Novel PET Imaging Tracer Noninvasively Identifies Cancer Gene Mutation for More Precise Diagnosis
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 21 Dec 2023 |
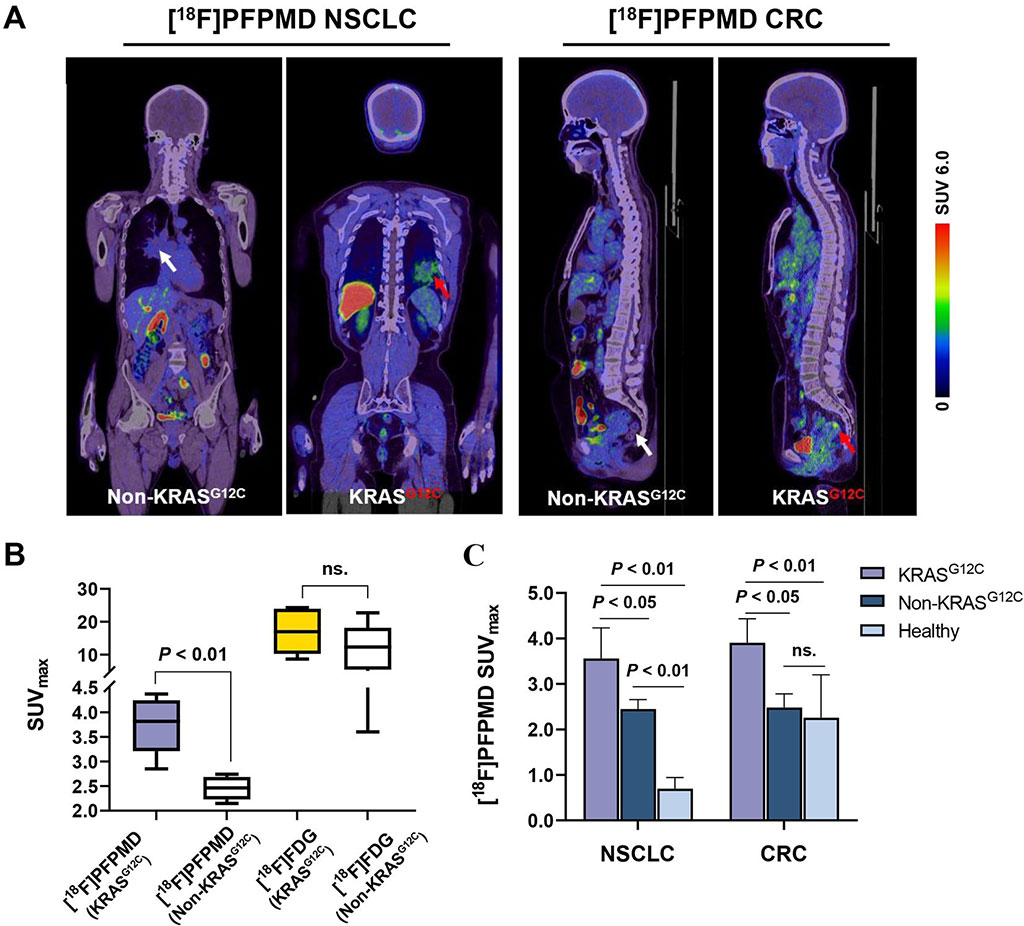
Kirsten rat sarcoma (KRAS) is a commonly mutated oncogene that is found in about 20-70% of cancer cases. Patients with KRAS mutations generally respond poorly to standard therapies. Hence, it is recommended to assess the mutation status in cancer patients to determine the most effective treatment. Presently, screening for KRAS mutation involves a biopsy combined with gene sequencing. However, biopsies can be accompanied by significant complications and have limited use owing to the quality of the tissue sample. This creates an urgent need for accurate yet noninvasive methods for the evaluation of the KRAS mutation status. Now, a study has found a novel PET imaging tracer to safely and effectively detect the common KRAS cancer gene mutation that is an important molecular marker for tumor-targeted therapy. Early identification of this can allow physicians to tailor treatment plans for patients to achieve the best results.
