Advanced Imaging Reveals Hidden Metastases in High-Risk Prostate Cancer Patients
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 06 Jan 2025 |
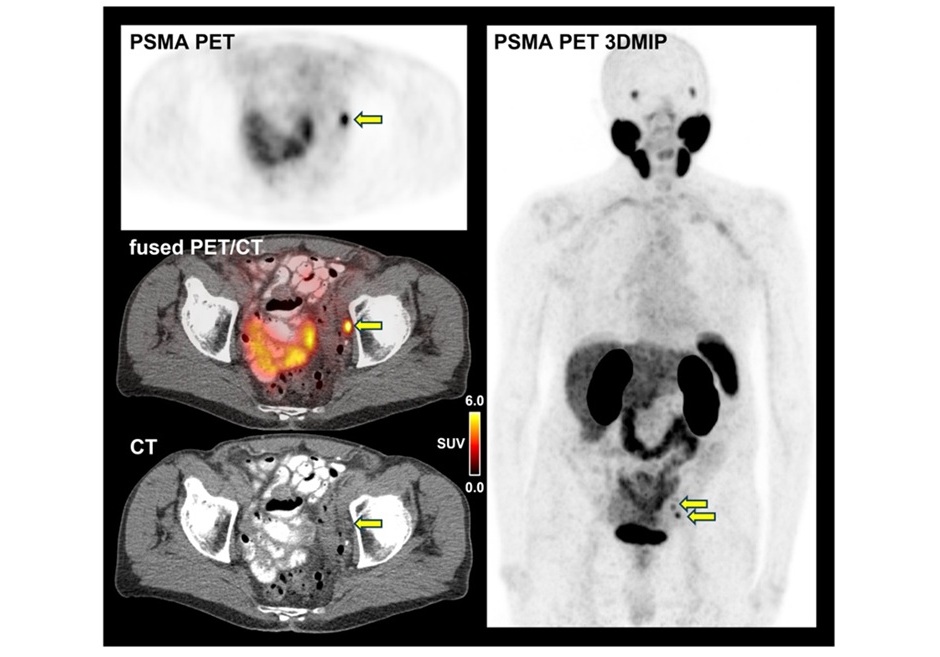
Prostate-specific membrane antigen–positron emission tomography (PSMA-PET) imaging has become an essential tool in transforming the way prostate cancer is staged. Using small amounts of radioactive “tracers,” or radiotracers, that bind to prostate cancer cells, PSMA-PET makes these cells visible on PET scans. In contrast to traditional imaging, which primarily provides anatomical details, PSMA-PET offers functional imaging that highlights the cancer’s biological activity, significantly improving disease staging accuracy. While PSMA-PET’s clinical adoption has revolutionized prostate cancer imaging, treatment decisions still often rely on clinical trials that did not incorporate this advanced imaging technique for patient selection. Now, a new study has shown that high-risk nonmetastatic hormone-sensitive prostate cancer may be more advanced than previously believed. Published in JAMA Network Open, the study found that nearly half of high-risk prostate cancer patients, initially classified as nonmetastatic by conventional imaging, were later found to have metastatic disease when assessed using PSMA-PET. This suggests that traditional imaging might often underestimate the extent of cancer spread.
To further investigate the advantages of PSMA-PET over conventional imaging, researchers at the UCLA Health Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center (Los Angeles, CA, USA) conducted a post hoc, retrospective cross-sectional study using data from 182 patients with high-risk recurrent prostate cancers who were previously thought to have disease limited to the prostate and eligible for the EMBARK trial. This clinical trial had previously demonstrated that adding enzalutamide, a type of hormone therapy, to androgen deprivation therapy improved metastasis-free survival. However, the trial relied on conventional imaging to classify patients, a method the researchers believe might have underestimated the disease’s spread in some instances. In this cohort, the researchers found that PSMA-PET detected cancer metastases in 46% of patients, even though traditional imaging had shown no evidence of spread. Moreover, based on PSMA-PET, 24% of the patients had five or more lesions missed by conventional imaging.
These findings challenge the conclusions of earlier studies, such as the EMBARK trial, and advocate for the inclusion of PSMA-PET in patient selection for future clinical and trial interventions in prostate cancer. They also suggest a need to reassess treatment strategies and open the possibility for potentially curative treatments, like targeted radiotherapy, for some patients. The results raise important questions about how new imaging technologies should be integrated into standard clinical care. While the study highlights the significant potential of PSMA-PET, ongoing research is needed to better understand its impact on long-term patient outcomes and how it can best inform therapy, as noted by the researchers.
