New Immuno-PET Imaging Technique Identifies Glioblastoma Patients Who Would Benefit from Immunotherapy
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 04 Nov 2024 |
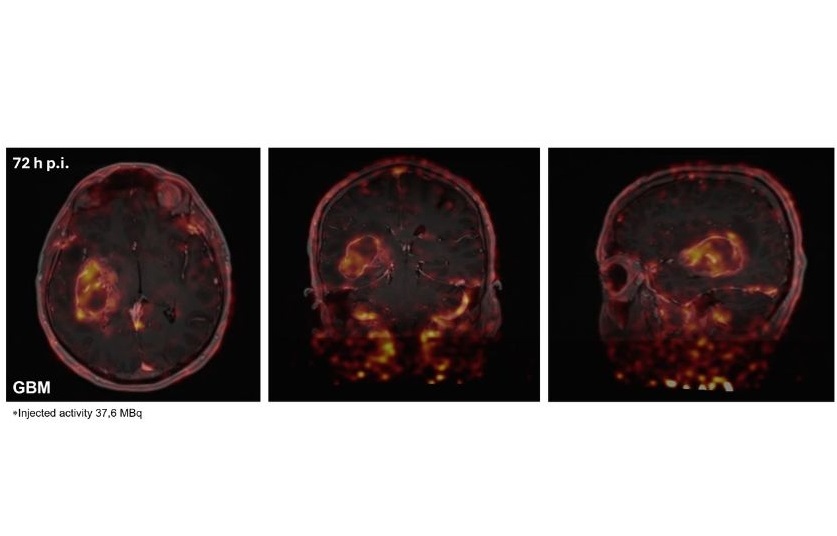
Glioblastoma is a type of brain tumor associated with a very poor prognosis, with average survival rates of 12 to 18 months and only 5% of patients surviving beyond five years. Research has shown that certain patients, particularly those with aggressive tumors, may respond favorably to immunotherapy drugs; however, there is currently no method to assess this without a tumor biopsy. Elevated levels of the PD-L1 protein have been detected in rapidly progressing glioblastoma tumors. This protein functions as a brake on the immune system, and targeting PD-L1 to inhibit its activity could potentially reactivate the immune response against the cancer. Historically, a biopsy has been the sole method for evaluating PD-L1 levels in brain tumors. However, biopsies provide only a static snapshot of protein levels at the time of sampling, and there can be a significant delay in treatment decisions, during which protein levels may fluctuate. Due to the risks associated with infection and bleeding, biopsies are seldom performed for glioblastomas before surgery to remove the tumor, leaving many patients without access to potentially beneficial treatments. Consequently, the difficulties in assessing PD-L1 levels without a biopsy have led to the exclusion of patients with newly diagnosed primary brain tumors from early-phase clinical trials. A new imaging technique may now allow patients with aggressive brain tumors to access cutting-edge immunotherapy treatments.
Researchers at The Institute of Cancer Research (London, UK) have developed a novel immuno-PET imaging technique that could identify which glioblastoma patients are likely to benefit from immunotherapy and track their response over time. They created a radiotracer—a radioactive molecule linked to an antibody—that specifically binds to the PD-L1 protein, enabling measurement of its levels in glioblastoma patients. Findings published in the journal Neuro-Oncology demonstrated that the radiotracer effectively binds to PD-L1 on tumor and immune cells, as seen in PET scans. Eight newly diagnosed glioblastoma patients received the tracer intravenously, followed by PET scans at 48 and 72 hours post-injection. The PET scans revealed successful binding of the tracer to PD-L1 positive cells in the tumor and throughout the body. These findings were then compared with biopsies collected during surgical tumor removal.
Among the patients, five were randomly selected to receive pembrolizumab prior to surgery. Pembrolizumab is a monoclonal antibody that inhibits PD-L1 by targeting its interaction with a protein called PD-1. The researchers observed lower levels of the tracer in the tumors of these patients, suggesting that the drug effectively acts on the PD-L1 protein, thus removing the immune system's inhibitory effects and allowing it to combat the cancer. Additionally, these patients showed increased tracer levels in lymph tissues, indicating that the drug was activating immune cells throughout the body. Notably, three of these five patients experienced stabilization of their cancer without further growth. The researchers plan to investigate the relationship between the patients' responses to the drug and the levels of PD-L1 in their tumors prior to treatment. The clinical trial aims to enroll 36 glioblastoma patients to assess the effectiveness of pembrolizumab administered before surgery, as well as to evaluate whether PET imaging with the radiotracer can be used to monitor progress and adjust treatment as necessary. Furthermore, the team has developed an alternative radiotracer that may prove even more effective than the antibody used in this study. This smaller molecule is expected to pass through the blood-brain barrier more easily, allowing for PET scans to be performed just one hour after injection. The researchers are hopeful about testing this new molecule in similar studies in the future.
“This study could revolutionize glioblastoma treatment, as we’ve shown that it is possible to image an immunotherapy target with our radiotracer. Being able to take a scan of the patient’s body and see the levels of this target means that we can predict the patients’ response, see their immune system responding to the treatment, and alter treatment where necessary – providing a personalized treatment plan based on the unique characteristics of their tumor, all without the need for a pre-surgery biopsy,” said Dr. Gabriela Kramer-Marek, Associate Professor and Group Leader in Preclinical Molecular Imaging at The Institute of Cancer Research. “I look forward to seeing the results of our larger clinical trial to assess how effective this immunotherapy is in glioblastoma patients – and I hope that our radiotracer will tell us more about the biology behind why some tumors are more responsive than others.”
