Ultrasound Technology Breaks Blood-Brain Barrier for Glioblastoma Treatment
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 11 Jun 2024 |
Despite extensive molecular studies, the outlook for patients diagnosed with the aggressive brain cancer known as glioblastoma (GBM) continues to be poor. This is partly due to the blood-brain barrier (BBB), which blocks most treatments from reaching the brain effectively. For example, modern antibody-based therapies that have been successful in treating many solid tumors fail to cross the BBB. GBM cells tend to spread and invade areas of the brain that appear normal on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans due to the BBB's resistance to many drugs administered systemically. Even after surgical removal of the tumor-visible region, the presence of invasive residual cells often leads to cancer returning, with patients typically facing the inevitable progression of the disease. In a major advancement for the treatment of GBM, researchers have used ultrasound technology to breach the BBB, delivering a small combination of chemotherapy and immunotherapy drugs. This approach has shown potential in enhancing the immune system's ability to recognize and attack cancer cells, leading to a new treatment method.
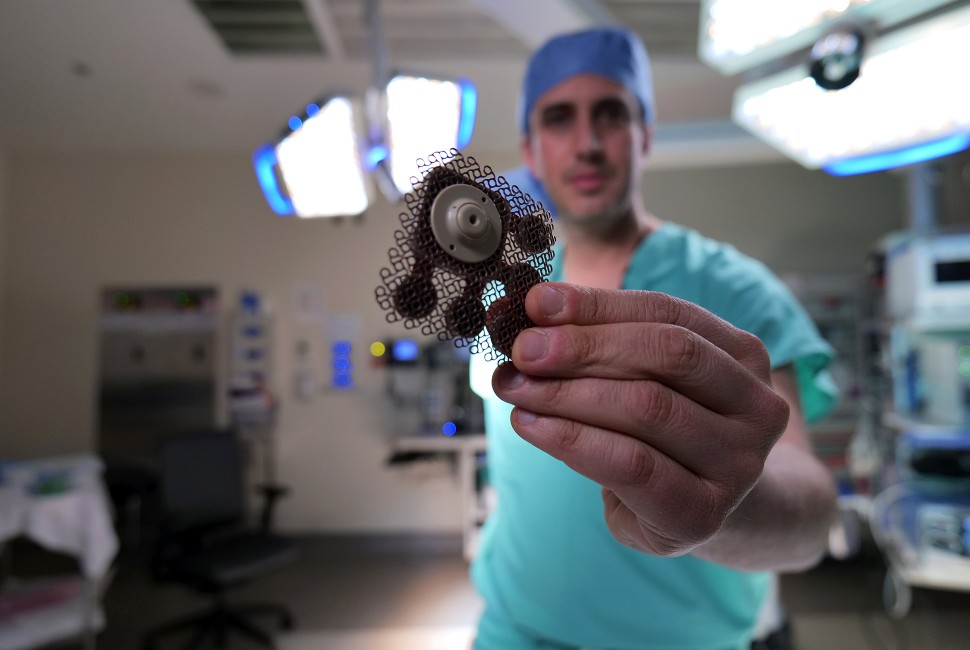
In this groundbreaking study, researchers at Northwestern Medicine (Chicago, IL, USA) achieved several breakthroughs. For the first time, they used a skull-implantable ultrasound device (SonoCloud-9; Carthera; Lyon, France) that increased the brain's absorption of the chemotherapy drug doxorubicin and immune checkpoint blockade antibodies, a new combination of immunotherapy treatments. This device creates microbubbles that temporarily disrupt the BBB, permitting the entry of immunotherapy into the brain. They also discovered that administering a smaller dose of doxorubicin, compared to traditional chemotherapy regimens, along with the immune checkpoint antibodies, significantly enhances the immune system's ability to identify malignant GBM cells and revitalizes the lymphocytes (immune cells) responsible for attacking the cancer cells.
An immune checkpoint blockade antibody prevents cancer cells from deactivating the immune system. The immune system naturally has checkpoints to prevent excessive damage to the body while fighting cancer and infections. GBM manipulates these checkpoints to prevent attacks from the immune system, specifically the lymphocytes. Moreover, within the GBM tumor environment, there are prevalent cells known as macrophages and microglia. These cells are typically manipulated by GBM to suppress lymphocyte activity. The study indicated that the combination of chemotherapy and antibodies alters these cells, empowering the lymphocytes to detect and destroy the cancer cells effectively.