Researchers at Fourth Military Medical University (Xi’an, China) conducted this first-in-human study to develop a KRAS-targeted radiotracer and examine its targeting potential in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and colorectal cancer (CRC). The researchers created an oncoprotein-targeted PET tracer, 18F-PFPMD, based on a recently FDA-approved KRASG12C inhibitor. The team conducted both in vitro and in vivo studies to assess the tracer’s targeting specificity and imaging ability. The researchers also carried out further evaluation in healthy volunteers, NSCLC patients, and CRC patients.
The researchers obtained 18F-PFPMD with a high radiochemical yield, radiochemical purity, and stability and proved that it could selectively bind to the KRASG12C protein in preclinical studies. They found the tracer to be safe for humans, with the ability to clear rapidly from the gallbladder and intestines. Among NSCLC and CRC patients, the accumulation of 18F-PFPMD was much higher in tumors with the KRASG12C mutation as compared to those without the mutation.
“This research reveals that 18F-PFPMD is a promising molecular imaging tool of significant clinical relevance,” said Jing Wang, MD, PhD, nuclear medicine physician at Xijing Hospital of Fourth Military Medical University. “Moving forward, the tracer could be useful to screen the KRASG12C mutation status, as well as for patient selection of KRASG12C targeted therapy. Moreover, it could be used for monitoring therapeutic response and drug resistance for cancer patients.”
Related Links:
Fourth Military Medical University
Latest Nuclear Medicine News
- Novel Bacteria-Specific PET Imaging Approach Detects Hard-To-Diagnose Lung Infections
- New Imaging Approach Could Reduce Need for Biopsies to Monitor Prostate Cancer
- Novel Radiolabeled Antibody Improves Diagnosis and Treatment of Solid Tumors
- Novel PET Imaging Approach Offers Never-Before-Seen View of Neuroinflammation
- Novel Radiotracer Identifies Biomarker for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
- Innovative PET Imaging Technique to Help Diagnose Neurodegeneration
- New Molecular Imaging Test to Improve Lung Cancer Diagnosis
- Novel PET Technique Visualizes Spinal Cord Injuries to Predict Recovery
- Next-Gen Tau Radiotracers Outperform FDA-Approved Imaging Agents in Detecting Alzheimer’s
