
AI Tool Predicts Relapse of Pediatric Brain Cancer from Brain MRI Scans
Many pediatric gliomas are treatable with surgery alone, but relapses can be catastrophic. Predicting which patients are at risk for recurrence remains challenging, leading to frequent follow-ups with... Read more
AI Tool Tracks Effectiveness of Multiple Sclerosis Treatments Using Brain MRI Scans
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a condition in which the immune system attacks the brain and spinal cord, leading to impairments in movement, sensation, and cognition. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) markers... Read more
Ultra-Powerful MRI Scans Enable Life-Changing Surgery in Treatment-Resistant Epileptic Patients
Approximately 360,000 individuals in the UK suffer from focal epilepsy, a condition in which seizures spread from one part of the brain. Around a third of these patients experience persistent seizures... Read moreNuclear Medicine
view channel
Novel Radiolabeled Antibody Improves Diagnosis and Treatment of Solid Tumors
Interleukin-13 receptor α-2 (IL13Rα2) is a cell surface receptor commonly found in solid tumors such as glioblastoma, melanoma, and breast cancer. It is minimally expressed in normal tissues, making it... Read more
Novel PET Imaging Approach Offers Never-Before-Seen View of Neuroinflammation
COX-2, an enzyme that plays a key role in brain inflammation, can be significantly upregulated by inflammatory stimuli and neuroexcitation. Researchers suggest that COX-2 density in the brain could serve... Read moreGeneral/Advanced Imaging
view channel
AI-Powered Imaging System Improves Lung Cancer Diagnosis
Given the need to detect lung cancer at earlier stages, there is an increasing need for a definitive diagnostic pathway for patients with suspicious pulmonary nodules. However, obtaining tissue samples... Read more
AI Model Significantly Enhances Low-Dose CT Capabilities
Lung cancer remains one of the most challenging diseases, making early diagnosis vital for effective treatment. Fortunately, advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) are revolutionizing lung cancer... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more
Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in medical diagnostics market is expanding with early disease detection being one of its key applications and image recognition becoming a compelling consumer proposition... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
GE HealthCare and NVIDIA Collaboration to Reimagine Diagnostic Imaging
GE HealthCare (Chicago, IL, USA) has entered into a collaboration with NVIDIA (Santa Clara, CA, USA), expanding the existing relationship between the two companies to focus on pioneering innovation in... Read more
Patient-Specific 3D-Printed Phantoms Transform CT Imaging
New research has highlighted how anatomically precise, patient-specific 3D-printed phantoms are proving to be scalable, cost-effective, and efficient tools in the development of new CT scan algorithms... Read more
Siemens and Sectra Collaborate on Enhancing Radiology Workflows
Siemens Healthineers (Forchheim, Germany) and Sectra (Linköping, Sweden) have entered into a collaboration aimed at enhancing radiologists' diagnostic capabilities and, in turn, improving patient care... Read more




















