Enhanced Ultrasound Superior to MRI for Diagnosing Certain Liver and Kidney Tumors
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 27 Feb 2023 |
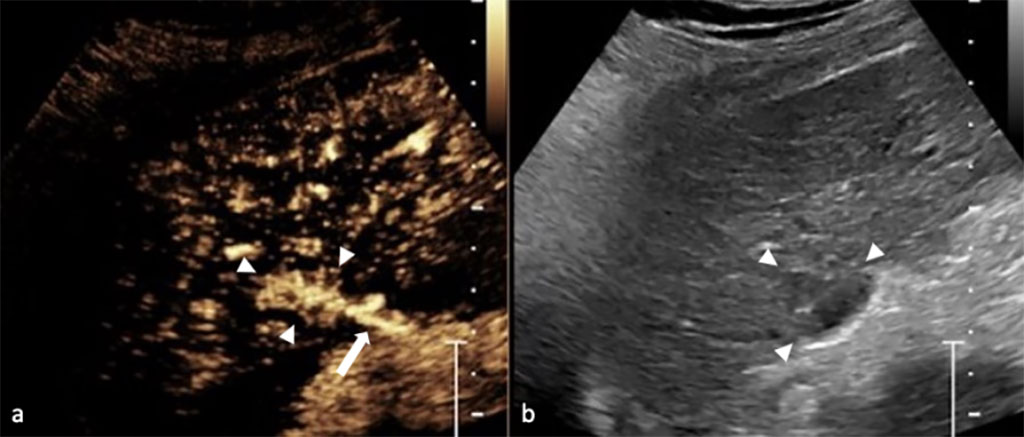
Contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS) is a non-invasive imaging tool that is routinely used across the world to identify and characterize cancers, diagnose heart and vascular disease, monitor chronic gastro-intestinal diseases and therapy. Ultrasound contrast agents are administered intravenously to enhance the images produced by ultrasound scans, enabling the visualization of abnormal microvascular blood flow patterns in real time. Now, two new studies have revealed that CEUS is more accurate and reliable than MRI for examining certain liver and kidney nodules.
The two new studies were highlighted by the International Contrast Ultrasound Society (ICUS, Chicago, IL, USA; www.icus-society.org), a non-profit medical society dedicated to advancing the medically appropriate use of CEUS to improve patient care and outcomes. In the liver CEUS study, which followed 196 patients for two years, the researchers found that CEUS scans are at least equivalent if not superior to MRI for evaluating these liver lesions, and CEUS should be the first investigation for nodules found on surveillance for liver cancer. The study showed that CEUS offers superior sensitivity when compared to MRI (81% vs. 64%) for the diagnosis of malignancy, without compromising specificity (92% vs. 93%). In addition, CEUS was more likely than MRI to reproduce and characterize the nodule found on screening (97% vs. 78.5%). The liver study represents the first prospective comparison of CEUS and contrast-enhanced MRI for assessment of newly-discovered liver nodules. Based on these findings, the researchers have called upon the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases (AASLD) to include CEUS in its liver imaging guidelines, along with MRI and CT. However, MRI still remains an essential tool for managing patients with malignant tumors, particularly for staging these tumors prior to treatment, according to the researchers.
“We found that CEUS is a better and less expensive first-step evaluation for newly-discovered liver nodules,” said Dr. Stephanie Wilson, principal investigator of the liver CEUS study. “CEUS found malignant or pre-malignant diagnoses that would likely have been missed or delayed if we had not used CEUS in these patients. In addition, CEUS quickly and reliably identified benign lesions and pseudo-lesions, sparing these patients the costs and risks associated with unnecessary downstream testing and procedures.”
Meanwhile, the kidney CEUS study reviewed clinical data over a 10 year period to assess the accuracy of CEUS diagnoses of benign kidney nodules in 341 patients. Their blinded analysis found that none of the CEUS diagnoses changed during that period.
“Our data confirm that when CEUS determines a kidney mass is benign, the mass is benign and no further follow up is needed - sparing the patient from unnecessary downstream tests, anxiety and costs,” according to Dr. Richard G. Barr, the lead author of the kidney CEUS study. “It is important to remember that ultrasound contrast agents do not contain iodinated dye and do not harm the kidneys, making CEUS the examination of choice for patients with renal insufficiency.”
“In addition, CEUS allows for improved visualization of enhancement patterns in real time, the thin slice thickness of CEUS allows for evaluation of small nodules, multiplanar imaging allows for improved visualization and confirmation of enhancement, and multiple doses may be used during the same examination to provide an opportunity to image the lesion thoroughly,” Dr. Barr added. “Further, due to radiation exposure associated with CT, we believe CT should not be used as the first line imaging modality for assessing cystic lesions that are most probably benign in character.”
