AI May Benefit Decision-Making in Less Experienced Clinicians Assessing Heart Ultrasounds
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 09 Sep 2024 |

Coronary artery disease (CAD) is a leading cause of death globally, causing over 9 million deaths worldwide and 63,000 annually in the UK alone. Stress echocardiography (SE), which is an ultrasound of the heart taken at rest and during stress, is crucial for assessing the risk of heart attacks and death in patients with known or suspected CAD. SE is not only among the most frequently used diagnostic tests for CAD but is also the primary imaging method available across the UK for this diagnosis. However, its accuracy ranges significantly, from 60% to 94%, influenced by the clinician's expertise and the quality of the images. The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into healthcare presents significant potential to aid clinicians in diagnosing more swiftly and accurately, thus initiating treatments earlier. Now, a large randomized trial found no substantial evidence to suggest that AI assistance in clinical decision-making for heart ultrasound assessments improves detection rates compared to traditional practices for identifying patients with suspected heart disease who might benefit from invasive treatments. Nonetheless, the study highlighted that AI could enhance decision-making capabilities for less experienced clinicians and showed promise in particularly complex clinical sub-groups.
Developed by researchers at the University of Oxford (Oxford, UK) EchoGo Pro automates the interpretation of SE images by integrating novel image features with AI technology. This software's effectiveness was tested through the PROTEUS randomized controlled trial, which involved patients aged 18 and older referred for SE at 20 UK hospitals from November 2021 to June 2023 to investigate suspected CAD. The study involved 2,341 patients (average age 64 years; 45% female; 20% with pre-existing heart disease), who were randomly assigned to either standard clinical decision-making or AI-enhanced decision-making where clinicians used an AI-generated image analysis report (EchoGo Pro) during their image assessments to evaluate the likelihood of severe CAD. The main focus of the study was to compare the effectiveness of standard versus AI-augmented decision-making in directing patients towards invasive coronary angiograms and monitoring acute coronary events within a six-month period. By December 2023, 2,213 participants (94.5%) had completed the six-month follow-up.
Overall, 85 patients were referred for angiography post-SE. Among those not referred, 41 suffered acute coronary syndromes (nonfatal heart attacks) or cardiac deaths within six months, indicating potential misjudgments in referral decisions. The analysis revealed that AI-assisted decision-making did not show non-inferiority compared to traditional clinical decision-making in appropriately directing patients for coronary angiography. Among those referred, 27 out of 36 in the control group and 34 out of 49 in the AI group were deemed correct referrals. Regarding patients who suffered adverse events despite not being referred for angiography, there were 22 in the control group and 19 in the AI group, though the differences were not statistically significant. However, additional analyses indicated that AI could improve decision-making among less experienced clinicians and in complex cases where image interpretation is challenging.
“It is well reported that clinician performance in interpreting stress echocardiograms ranges widely according to the experience level of the operator,” said lead author Dr. Ross Upton from the University of Oxford. “The results of this trial suggest that AI has the potential to bring all operators, regardless of experience, up to the same level of accuracy. While the PROTEUS trial did not demonstrate meaningful differences in all-comers, the AI diagnostic may also benefit specific subgroups of patients in whom decision making is known to be more complex.”
Related Links:
University of Oxford
Latest Ultrasound News
- Wireless Chronic Pain Management Device to Reduce Need for Painkillers and Surgery
- New Medical Ultrasound Imaging Technique Enables ICU Bedside Monitoring
- New Incision-Free Technique Halts Growth of Debilitating Brain Lesions
- AI-Powered Lung Ultrasound Outperforms Human Experts in Tuberculosis Diagnosis
- AI Identifies Heart Valve Disease from Common Imaging Test
- Novel Imaging Method Enables Early Diagnosis and Treatment Monitoring of Type 2 Diabetes
- Ultrasound-Based Microscopy Technique to Help Diagnose Small Vessel Diseases
