World’s First Brain Stimulation Treatment for Neurological Diseases Uses Ultrasound Technology
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 19 Dec 2023 |
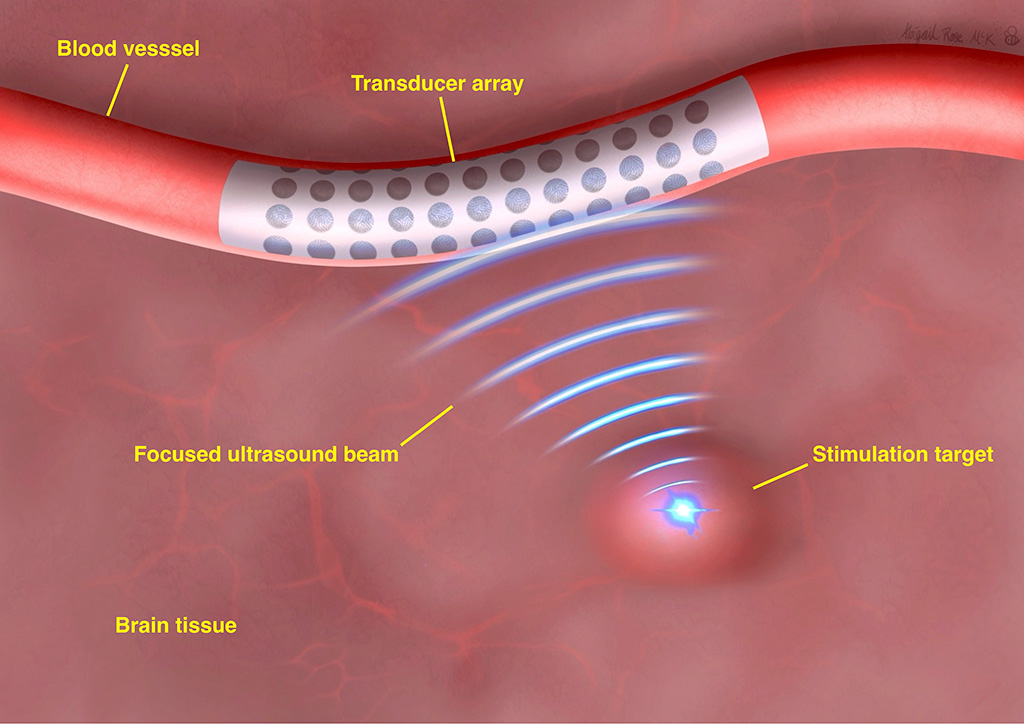
The effectiveness of drug treatments for individuals with neurological diseases like Parkinson's disease and epilepsy often diminishes over time, necessitating alternative therapeutic approaches. Movement symptoms in such conditions are typically the result of disorganized neural signals in the brain areas governing movement. Deep brain stimulation, a technique that disrupts these erratic signals, has shown promise in managing tremors and other movement-related symptoms. It also holds the potential for controlling, and possibly even preventing, seizures in epilepsy patients. Now, researchers are exploring a groundbreaking brain stimulation treatment that employs ultrasound, delivered through a device located inside a brain blood vessel, to address symptoms of neurological disorders.
A group of biomedical engineers at The University of Melbourne (Victoria, Australia), along with their colleagues, are developing ‘endovascular focused ultrasound’ technology, which could substantially enhance the lives of those with neurological diseases. Currently, electrical brain stimulation is a treatment option, but it requires invasive brain surgery to implant electrodes and often lacks precision in stimulating the correct brain regions. The accuracy of electrode placement is crucial; slight misplacements can lead to diminished efficacy and unintended side effects. The team's endovascular-focused ultrasound technology, anticipated to be available in over a decade, presents a safer alternative to existing treatments, avoiding the need for open brain surgery and utilizing ultrasound instead of electrical stimulation.
This innovative method involves inserting an array of tiny transducers permanently into a brain blood vessel, likely through the jugular vein, akin to current stent insertion practices in the heart and brain. These transducers would be connected to a chest-implanted device similar to a pacemaker, which would power and control the ultrasound stimulation. Thanks to advancements in nanofabrication technology, which is also used in computer chip manufacturing, researchers can produce extraordinarily small ultrasound transducers. These transducers are fine enough to fit inside a blood vessel, being narrower than human hair. When arranged in an array, they can precisely focus the ultrasound beam on a specific brain target, minimizing stimulation to surrounding tissue. The team aims for a successful initial demonstration of this novel brain stimulation method within a three-year project timeline and is hopeful that the first human trials could commence by 2030.
“We have demonstrated preliminary safety and efficacy of implanting neurotechnology within cortical blood vessels to enable people with paralysis to control external equipment with their minds,” said Professor Nicholas Opie from the University of Melbourne Department of Medicine. “Ultrasound is a new method of stimulating the brain and has the potential to provide transformative treatments for people with neurological disorders such as Parkinson’s, epilepsy and depression.”