- Breakthrough Method Detects Inflammation in Body Using PET Imaging
- Advanced Imaging Reveals Hidden Metastases in High-Risk Prostate Cancer Patients
- Combining Advanced Imaging Technologies Offers Breakthrough in Glioblastoma Treatment
- New Molecular Imaging Agent Accurately Identifies Crucial Cancer Biomarker
- New Scans Light Up Aggressive Tumors for Better Treatment
- AI Stroke Brain Scan Readings Twice as Accurate as Current Method
- AI Analysis of PET/CT Images Predicts Side Effects of Immunotherapy in Lung Cancer
Channels
Radiography
view channel
New AI Tool Helps Doctors Read Chest X‑Rays Better
The U.S. health care system ranks poorly in critical health indicators, including life expectancy, and patients often seek better outcomes with fewer costs. Doctors aim for precise, first-time diagnoses,... Read more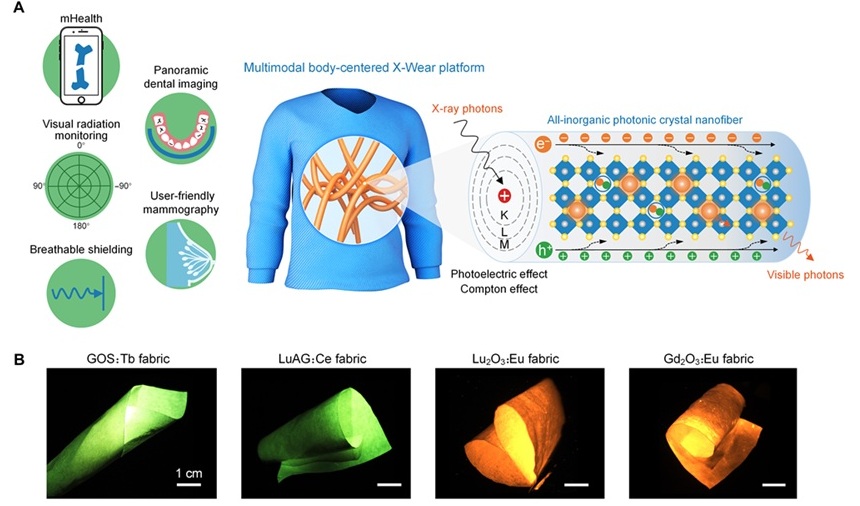
Wearable X-Ray Imaging Detecting Fabric to Provide On-The-Go Diagnostic Scanning
X-rays have been instrumental in modern medical diagnostics since their discovery, from imaging broken bones to screening for early signs of breast cancer. However, traditional X-ray detectors, primarily... Read moreMRI
view channel
AI-Assisted Model Enhances MRI Heart Scans
A cardiac MRI can reveal critical information about the heart’s function and any abnormalities, but traditional scans take 30 to 90 minutes and often suffer from poor image quality due to patient movement.... Read more
AI Model Outperforms Doctors at Identifying Patients Most At-Risk of Cardiac Arrest
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is one of the most common inherited heart conditions and a leading cause of sudden cardiac death in young individuals and athletes. While many patients live normal lives, some... Read moreUltrasound
view channel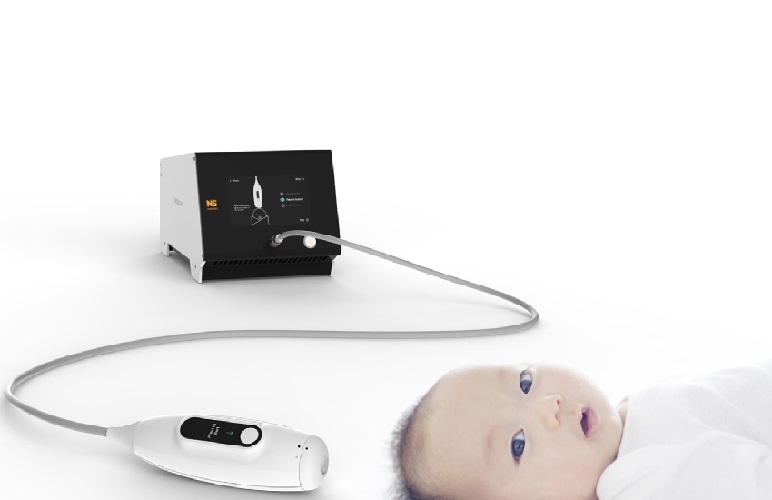
Non-Invasive Ultrasound-Based Tool Accurately Detects Infant Meningitis
Meningitis, an inflammation of the membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord, can be fatal in infants if not diagnosed and treated early. Even when treated, it may leave lasting damage, such as cognitive... Read more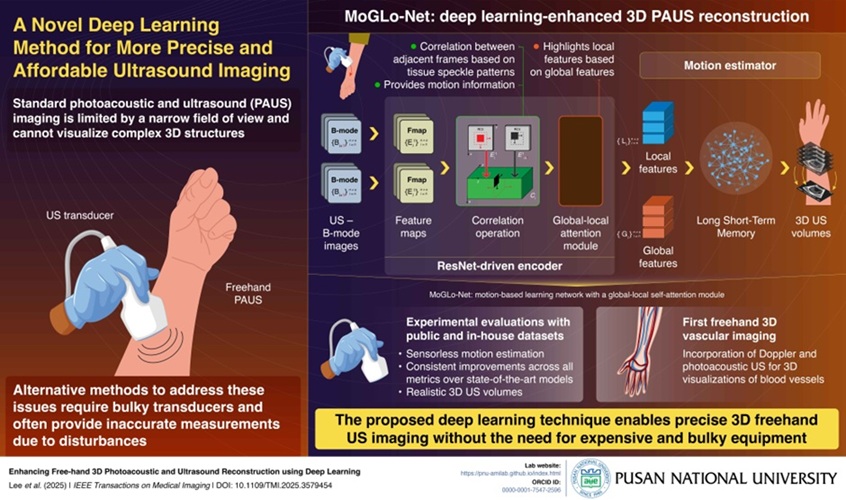
Breakthrough Deep Learning Model Enhances Handheld 3D Medical Imaging
