Ultrasound Imaging Technology Allows Doctors to Watch Spinal Cord Activity during Surgery 
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 11 Mar 2024 |
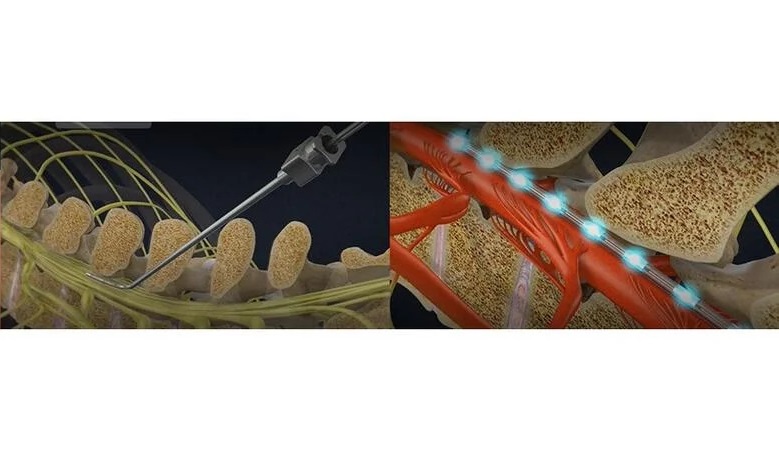
Back pain treatments during surgery have historically been difficult to evaluate effectively, largely because patients under anesthesia cannot communicate their pain levels. Furthermore, imaging the spinal cord – a crucial part of back pain treatment assessment – presents its own challenges. The spinal cord, referred to as an "unfriendly area" for traditional imaging, is subject to significant motion artifacts caused by heart pulsation and breathing, which introduce unwanted noise into the signal. These factors make the spinal cord a challenging target for standard neuroimaging techniques. Now, for the first time, an ultrasound imaging technology enables the generation of high-resolution images of the human spinal cord during surgery, marking a significant advancement that could provide relief for millions suffering from chronic back pain.
The technology, known as fUSI or functional ultrasound imaging, has been developed by scientists at UC Riverside (Riverside, CA, USA) and enables clinicians to observe the spinal cord and map its response to various treatments in real-time. Notably, the fUSI scanner is mobile and does not require the extensive infrastructure typically associated with classical neuroimaging methods like functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI). Additionally, fUSI has a reduced sensitivity to motion artifacts compared to other imaging techniques. It works by emitting sound waves into the targeted area, and the red blood cells in that region echo the sound back, producing a detailed image.
The application of fUSI was tested on six patients suffering from chronic low back pain, all of whom were scheduled for last-resort pain surgery, as no other treatments, including medication, had provided relief. In these procedures, clinicians stimulated the spinal cord with electrodes, hoping that the electrical stimulation would lessen the patients’ pain and enhance their quality of life. The results revealed that fUSI could detect changes in blood flow at unprecedentedly low speeds, less than one millimeter per second, marking a significant improvement over the two-centimeter-per-second detection capability of fMRI. This level of sensitivity suggests that the success rate of such surgeries, currently around 50%, could be significantly improved with the use of fUSI. Going forward, the researchers also plan to demonstrate fUSI's potential in optimizing treatments for individuals who have lost bladder control due to spinal cord injuries or aging.
“With less risk of damage than older methods, fUSI will enable more effective pain treatments that are optimized for individual patients,” said Vasileios Christopoulos, assistant professor of bioengineering at UC Riverside, who is pioneering the use of fUSI for spinal cord imaging. “It is a very exciting development.”