- Smart Ultrasound-Activated Immune Cells Destroy Cancer Cells for Extended Periods
- Tiny Magnetic Robot Takes 3D Scans from Deep Within Body
- High Resolution Ultrasound Speeds Up Prostate Cancer Diagnosis
- World's First Wireless, Handheld, Whole-Body Ultrasound with Single PZT Transducer Makes Imaging More Accessible
- Artificial Intelligence Detects Undiagnosed Liver Disease from Echocardiograms
- Ultrasound Imaging Non-Invasively Tracks Tumor Response to Radiation and Immunotherapy
- AI Improves Detection of Congenital Heart Defects on Routine Prenatal Ultrasounds
- AI Diagnoses Lung Diseases from Ultrasound Videos with 96.57% Accuracy
- New Contrast Agent for Ultrasound Imaging Ensures Affordable and Safer Medical Diagnostics
Channels
Radiography
view channel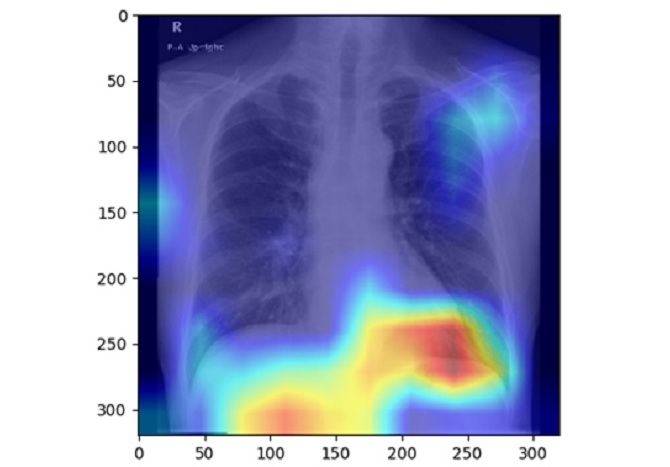
AI Detects Fatty Liver Disease from Chest X-Rays
Fatty liver disease, which results from excess fat accumulation in the liver, is believed to impact approximately one in four individuals globally. If not addressed in time, it can progress to severe conditions... Read more
AI Detects Hidden Heart Disease in Existing CT Chest Scans
Coronary artery calcium (CAC) is a major indicator of cardiovascular risk, but its assessment typically requires a specialized “gated” CT scan that synchronizes with the heartbeat. In contrast, most chest... Read moreMRI
view channel
New MRI Technique Reveals Hidden Heart Issues
Traditional exercise stress tests conducted within an MRI machine require patients to lie flat, a position that artificially improves heart function by increasing stroke volume due to gravity-driven blood... Read more
Shorter MRI Exam Effectively Detects Cancer in Dense Breasts
Women with extremely dense breasts face a higher risk of missed breast cancer diagnoses, as dense glandular and fibrous tissue can obscure tumors on mammograms. While breast MRI is recommended for supplemental... Read moreNuclear Medicine
view channel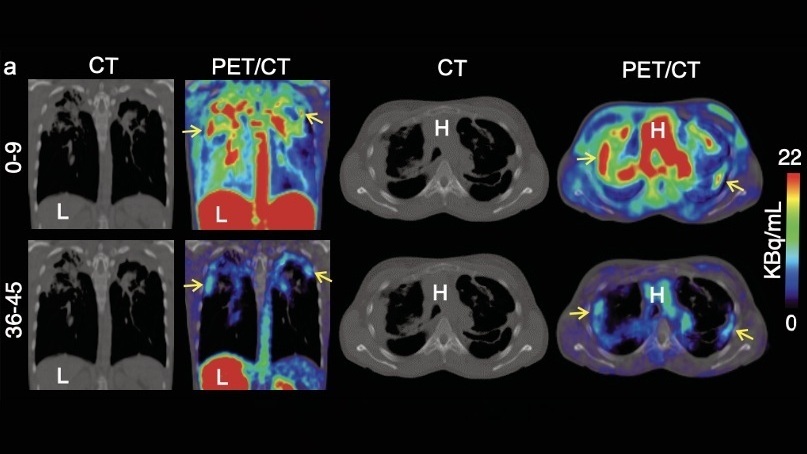
Novel Bacteria-Specific PET Imaging Approach Detects Hard-To-Diagnose Lung Infections
Mycobacteroides abscessus is a rapidly growing mycobacteria that primarily affects immunocompromised patients and those with underlying lung diseases, such as cystic fibrosis or chronic obstructive pulmonary... Read more
New Imaging Approach Could Reduce Need for Biopsies to Monitor Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer is the second leading cause of cancer-related death among men in the United States. However, the majority of older men diagnosed with prostate cancer have slow-growing, low-risk forms of... Read moreGeneral/Advanced Imaging
view channel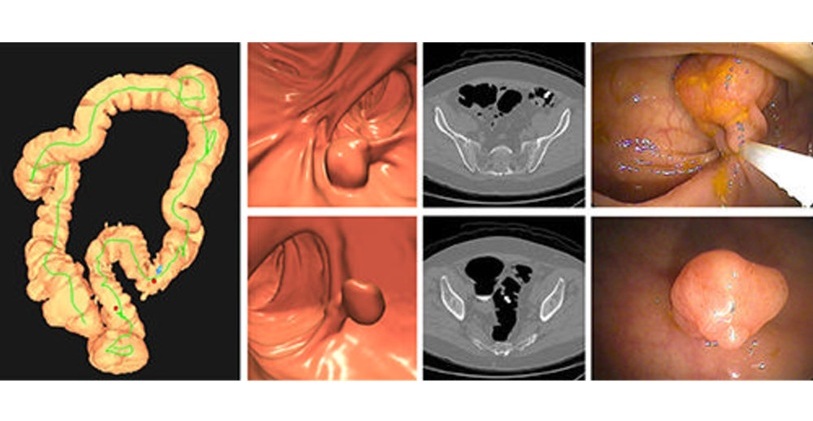
CT Colonography Beats Stool DNA Testing for Colon Cancer Screening
As colorectal cancer remains the second leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide, early detection through screening is vital to reduce advanced-stage treatments and associated costs.... Read more
First-Of-Its-Kind Wearable Device Offers Revolutionary Alternative to CT Scans
Currently, patients with conditions such as heart failure, pneumonia, or respiratory distress often require multiple imaging procedures that are intermittent, disruptive, and involve high levels of radiation.... Read more
AI-Based CT Scan Analysis Predicts Early-Stage Kidney Damage Due to Cancer Treatments
Radioligand therapy, a form of targeted nuclear medicine, has recently gained attention for its potential in treating specific types of tumors. However, one of the potential side effects of this therapy... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more
Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in medical diagnostics market is expanding with early disease detection being one of its key applications and image recognition becoming a compelling consumer proposition... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
GE HealthCare and NVIDIA Collaboration to Reimagine Diagnostic Imaging
GE HealthCare (Chicago, IL, USA) has entered into a collaboration with NVIDIA (Santa Clara, CA, USA), expanding the existing relationship between the two companies to focus on pioneering innovation in... Read more
Patient-Specific 3D-Printed Phantoms Transform CT Imaging
New research has highlighted how anatomically precise, patient-specific 3D-printed phantoms are proving to be scalable, cost-effective, and efficient tools in the development of new CT scan algorithms... Read more
Siemens and Sectra Collaborate on Enhancing Radiology Workflows
Siemens Healthineers (Forchheim, Germany) and Sectra (Linköping, Sweden) have entered into a collaboration aimed at enhancing radiologists' diagnostic capabilities and, in turn, improving patient care... Read more