OCT Intravascular Imaging Improves Stenting Procedure Outcomes
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 04 Sep 2023 |
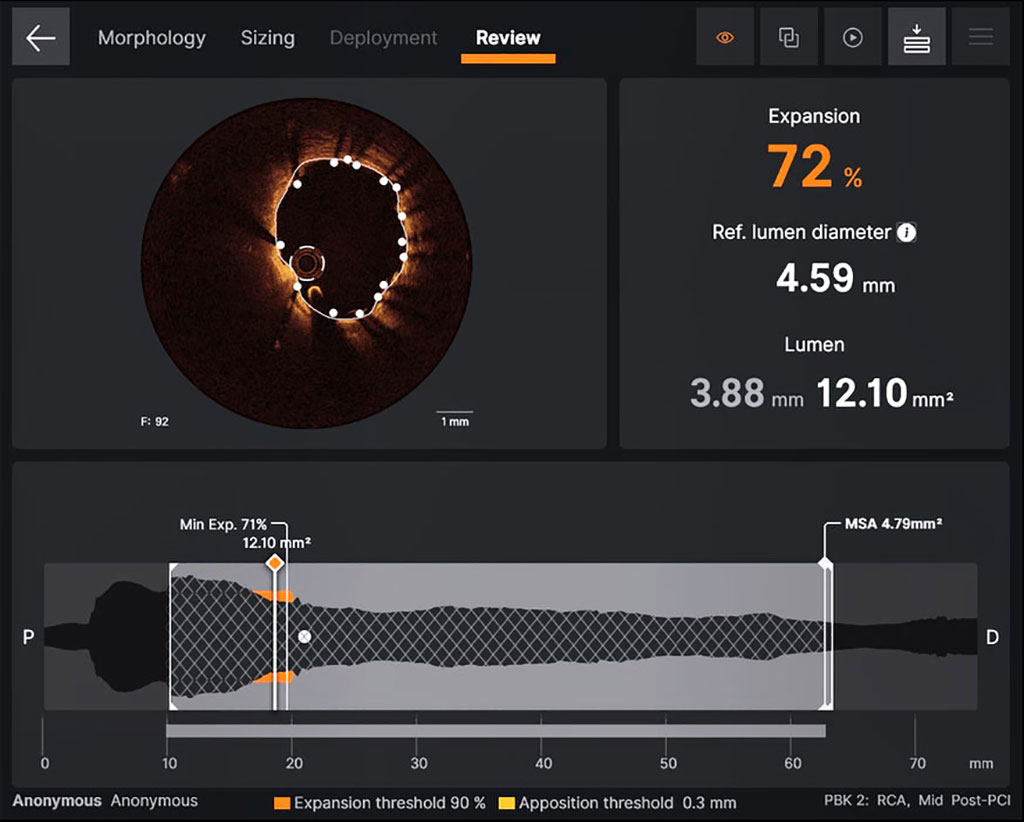
Individuals diagnosed with coronary artery disease—a condition marked by the buildup of plaque within arteries leading to chest pain, shortness of breath, and heart attacks—often undergo percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI). This non-surgical procedure involves interventional cardiologists employing a catheter to position stents within blocked coronary arteries, thereby restoring blood flow. The most prevalent guidance method for PCI is angiography, which employs X-rays and a specialized dye (contrast material) to visualize blood flow through heart arteries and highlight any blockages. However, angiography has its limitations. It struggles to accurately determine artery size and plaque composition, and is suboptimal in identifying issues like stent expansion post-PCI and other complications that impact the procedure's effectiveness and safety. Intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) is an alternative technique offering a more precise and specific view of coronary arteries. Although studies confirm that IVUS-guided PCI surpasses angiography-guided PCI, leading to reduced cardiovascular events, its usage remains limited due to challenges in image interpretation.
A more recent technique is optical coherence tomography (OCT), which employs light, rather than sound, to create images of blockages. OCT images exhibit superior resolution, accuracy, and detail compared to IVUS, with easier interpretability. Despite these advantages, OCT is only applied in 3% of PCI cases, partially due to limited study data. The aim of this new trial is to alter this landscape. Now, a new study has found that using OCT to guide stent implantation during PCI can enhance safety and yield better outcomes for heart disease patients than relying solely on angiography. These findings are from the ILUMIEN IV: OPTIMAL PCI study which is the largest clinical trial of its kind comparing the two methods for this procedure.