Related Links:
UC Riverside
Latest Ultrasound News
- Tiny Magnetic Robot Takes 3D Scans from Deep Within Body
- High Resolution Ultrasound Speeds Up Prostate Cancer Diagnosis
- World's First Wireless, Handheld, Whole-Body Ultrasound with Single PZT Transducer Makes Imaging More Accessible
- Artificial Intelligence Detects Undiagnosed Liver Disease from Echocardiograms
- Ultrasound Imaging Non-Invasively Tracks Tumor Response to Radiation and Immunotherapy
- AI Improves Detection of Congenital Heart Defects on Routine Prenatal Ultrasounds
- AI Diagnoses Lung Diseases from Ultrasound Videos with 96.57% Accuracy
- New Contrast Agent for Ultrasound Imaging Ensures Affordable and Safer Medical Diagnostics
- Ultrasound-Directed Microbubbles Boost Immune Response Against Tumors
- POC Ultrasound Enhances Early Pregnancy Care and Cuts Emergency Visits
- AI-Based Models Outperform Human Experts at Identifying Ovarian Cancer in Ultrasound Images
- Automated Breast Ultrasound Provides Alternative to Mammography in Low-Resource Settings
- Transparent Ultrasound Transducer for Photoacoustic and Ultrasound Endoscopy to Improve Diagnostic Accuracy
- Wearable Ultrasound Patch Enables Continuous Blood Pressure Monitoring
- AI Image-Recognition Program Reads Echocardiograms Faster, Cuts Results Wait Time
- Ultrasound Device Non-Invasively Improves Blood Circulation in Lower Limbs
Channels
Radiography
view channel
Higher Chest X-Ray Usage Catches Lung Cancer Earlier and Improves Survival
Lung cancer continues to be the leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide. While advanced technologies like CT scanners play a crucial role in detecting lung cancer, more accessible and affordable... Read more
AI-Powered Mammograms Predict Cardiovascular Risk
The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends that women in middle age and older undergo a mammogram, which is an X-ray of the breast, every one or two years to screen for breast cancer.... Read moreMRI
view channel
Ultra-Powerful MRI Scans Enable Life-Changing Surgery in Treatment-Resistant Epileptic Patients
Approximately 360,000 individuals in the UK suffer from focal epilepsy, a condition in which seizures spread from one part of the brain. Around a third of these patients experience persistent seizures... Read more
AI-Powered MRI Technology Improves Parkinson’s Diagnoses
Current research shows that the accuracy of diagnosing Parkinson’s disease typically ranges from 55% to 78% within the first five years of assessment. This is partly due to the similarities shared by Parkinson’s... Read more
Biparametric MRI Combined with AI Enhances Detection of Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer
Artificial intelligence (AI) technologies are transforming the way medical images are analyzed, offering unprecedented capabilities in quantitatively extracting features that go beyond traditional visual... Read more
First-Of-Its-Kind AI-Driven Brain Imaging Platform to Better Guide Stroke Treatment Options
Each year, approximately 800,000 people in the U.S. experience strokes, with marginalized and minoritized groups being disproportionately affected. Strokes vary in terms of size and location within the... Read moreNuclear Medicine
view channel
Novel Radiotracer Identifies Biomarker for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC), which represents 15-20% of all breast cancer cases, is one of the most aggressive subtypes, with a five-year survival rate of about 40%. Due to its significant heterogeneity... Read more
Innovative PET Imaging Technique to Help Diagnose Neurodegeneration
Neurodegenerative diseases, such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and Alzheimer’s disease, are often diagnosed only after physical symptoms appear, by which time treatment may no longer be effective.... Read moreGeneral/Advanced Imaging
view channel
AI Model Significantly Enhances Low-Dose CT Capabilities
Lung cancer remains one of the most challenging diseases, making early diagnosis vital for effective treatment. Fortunately, advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) are revolutionizing lung cancer... Read more
Ultra-Low Dose CT Aids Pneumonia Diagnosis in Immunocompromised Patients
Lung infections can be life-threatening for patients with weakened immune systems, making timely diagnosis crucial. While CT scans are considered the gold standard for detecting pneumonia, repeated scans... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more
Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in medical diagnostics market is expanding with early disease detection being one of its key applications and image recognition becoming a compelling consumer proposition... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
GE HealthCare and NVIDIA Collaboration to Reimagine Diagnostic Imaging
GE HealthCare (Chicago, IL, USA) has entered into a collaboration with NVIDIA (Santa Clara, CA, USA), expanding the existing relationship between the two companies to focus on pioneering innovation in... Read more
Patient-Specific 3D-Printed Phantoms Transform CT Imaging
New research has highlighted how anatomically precise, patient-specific 3D-printed phantoms are proving to be scalable, cost-effective, and efficient tools in the development of new CT scan algorithms... Read more
Siemens and Sectra Collaborate on Enhancing Radiology Workflows
Siemens Healthineers (Forchheim, Germany) and Sectra (Linköping, Sweden) have entered into a collaboration aimed at enhancing radiologists' diagnostic capabilities and, in turn, improving patient care... Read more












![Image: [18F]3F4AP in a human subject after mild incomplete spinal cord injury (Photo courtesy of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine, DOI:10.2967/jnumed.124.268242) Image: [18F]3F4AP in a human subject after mild incomplete spinal cord injury (Photo courtesy of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine, DOI:10.2967/jnumed.124.268242)](https://globetechcdn.com/mobile_medicalimaging/images/stories/articles/article_images/2025-02-24/Brugarolas_F8.large.jpg)