“This is the first report in humans where an ultrasound device has been used to deliver drugs and antibodies to glioblastoma to change the immune system, so it can recognize and attack the brain cancer,” said Adam Sonabend, MD, associate professor of Neurological Surgery and a Northwestern Medicine neurosurgeon. “This could be a major advance for the treatment of glioblastoma, which has been a frustratingly difficult cancer to treat, in part due to poor penetration of circulating drugs and antibodies into the brain.”
Related Links:
Northwestern Medicine
Carthera
Latest Ultrasound News
- Wireless Chronic Pain Management Device to Reduce Need for Painkillers and Surgery
- New Medical Ultrasound Imaging Technique Enables ICU Bedside Monitoring
- New Incision-Free Technique Halts Growth of Debilitating Brain Lesions
- AI-Powered Lung Ultrasound Outperforms Human Experts in Tuberculosis Diagnosis
- AI Identifies Heart Valve Disease from Common Imaging Test
- Novel Imaging Method Enables Early Diagnosis and Treatment Monitoring of Type 2 Diabetes
- Ultrasound-Based Microscopy Technique to Help Diagnose Small Vessel Diseases
- Smart Ultrasound-Activated Immune Cells Destroy Cancer Cells for Extended Periods
- Tiny Magnetic Robot Takes 3D Scans from Deep Within Body
- High Resolution Ultrasound Speeds Up Prostate Cancer Diagnosis
- World's First Wireless, Handheld, Whole-Body Ultrasound with Single PZT Transducer Makes Imaging More Accessible
- Artificial Intelligence Detects Undiagnosed Liver Disease from Echocardiograms
- Ultrasound Imaging Non-Invasively Tracks Tumor Response to Radiation and Immunotherapy
- AI Improves Detection of Congenital Heart Defects on Routine Prenatal Ultrasounds
- AI Diagnoses Lung Diseases from Ultrasound Videos with 96.57% Accuracy
- New Contrast Agent for Ultrasound Imaging Ensures Affordable and Safer Medical Diagnostics
Channels
Radiography
view channel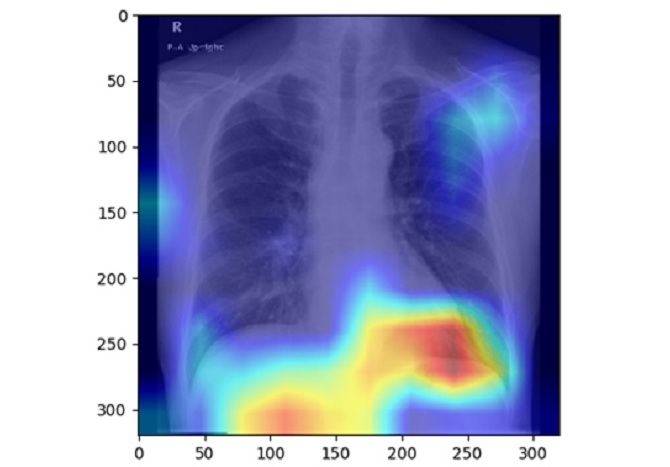
AI Detects Fatty Liver Disease from Chest X-Rays
Fatty liver disease, which results from excess fat accumulation in the liver, is believed to impact approximately one in four individuals globally. If not addressed in time, it can progress to severe conditions... Read more
AI Detects Hidden Heart Disease in Existing CT Chest Scans
Coronary artery calcium (CAC) is a major indicator of cardiovascular risk, but its assessment typically requires a specialized “gated” CT scan that synchronizes with the heartbeat. In contrast, most chest... Read moreMRI
view channel
AI Model Outperforms Doctors at Identifying Patients Most At-Risk of Cardiac Arrest
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is one of the most common inherited heart conditions and a leading cause of sudden cardiac death in young individuals and athletes. While many patients live normal lives, some... Read more
New MRI Technique Reveals Hidden Heart Issues