The ILUMIEN IV: OPTIMAL PCI trial randomized 2,487 patients to OCT-guided PCI using a device manufactured by Abbott (Abbott Park, IL, USA) and angiography-guided PCI. The trial was conducted between May 2018 and December 2020 across 80 centers in 18 countries, with patients unaware of their assigned guided procedure. Researchers assessed post-PCI dimensions of the stented area since stent re-narrowing over time can necessitate repeat revascularization procedures. Notably, the OCT group displayed a significantly larger stent area immediately after the procedure compared to the angiography-guided group—a .36mm2 increase. OCT guidance also correlated with fewer procedural complications compared to angiography guidance.
Additionally, the study examined target lesion failure (TLF), a combination of cardiac death, target-vessel myocardial infarction, or ischemia-driven target-vessel revascularization. Two years post-procedure, 88 patients in the OCT group experienced TLF, in contrast to 99 patients in the angiography group. Although this difference did not reach statistical significance, the study delved further into stent thrombosis rates, a severe PCI complication. Within two years of PCI, six patients in the OCT group experienced stent thrombosis, while 17 patients in the angiography group encountered this issue—showing OCT's 65% reduction in such instances. Importantly, 96% of patients experiencing stent thrombosis in the trial subsequently faced death or myocardial infarction, highlighting the importance of preventing such events.
“The ILUMIEN IV trial demonstrated that OCT-guided PCI compared with angiography-guided PCI improves stent implantation results and the safety of the procedure, with less stent thrombosis, the most devastating complication of stenting,” said senior author Gregg W. Stone, MD. “However, while there were numerically fewer cardiac deaths and myocardial infarctions (MIs) in the OCT group, the differences between groups in the primary composite outcome of cardiac death or MIs or repeat revascularization related to the treated vessel was not significant.”
Related Links:
Abbott
Latest Radiography News
- AI-Powered Imaging Technique Shows Promise in Evaluating Patients for PCI
- Higher Chest X-Ray Usage Catches Lung Cancer Earlier and Improves Survival
- AI-Powered Mammograms Predict Cardiovascular Risk
- Generative AI Model Significantly Reduces Chest X-Ray Reading Time
- AI-Powered Mammography Screening Boosts Cancer Detection in Single-Reader Settings
- Photon Counting Detectors Promise Fast Color X-Ray Images
- AI Can Flag Mammograms for Supplemental MRI
- 3D CT Imaging from Single X-Ray Projection Reduces Radiation Exposure
- AI Method Accurately Predicts Breast Cancer Risk by Analyzing Multiple Mammograms
- Printable Organic X-Ray Sensors Could Transform Treatment for Cancer Patients
- Highly Sensitive, Foldable Detector to Make X-Rays Safer
- Novel Breast Cancer Screening Technology Could Offer Superior Alternative to Mammogram
- Artificial Intelligence Accurately Predicts Breast Cancer Years Before Diagnosis
- AI-Powered Chest X-Ray Detects Pulmonary Nodules Three Years Before Lung Cancer Symptoms
- AI Model Identifies Vertebral Compression Fractures in Chest Radiographs
- Advanced 3D Mammography Detects More Breast Cancers
Channels
MRI
view channel
Ultra-Powerful MRI Scans Enable Life-Changing Surgery in Treatment-Resistant Epileptic Patients
Approximately 360,000 individuals in the UK suffer from focal epilepsy, a condition in which seizures spread from one part of the brain. Around a third of these patients experience persistent seizures... Read more
AI-Powered MRI Technology Improves Parkinson’s Diagnoses
Current research shows that the accuracy of diagnosing Parkinson’s disease typically ranges from 55% to 78% within the first five years of assessment. This is partly due to the similarities shared by Parkinson’s... Read more
Biparametric MRI Combined with AI Enhances Detection of Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer
Artificial intelligence (AI) technologies are transforming the way medical images are analyzed, offering unprecedented capabilities in quantitatively extracting features that go beyond traditional visual... Read more
First-Of-Its-Kind AI-Driven Brain Imaging Platform to Better Guide Stroke Treatment Options
Each year, approximately 800,000 people in the U.S. experience strokes, with marginalized and minoritized groups being disproportionately affected. Strokes vary in terms of size and location within the... Read moreUltrasound
view channel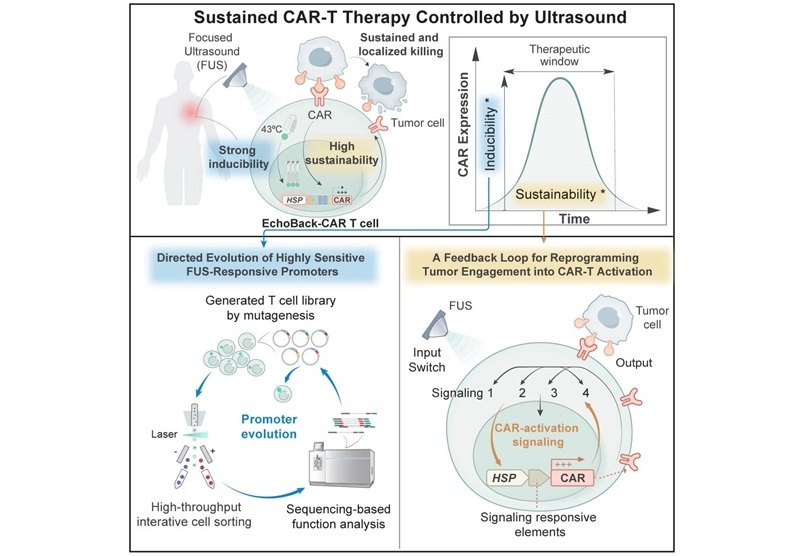
Smart Ultrasound-Activated Immune Cells Destroy Cancer Cells for Extended Periods
Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy has emerged as a highly promising cancer treatment, especially for bloodborne cancers like leukemia. This highly personalized therapy involves extracting... Read more
Tiny Magnetic Robot Takes 3D Scans from Deep Within Body
Colorectal cancer ranks as one of the leading causes of cancer-related mortality worldwide. However, when detected early, it is highly treatable. Now, a new minimally invasive technique could significantly... Read more
High Resolution Ultrasound Speeds Up Prostate Cancer Diagnosis
Each year, approximately one million prostate cancer biopsies are conducted across Europe, with similar numbers in the USA and around 100,000 in Canada. Most of these biopsies are performed using MRI images... Read more
World's First Wireless, Handheld, Whole-Body Ultrasound with Single PZT Transducer Makes Imaging More Accessible
Ultrasound devices play a vital role in the medical field, routinely used to examine the body's internal tissues and structures. While advancements have steadily improved ultrasound image quality and processing... Read moreNuclear Medicine
view channel
Novel PET Imaging Approach Offers Never-Before-Seen View of Neuroinflammation
COX-2, an enzyme that plays a key role in brain inflammation, can be significantly upregulated by inflammatory stimuli and neuroexcitation. Researchers suggest that COX-2 density in the brain could serve... Read more
Novel Radiotracer Identifies Biomarker for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC), which represents 15-20% of all breast cancer cases, is one of the most aggressive subtypes, with a five-year survival rate of about 40%. Due to its significant heterogeneity... Read moreGeneral/Advanced Imaging
view channel
AI-Powered Imaging System Improves Lung Cancer Diagnosis
Given the need to detect lung cancer at earlier stages, there is an increasing need for a definitive diagnostic pathway for patients with suspicious pulmonary nodules. However, obtaining tissue samples... Read more
AI Model Significantly Enhances Low-Dose CT Capabilities
Lung cancer remains one of the most challenging diseases, making early diagnosis vital for effective treatment. Fortunately, advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) are revolutionizing lung cancer... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more
Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in medical diagnostics market is expanding with early disease detection being one of its key applications and image recognition becoming a compelling consumer proposition... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
GE HealthCare and NVIDIA Collaboration to Reimagine Diagnostic Imaging
GE HealthCare (Chicago, IL, USA) has entered into a collaboration with NVIDIA (Santa Clara, CA, USA), expanding the existing relationship between the two companies to focus on pioneering innovation in... Read more
Patient-Specific 3D-Printed Phantoms Transform CT Imaging
New research has highlighted how anatomically precise, patient-specific 3D-printed phantoms are proving to be scalable, cost-effective, and efficient tools in the development of new CT scan algorithms... Read more
Siemens and Sectra Collaborate on Enhancing Radiology Workflows
Siemens Healthineers (Forchheim, Germany) and Sectra (Linköping, Sweden) have entered into a collaboration aimed at enhancing radiologists' diagnostic capabilities and, in turn, improving patient care... Read more
