“We anticipated that PSMA-PET would detect more suspicious findings compared to conventional imaging. However, it was informative to uncover such a high number of metastatic findings in a well-defined cohort of patients resembling the EMBARK trial population that was supposed to only include those without metastases,” said Dr. Adrien Holzgreve, a visiting assistant professor at the David Geffen School of Medicine and first author of the study. “We have good rationales to assume that it is helpful to primarily rely on PSMA-PET findings. But more high-quality prospective data would be needed to claim superiority of PSMA-PET for treatment-guidance in terms of patient outcome. However, we are confident PSMA-PET will continue to advance prostate cancer staging and guide personalized therapies.”
Latest Nuclear Medicine News
- Novel Bacteria-Specific PET Imaging Approach Detects Hard-To-Diagnose Lung Infections
- New Imaging Approach Could Reduce Need for Biopsies to Monitor Prostate Cancer
- Novel Radiolabeled Antibody Improves Diagnosis and Treatment of Solid Tumors
- Novel PET Imaging Approach Offers Never-Before-Seen View of Neuroinflammation
- Novel Radiotracer Identifies Biomarker for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
- Innovative PET Imaging Technique to Help Diagnose Neurodegeneration
- New Molecular Imaging Test to Improve Lung Cancer Diagnosis
- Novel PET Technique Visualizes Spinal Cord Injuries to Predict Recovery
- Next-Gen Tau Radiotracers Outperform FDA-Approved Imaging Agents in Detecting Alzheimer’s
- Breakthrough Method Detects Inflammation in Body Using PET Imaging
- Combining Advanced Imaging Technologies Offers Breakthrough in Glioblastoma Treatment
- New Molecular Imaging Agent Accurately Identifies Crucial Cancer Biomarker
- New Scans Light Up Aggressive Tumors for Better Treatment
- AI Stroke Brain Scan Readings Twice as Accurate as Current Method
- AI Analysis of PET/CT Images Predicts Side Effects of Immunotherapy in Lung Cancer
- New Imaging Agent to Drive Step-Change for Brain Cancer Imaging
Channels
Radiography
view channel
AI Detects Hidden Heart Disease in Existing CT Chest Scans
Coronary artery calcium (CAC) is a major indicator of cardiovascular risk, but its assessment typically requires a specialized “gated” CT scan that synchronizes with the heartbeat. In contrast, most chest... Read more
Ultra-Lightweight AI Model Runs Without GPU to Break Barriers in Lung Cancer Diagnosis
Artificial intelligence (AI) models typically demand enormous datasets and expensive GPU servers, creating a significant barrier to wider adoption, especially in resource-limited settings.... Read more
AI Radiology Tool Identifies Life-Threatening Conditions in Milliseconds
Radiology is emerging as one of healthcare’s most pressing bottlenecks. By 2033, the U.S. could face a shortage of up to 42,000 radiologists, even as imaging volumes grow by 5% annually.... Read more
Machine Learning Algorithm Identifies Cardiovascular Risk from Routine Bone Density Scans
A new study published in the Journal of Bone and Mineral Research reveals that an automated machine learning program can predict the risk of cardiovascular events and falls or fractures by analyzing bone... Read moreMRI
view channel
New MRI Technique Reveals Hidden Heart Issues