Related Links:
ICUS
Latest Ultrasound News
- Wireless Chronic Pain Management Device to Reduce Need for Painkillers and Surgery
- New Medical Ultrasound Imaging Technique Enables ICU Bedside Monitoring
- New Incision-Free Technique Halts Growth of Debilitating Brain Lesions
- AI-Powered Lung Ultrasound Outperforms Human Experts in Tuberculosis Diagnosis
- AI Identifies Heart Valve Disease from Common Imaging Test
- Novel Imaging Method Enables Early Diagnosis and Treatment Monitoring of Type 2 Diabetes
- Ultrasound-Based Microscopy Technique to Help Diagnose Small Vessel Diseases
- Smart Ultrasound-Activated Immune Cells Destroy Cancer Cells for Extended Periods
- Tiny Magnetic Robot Takes 3D Scans from Deep Within Body
- High Resolution Ultrasound Speeds Up Prostate Cancer Diagnosis
- World's First Wireless, Handheld, Whole-Body Ultrasound with Single PZT Transducer Makes Imaging More Accessible
- Artificial Intelligence Detects Undiagnosed Liver Disease from Echocardiograms
- Ultrasound Imaging Non-Invasively Tracks Tumor Response to Radiation and Immunotherapy
- AI Improves Detection of Congenital Heart Defects on Routine Prenatal Ultrasounds
- AI Diagnoses Lung Diseases from Ultrasound Videos with 96.57% Accuracy
- New Contrast Agent for Ultrasound Imaging Ensures Affordable and Safer Medical Diagnostics
Channels
Radiography
view channel
AI Detects Hidden Heart Disease in Existing CT Chest Scans
Coronary artery calcium (CAC) is a major indicator of cardiovascular risk, but its assessment typically requires a specialized “gated” CT scan that synchronizes with the heartbeat. In contrast, most chest... Read more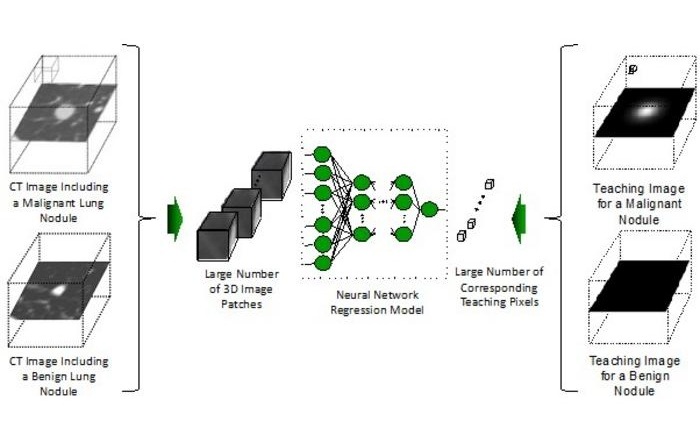
Ultra-Lightweight AI Model Runs Without GPU to Break Barriers in Lung Cancer Diagnosis
Artificial intelligence (AI) models typically demand enormous datasets and expensive GPU servers, creating a significant barrier to wider adoption, especially in resource-limited settings.... Read more
AI Radiology Tool Identifies Life-Threatening Conditions in Milliseconds
Radiology is emerging as one of healthcare’s most pressing bottlenecks. By 2033, the U.S. could face a shortage of up to 42,000 radiologists, even as imaging volumes grow by 5% annually.... Read more
Machine Learning Algorithm Identifies Cardiovascular Risk from Routine Bone Density Scans
A new study published in the Journal of Bone and Mineral Research reveals that an automated machine learning program can predict the risk of cardiovascular events and falls or fractures by analyzing bone... Read moreMRI
view channel
New MRI Technique Reveals Hidden Heart Issues
Traditional exercise stress tests conducted within an MRI machine require patients to lie flat, a position that artificially improves heart function by increasing stroke volume due to gravity-driven blood... Read more
Shorter MRI Exam Effectively Detects Cancer in Dense Breasts