Traditional exercise stress tests conducted within an MRI machine require patients to lie flat, a position that artificially improves heart function by increasing stroke volume due to gravity-driven blood... Read moreNuclear Medicine
view channel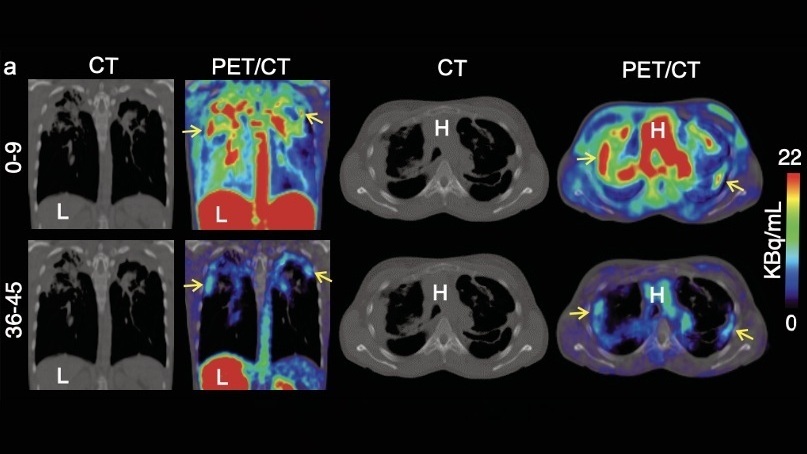
Novel Bacteria-Specific PET Imaging Approach Detects Hard-To-Diagnose Lung Infections
Mycobacteroides abscessus is a rapidly growing mycobacteria that primarily affects immunocompromised patients and those with underlying lung diseases, such as cystic fibrosis or chronic obstructive pulmonary... Read more
New Imaging Approach Could Reduce Need for Biopsies to Monitor Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer is the second leading cause of cancer-related death among men in the United States. However, the majority of older men diagnosed with prostate cancer have slow-growing, low-risk forms of... Read moreGeneral/Advanced Imaging
view channel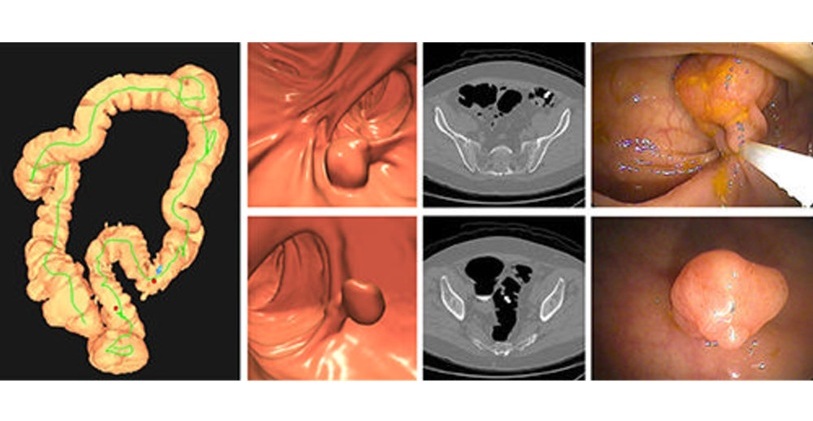
CT Colonography Beats Stool DNA Testing for Colon Cancer Screening
As colorectal cancer remains the second leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide, early detection through screening is vital to reduce advanced-stage treatments and associated costs.... Read more
First-Of-Its-Kind Wearable Device Offers Revolutionary Alternative to CT Scans
Currently, patients with conditions such as heart failure, pneumonia, or respiratory distress often require multiple imaging procedures that are intermittent, disruptive, and involve high levels of radiation.... Read more
AI-Based CT Scan Analysis Predicts Early-Stage Kidney Damage Due to Cancer Treatments
Radioligand therapy, a form of targeted nuclear medicine, has recently gained attention for its potential in treating specific types of tumors. However, one of the potential side effects of this therapy... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more
Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in medical diagnostics market is expanding with early disease detection being one of its key applications and image recognition becoming a compelling consumer proposition... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
GE HealthCare and NVIDIA Collaboration to Reimagine Diagnostic Imaging
GE HealthCare (Chicago, IL, USA) has entered into a collaboration with NVIDIA (Santa Clara, CA, USA), expanding the existing relationship between the two companies to focus on pioneering innovation in... Read more
Patient-Specific 3D-Printed Phantoms Transform CT Imaging
New research has highlighted how anatomically precise, patient-specific 3D-printed phantoms are proving to be scalable, cost-effective, and efficient tools in the development of new CT scan algorithms... Read more
Siemens and Sectra Collaborate on Enhancing Radiology Workflows
Siemens Healthineers (Forchheim, Germany) and Sectra (Linköping, Sweden) have entered into a collaboration aimed at enhancing radiologists' diagnostic capabilities and, in turn, improving patient care... Read more




 Guided Devices.jpg)