Traditional exercise stress tests conducted within an MRI machine require patients to lie flat, a position that artificially improves heart function by increasing stroke volume due to gravity-driven blood... Read more
Shorter MRI Exam Effectively Detects Cancer in Dense Breasts
Women with extremely dense breasts face a higher risk of missed breast cancer diagnoses, as dense glandular and fibrous tissue can obscure tumors on mammograms. While breast MRI is recommended for supplemental... Read moreUltrasound
view channel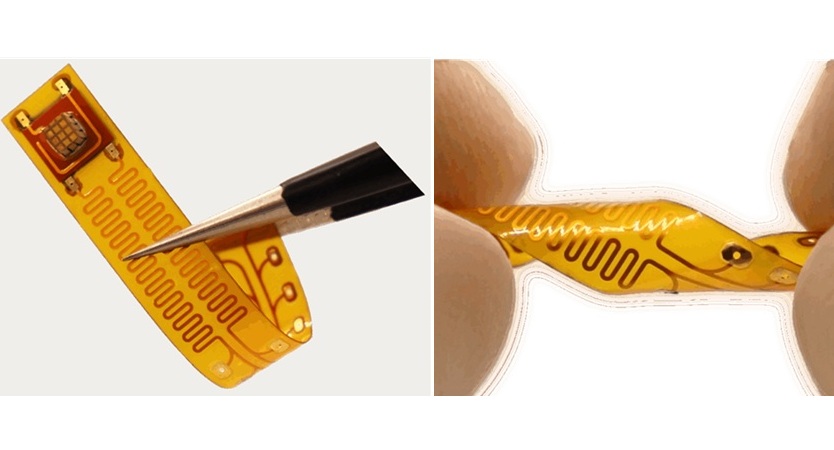
Wireless Chronic Pain Management Device to Reduce Need for Painkillers and Surgery
Chronic pain affects millions of people globally, often leading to long-term disability and dependence on opioid medications, which carry significant risks of side effects and addiction.... Read more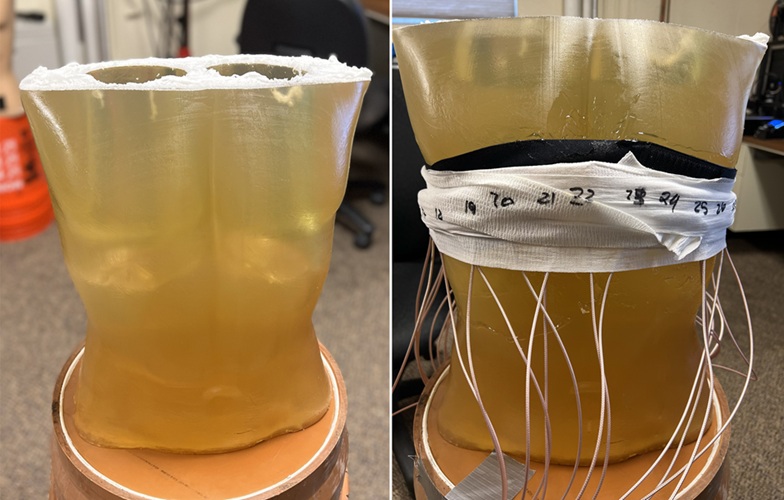
New Medical Ultrasound Imaging Technique Enables ICU Bedside Monitoring
Ultrasound computed tomography (USCT) presents a safer alternative to imaging techniques like X-ray computed tomography (commonly known as CT or “CAT” scans) because it does not produce ionizing radiation.... Read moreGeneral/Advanced Imaging
view channel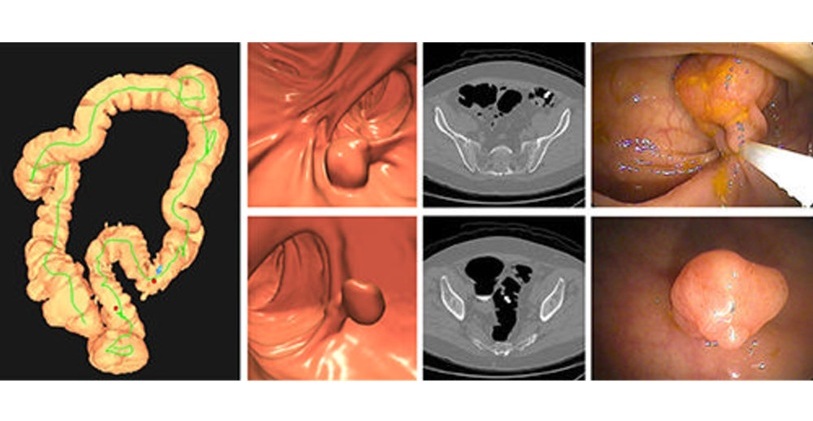
CT Colonography Beats Stool DNA Testing for Colon Cancer Screening
As colorectal cancer remains the second leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide, early detection through screening is vital to reduce advanced-stage treatments and associated costs.... Read more
First-Of-Its-Kind Wearable Device Offers Revolutionary Alternative to CT Scans
Currently, patients with conditions such as heart failure, pneumonia, or respiratory distress often require multiple imaging procedures that are intermittent, disruptive, and involve high levels of radiation.... Read more
AI-Based CT Scan Analysis Predicts Early-Stage Kidney Damage Due to Cancer Treatments
Radioligand therapy, a form of targeted nuclear medicine, has recently gained attention for its potential in treating specific types of tumors. However, one of the potential side effects of this therapy... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more
Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in medical diagnostics market is expanding with early disease detection being one of its key applications and image recognition becoming a compelling consumer proposition... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
GE HealthCare and NVIDIA Collaboration to Reimagine Diagnostic Imaging
GE HealthCare (Chicago, IL, USA) has entered into a collaboration with NVIDIA (Santa Clara, CA, USA), expanding the existing relationship between the two companies to focus on pioneering innovation in... Read more
Patient-Specific 3D-Printed Phantoms Transform CT Imaging
New research has highlighted how anatomically precise, patient-specific 3D-printed phantoms are proving to be scalable, cost-effective, and efficient tools in the development of new CT scan algorithms... Read more
Siemens and Sectra Collaborate on Enhancing Radiology Workflows
Siemens Healthineers (Forchheim, Germany) and Sectra (Linköping, Sweden) have entered into a collaboration aimed at enhancing radiologists' diagnostic capabilities and, in turn, improving patient care... Read more













.jpeg)