Women with extremely dense breasts face a higher risk of missed breast cancer diagnoses, as dense glandular and fibrous tissue can obscure tumors on mammograms. While breast MRI is recommended for supplemental... Read moreNuclear Medicine
view channel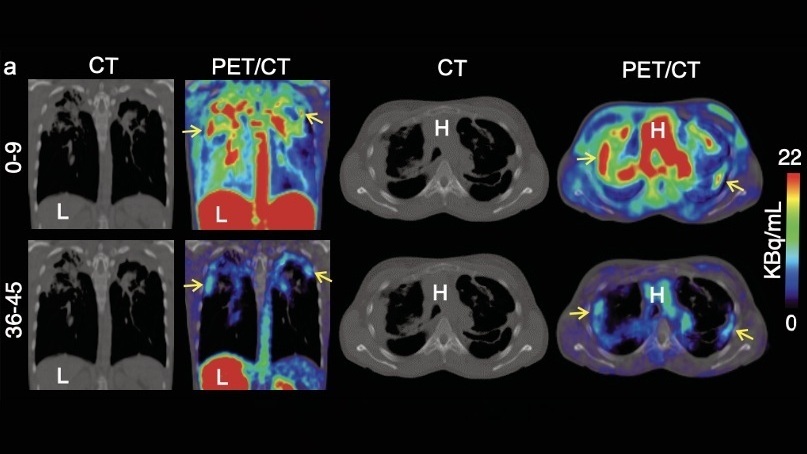
Novel Bacteria-Specific PET Imaging Approach Detects Hard-To-Diagnose Lung Infections
Mycobacteroides abscessus is a rapidly growing mycobacteria that primarily affects immunocompromised patients and those with underlying lung diseases, such as cystic fibrosis or chronic obstructive pulmonary... Read more
New Imaging Approach Could Reduce Need for Biopsies to Monitor Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer is the second leading cause of cancer-related death among men in the United States. However, the majority of older men diagnosed with prostate cancer have slow-growing, low-risk forms of... Read moreGeneral/Advanced Imaging
view channel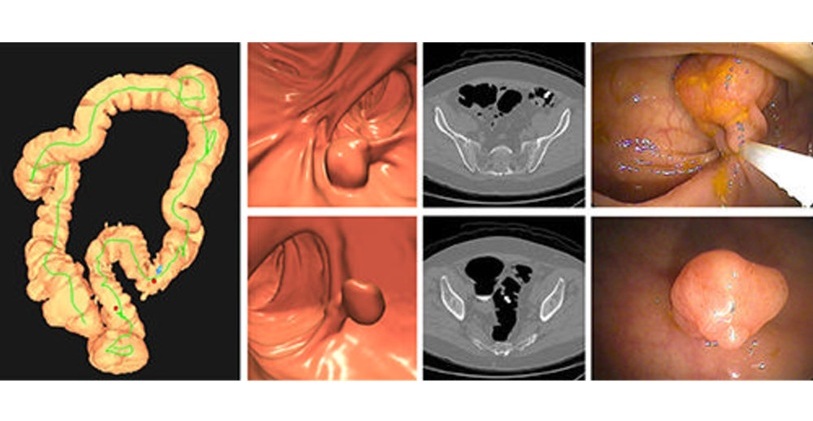
CT Colonography Beats Stool DNA Testing for Colon Cancer Screening
As colorectal cancer remains the second leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide, early detection through screening is vital to reduce advanced-stage treatments and associated costs.... Read more
First-Of-Its-Kind Wearable Device Offers Revolutionary Alternative to CT Scans
Currently, patients with conditions such as heart failure, pneumonia, or respiratory distress often require multiple imaging procedures that are intermittent, disruptive, and involve high levels of radiation.... Read more
AI-Based CT Scan Analysis Predicts Early-Stage Kidney Damage Due to Cancer Treatments
Radioligand therapy, a form of targeted nuclear medicine, has recently gained attention for its potential in treating specific types of tumors. However, one of the potential side effects of this therapy... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more
Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in medical diagnostics market is expanding with early disease detection being one of its key applications and image recognition becoming a compelling consumer proposition... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
GE HealthCare and NVIDIA Collaboration to Reimagine Diagnostic Imaging
GE HealthCare (Chicago, IL, USA) has entered into a collaboration with NVIDIA (Santa Clara, CA, USA), expanding the existing relationship between the two companies to focus on pioneering innovation in... Read more
Patient-Specific 3D-Printed Phantoms Transform CT Imaging
New research has highlighted how anatomically precise, patient-specific 3D-printed phantoms are proving to be scalable, cost-effective, and efficient tools in the development of new CT scan algorithms... Read more
Siemens and Sectra Collaborate on Enhancing Radiology Workflows
Siemens Healthineers (Forchheim, Germany) and Sectra (Linköping, Sweden) have entered into a collaboration aimed at enhancing radiologists' diagnostic capabilities and, in turn, improving patient care... Read more