Ultrasound imaging is a vital diagnostic technique used to visualize internal organs and tissues in real time and to guide procedures such as biopsies and injections. When paired with photoacoustic imaging... Read moreGeneral/Advanced Imaging
view channel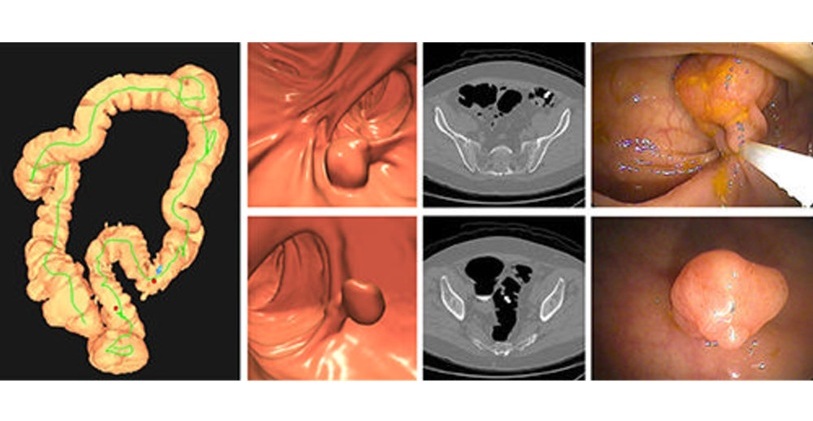
CT Colonography Beats Stool DNA Testing for Colon Cancer Screening
As colorectal cancer remains the second leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide, early detection through screening is vital to reduce advanced-stage treatments and associated costs.... Read more
First-Of-Its-Kind Wearable Device Offers Revolutionary Alternative to CT Scans
Currently, patients with conditions such as heart failure, pneumonia, or respiratory distress often require multiple imaging procedures that are intermittent, disruptive, and involve high levels of radiation.... Read more
AI-Based CT Scan Analysis Predicts Early-Stage Kidney Damage Due to Cancer Treatments
Radioligand therapy, a form of targeted nuclear medicine, has recently gained attention for its potential in treating specific types of tumors. However, one of the potential side effects of this therapy... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more
Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in medical diagnostics market is expanding with early disease detection being one of its key applications and image recognition becoming a compelling consumer proposition... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
GE HealthCare and NVIDIA Collaboration to Reimagine Diagnostic Imaging
GE HealthCare (Chicago, IL, USA) has entered into a collaboration with NVIDIA (Santa Clara, CA, USA), expanding the existing relationship between the two companies to focus on pioneering innovation in... Read more
Patient-Specific 3D-Printed Phantoms Transform CT Imaging
New research has highlighted how anatomically precise, patient-specific 3D-printed phantoms are proving to be scalable, cost-effective, and efficient tools in the development of new CT scan algorithms... Read more
Siemens and Sectra Collaborate on Enhancing Radiology Workflows
Siemens Healthineers (Forchheim, Germany) and Sectra (Linköping, Sweden) have entered into a collaboration aimed at enhancing radiologists' diagnostic capabilities and, in turn, improving patient care... Read more