Related Links:
The University of Melbourne
Latest Ultrasound News
- Wearable Ultrasound Imaging System to Enable Real-Time Disease Monitoring
- Ultrasound Technique Visualizes Deep Blood Vessels in 3D Without Contrast Agents
- Ultrasound Probe Images Entire Organ in 4D

- Disposable Ultrasound Patch Performs Better Than Existing Devices
- Non-Invasive Ultrasound-Based Tool Accurately Detects Infant Meningitis
- Breakthrough Deep Learning Model Enhances Handheld 3D Medical Imaging
- Pain-Free Breast Imaging System Performs One Minute Cancer Scan
- Wireless Chronic Pain Management Device to Reduce Need for Painkillers and Surgery
- New Medical Ultrasound Imaging Technique Enables ICU Bedside Monitoring
- New Incision-Free Technique Halts Growth of Debilitating Brain Lesions
- AI-Powered Lung Ultrasound Outperforms Human Experts in Tuberculosis Diagnosis
- AI Identifies Heart Valve Disease from Common Imaging Test
- Novel Imaging Method Enables Early Diagnosis and Treatment Monitoring of Type 2 Diabetes
- Ultrasound-Based Microscopy Technique to Help Diagnose Small Vessel Diseases
- Smart Ultrasound-Activated Immune Cells Destroy Cancer Cells for Extended Periods
- Tiny Magnetic Robot Takes 3D Scans from Deep Within Body
Channels
Radiography
view channel
X-Ray Breakthrough Captures Three Image-Contrast Types in Single Shot
Detecting early-stage cancer or subtle changes deep inside tissues has long challenged conventional X-ray systems, which rely only on how structures absorb radiation. This limitation keeps many microstructural... Read more
AI Generates Future Knee X-Rays to Predict Osteoarthritis Progression Risk
Osteoarthritis, a degenerative joint disease affecting over 500 million people worldwide, is the leading cause of disability among older adults. Current diagnostic tools allow doctors to assess damage... Read moreMRI
view channel
Novel Imaging Approach to Improve Treatment for Spinal Cord Injuries
Vascular dysfunction in the spinal cord contributes to multiple neurological conditions, including traumatic injuries and degenerative cervical myelopathy, where reduced blood flow can lead to progressive... Read more
AI-Assisted Model Enhances MRI Heart Scans
A cardiac MRI can reveal critical information about the heart’s function and any abnormalities, but traditional scans take 30 to 90 minutes and often suffer from poor image quality due to patient movement.... Read more
AI Model Outperforms Doctors at Identifying Patients Most At-Risk of Cardiac Arrest
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is one of the most common inherited heart conditions and a leading cause of sudden cardiac death in young individuals and athletes. While many patients live normal lives, some... Read moreNuclear Medicine
view channel
PET Imaging of Inflammation Predicts Recovery and Guides Therapy After Heart Attack
Acute myocardial infarction can trigger lasting heart damage, yet clinicians still lack reliable tools to identify which patients will regain function and which may develop heart failure.... Read more
Radiotheranostic Approach Detects, Kills and Reprograms Aggressive Cancers
Aggressive cancers such as osteosarcoma and glioblastoma often resist standard therapies, thrive in hostile tumor environments, and recur despite surgery, radiation, or chemotherapy. These tumors also... Read more
New Imaging Solution Improves Survival for Patients with Recurring Prostate Cancer
Detecting recurrent prostate cancer remains one of the most difficult challenges in oncology, as standard imaging methods such as bone scans and CT scans often fail to accurately locate small or early-stage tumors.... Read moreGeneral/Advanced Imaging
view channel
3D Scanning Approach Enables Ultra-Precise Brain Surgery
Precise navigation is critical in neurosurgery, yet even small alignment errors can affect outcomes when operating deep within the brain. A new 3D surface-scanning approach now provides a radiation-free... Read more
AI Tool Improves Medical Imaging Process by 90%
Accurately labeling different regions within medical scans, a process known as medical image segmentation, is critical for diagnosis, surgery planning, and research. Traditionally, this has been a manual... Read more
New Ultrasmall, Light-Sensitive Nanoparticles Could Serve as Contrast Agents
Medical imaging technologies face ongoing challenges in capturing accurate, detailed views of internal processes, especially in conditions like cancer, where tracking disease development and treatment... Read more
AI Algorithm Accurately Predicts Pancreatic Cancer Metastasis Using Routine CT Images
In pancreatic cancer, detecting whether the disease has spread to other organs is critical for determining whether surgery is appropriate. If metastasis is present, surgery is not recommended, yet current... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more
Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in medical diagnostics market is expanding with early disease detection being one of its key applications and image recognition becoming a compelling consumer proposition... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
GE HealthCare and NVIDIA Collaboration to Reimagine Diagnostic Imaging
GE HealthCare (Chicago, IL, USA) has entered into a collaboration with NVIDIA (Santa Clara, CA, USA), expanding the existing relationship between the two companies to focus on pioneering innovation in... Read more
Patient-Specific 3D-Printed Phantoms Transform CT Imaging
New research has highlighted how anatomically precise, patient-specific 3D-printed phantoms are proving to be scalable, cost-effective, and efficient tools in the development of new CT scan algorithms... Read more
Siemens and Sectra Collaborate on Enhancing Radiology Workflows
Siemens Healthineers (Forchheim, Germany) and Sectra (Linköping, Sweden) have entered into a collaboration aimed at enhancing radiologists' diagnostic capabilities and, in turn, improving patient care... Read more








 Guided Devices.jpg)