World’s First Reference Material to Improve Accuracy of MRI and CT Diagnosis of Fatty Liver
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 01 Jul 2024 |
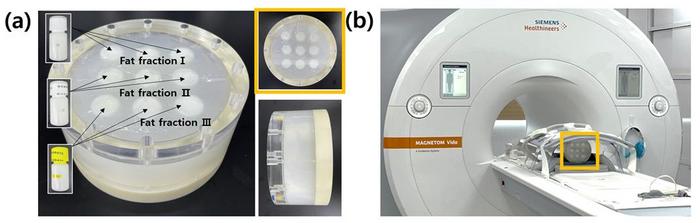
MRI and CT scans are essential for diagnosing conditions like fatty liver disease because they can non-invasively evaluate body fat, unlike invasive biopsy methods. However, the inconsistency in fat measurement values across different hospitals, manufacturers, and models poses a challenge, mainly because there are no established calibration standards. This variability makes it difficult for doctors, who must rely on their expertise and intuition, complicating multi-center clinical trials and big data research that require uniform measurements. Existing phantoms, designed to mimic body fat, have stability issues due to their composition, which includes about ten additives like artificial surfactants, and there is no objective method for verifying the precise content of these substances. Scientists have now developed the world’s first reference material to improve the accuracy of body fat measurements conducted through MRI and CT scans.
This new reference material, developed by the Korea Research Institute of Standards and Science (KRISS, Daejeon, South Korea), is an additive-free emulsion of water and fat, offering more accurate measurements of fat content. It has been designed for high stability and uniformity. The innovation was due to a collaborative effort within three KRISS departments, combining expertise in chemical water measurement and ultrasonic emulsification technology tailored for medical imaging applications. When used within a phantom, this reference material can standardize fat measurements across different systems by analyzing the water content to calculate the fat percentage.
The application of this new reference material and phantom is set to enhance the accuracy of medical imaging measurements and the reliability of diagnoses across various institutions. It also aims to provide a standard reference for aggregating multi-device and multi-center data in clinical studies, including those for obesity-related treatments. Siemens Healthineers (Forchheim, Germany) is already incorporating this breakthrough in its research to measure fat content with MRI machines. This research was published in the international journal Metrologia (IF: 2.4) in January. KRISS is planning further research to offer more refined concentrations of the reference material and help establish a new system for evaluating the performance of medical imaging devices based on extensive multi-center data.
"We will use this reference material in future clinical trials and patient-specific disease diagnosis to obtain more accurate and consistent data," said Professor Dong Wook Kim from the Department of Radiology at Asan Medical Center, who supported the validation of the reference material.
Related Links:
KRISS
Siemens Healthineers
Latest General/Advanced Imaging News
- AI-Powered Imaging System Improves Lung Cancer Diagnosis
- AI Model Significantly Enhances Low-Dose CT Capabilities
- Ultra-Low Dose CT Aids Pneumonia Diagnosis in Immunocompromised Patients
- AI Reduces CT Lung Cancer Screening Workload by Almost 80%
- Cutting-Edge Technology Combines Light and Sound for Real-Time Stroke Monitoring
- AI System Detects Subtle Changes in Series of Medical Images Over Time
- New CT Scan Technique to Improve Prognosis and Treatments for Head and Neck Cancers
- World’s First Mobile Whole-Body CT Scanner to Provide Diagnostics at POC
- Comprehensive CT Scans Could Identify Atherosclerosis Among Lung Cancer Patients
- AI Improves Detection of Colorectal Cancer on Routine Abdominopelvic CT Scans
- Super-Resolution Technology Enhances Clinical Bone Imaging to Predict Osteoporotic Fracture Risk
- AI-Powered Abdomen Map Enables Early Cancer Detection
- Deep Learning Model Detects Lung Tumors on CT
- AI Predicts Cardiovascular Risk from CT Scans
- Deep Learning Based Algorithms Improve Tumor Detection in PET/CT Scans
- New Technology Provides Coronary Artery Calcification Scoring on Ungated Chest CT Scans
Channels
Radiography
view channel
World's Largest Class Single Crystal Diamond Radiation Detector Opens New Possibilities for Diagnostic Imaging
Diamonds possess ideal physical properties for radiation detection, such as exceptional thermal and chemical stability along with a quick response time. Made of carbon with an atomic number of six, diamonds... Read more
AI-Powered Imaging Technique Shows Promise in Evaluating Patients for PCI
Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), also known as coronary angioplasty, is a minimally invasive procedure where small metal tubes called stents are inserted into partially blocked coronary arteries... Read moreUltrasound
view channel
AI Identifies Heart Valve Disease from Common Imaging Test
Tricuspid regurgitation is a condition where the heart's tricuspid valve does not close completely during contraction, leading to backward blood flow, which can result in heart failure. A new artificial... Read more
Novel Imaging Method Enables Early Diagnosis and Treatment Monitoring of Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is recognized as an autoimmune inflammatory disease, where chronic inflammation leads to alterations in pancreatic islet microvasculature, a key factor in β-cell dysfunction.... Read moreNuclear Medicine
view channel
Novel PET Imaging Approach Offers Never-Before-Seen View of Neuroinflammation
COX-2, an enzyme that plays a key role in brain inflammation, can be significantly upregulated by inflammatory stimuli and neuroexcitation. Researchers suggest that COX-2 density in the brain could serve... Read more
Novel Radiotracer Identifies Biomarker for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC), which represents 15-20% of all breast cancer cases, is one of the most aggressive subtypes, with a five-year survival rate of about 40%. Due to its significant heterogeneity... Read moreGeneral/Advanced Imaging
view channel
AI-Powered Imaging System Improves Lung Cancer Diagnosis
Given the need to detect lung cancer at earlier stages, there is an increasing need for a definitive diagnostic pathway for patients with suspicious pulmonary nodules. However, obtaining tissue samples... Read more
AI Model Significantly Enhances Low-Dose CT Capabilities
Lung cancer remains one of the most challenging diseases, making early diagnosis vital for effective treatment. Fortunately, advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) are revolutionizing lung cancer... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more
Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in medical diagnostics market is expanding with early disease detection being one of its key applications and image recognition becoming a compelling consumer proposition... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
GE HealthCare and NVIDIA Collaboration to Reimagine Diagnostic Imaging
GE HealthCare (Chicago, IL, USA) has entered into a collaboration with NVIDIA (Santa Clara, CA, USA), expanding the existing relationship between the two companies to focus on pioneering innovation in... Read more
Patient-Specific 3D-Printed Phantoms Transform CT Imaging
New research has highlighted how anatomically precise, patient-specific 3D-printed phantoms are proving to be scalable, cost-effective, and efficient tools in the development of new CT scan algorithms... Read more
Siemens and Sectra Collaborate on Enhancing Radiology Workflows
Siemens Healthineers (Forchheim, Germany) and Sectra (Linköping, Sweden) have entered into a collaboration aimed at enhancing radiologists' diagnostic capabilities and, in turn, improving patient care... Read more