Related Links:
The Institute of Cancer Research
Latest General/Advanced Imaging News
- AI Model Significantly Enhances Low-Dose CT Capabilities
- Ultra-Low Dose CT Aids Pneumonia Diagnosis in Immunocompromised Patients
- AI Reduces CT Lung Cancer Screening Workload by Almost 80%
- Cutting-Edge Technology Combines Light and Sound for Real-Time Stroke Monitoring
- AI System Detects Subtle Changes in Series of Medical Images Over Time
- New CT Scan Technique to Improve Prognosis and Treatments for Head and Neck Cancers
- World’s First Mobile Whole-Body CT Scanner to Provide Diagnostics at POC
- Comprehensive CT Scans Could Identify Atherosclerosis Among Lung Cancer Patients
- AI Improves Detection of Colorectal Cancer on Routine Abdominopelvic CT Scans
- Super-Resolution Technology Enhances Clinical Bone Imaging to Predict Osteoporotic Fracture Risk
- AI-Powered Abdomen Map Enables Early Cancer Detection
- Deep Learning Model Detects Lung Tumors on CT
- AI Predicts Cardiovascular Risk from CT Scans
- Deep Learning Based Algorithms Improve Tumor Detection in PET/CT Scans
- New Technology Provides Coronary Artery Calcification Scoring on Ungated Chest CT Scans
- Deep Learning Model Accurately Diagnoses COPD Using Single Inhalation Lung CT Scan
Channels
Radiography
view channel
Higher Chest X-Ray Usage Catches Lung Cancer Earlier and Improves Survival
Lung cancer continues to be the leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide. While advanced technologies like CT scanners play a crucial role in detecting lung cancer, more accessible and affordable... Read more
AI-Powered Mammograms Predict Cardiovascular Risk
The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends that women in middle age and older undergo a mammogram, which is an X-ray of the breast, every one or two years to screen for breast cancer.... Read moreMRI
view channel
Ultra-Powerful MRI Scans Enable Life-Changing Surgery in Treatment-Resistant Epileptic Patients
Approximately 360,000 individuals in the UK suffer from focal epilepsy, a condition in which seizures spread from one part of the brain. Around a third of these patients experience persistent seizures... Read more
AI-Powered MRI Technology Improves Parkinson’s Diagnoses
Current research shows that the accuracy of diagnosing Parkinson’s disease typically ranges from 55% to 78% within the first five years of assessment. This is partly due to the similarities shared by Parkinson’s... Read more
Biparametric MRI Combined with AI Enhances Detection of Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer
Artificial intelligence (AI) technologies are transforming the way medical images are analyzed, offering unprecedented capabilities in quantitatively extracting features that go beyond traditional visual... Read more
First-Of-Its-Kind AI-Driven Brain Imaging Platform to Better Guide Stroke Treatment Options
Each year, approximately 800,000 people in the U.S. experience strokes, with marginalized and minoritized groups being disproportionately affected. Strokes vary in terms of size and location within the... Read moreUltrasound
view channel
Tiny Magnetic Robot Takes 3D Scans from Deep Within Body
Colorectal cancer ranks as one of the leading causes of cancer-related mortality worldwide. However, when detected early, it is highly treatable. Now, a new minimally invasive technique could significantly... Read more
High Resolution Ultrasound Speeds Up Prostate Cancer Diagnosis
Each year, approximately one million prostate cancer biopsies are conducted across Europe, with similar numbers in the USA and around 100,000 in Canada. Most of these biopsies are performed using MRI images... Read more
World's First Wireless, Handheld, Whole-Body Ultrasound with Single PZT Transducer Makes Imaging More Accessible
Ultrasound devices play a vital role in the medical field, routinely used to examine the body's internal tissues and structures. While advancements have steadily improved ultrasound image quality and processing... Read moreGeneral/Advanced Imaging
view channel
AI Model Significantly Enhances Low-Dose CT Capabilities
Lung cancer remains one of the most challenging diseases, making early diagnosis vital for effective treatment. Fortunately, advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) are revolutionizing lung cancer... Read more
Ultra-Low Dose CT Aids Pneumonia Diagnosis in Immunocompromised Patients
Lung infections can be life-threatening for patients with weakened immune systems, making timely diagnosis crucial. While CT scans are considered the gold standard for detecting pneumonia, repeated scans... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more
Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in medical diagnostics market is expanding with early disease detection being one of its key applications and image recognition becoming a compelling consumer proposition... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
GE HealthCare and NVIDIA Collaboration to Reimagine Diagnostic Imaging
GE HealthCare (Chicago, IL, USA) has entered into a collaboration with NVIDIA (Santa Clara, CA, USA), expanding the existing relationship between the two companies to focus on pioneering innovation in... Read more
Patient-Specific 3D-Printed Phantoms Transform CT Imaging
New research has highlighted how anatomically precise, patient-specific 3D-printed phantoms are proving to be scalable, cost-effective, and efficient tools in the development of new CT scan algorithms... Read more
Siemens and Sectra Collaborate on Enhancing Radiology Workflows
Siemens Healthineers (Forchheim, Germany) and Sectra (Linköping, Sweden) have entered into a collaboration aimed at enhancing radiologists' diagnostic capabilities and, in turn, improving patient care... Read more