Advanced MRI Marks Breakthrough for Patients with Heart Stiffening Disease
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 31 Jul 2022 |
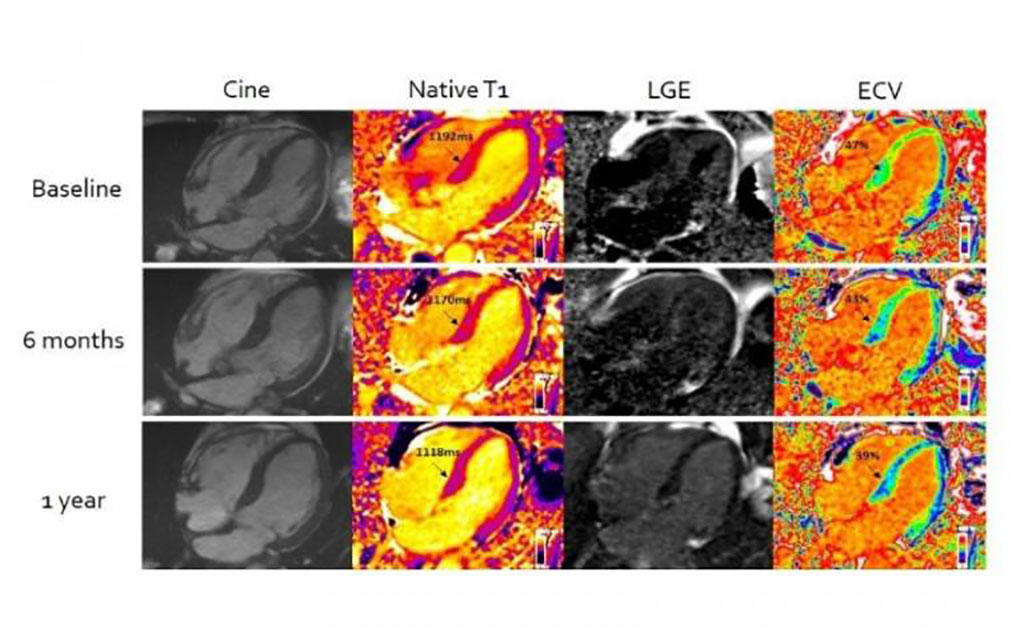
Light-chain cardiac amyloidosis (stiff heart syndrome) is a life-limiting condition that occurs when plaques of protein called amyloid build up in heart muscle, affecting its ability to pump blood, and without treatment can rapidly lead to heart failure and death. However, assessing the condition has been difficult, as while clinicians can detect the presence of amyloid in the heart, there has been no safe test to measure the amount. This has also meant there has been no way of measuring the therapeutic effect of chemotherapy – the normal first line treatment. A patient’s response is currently assessed with indirect biological markers, but these do not measure the amount (or reduction) of cardiac amyloid – the drug’s ultimate target – and doctors find the markers less useful when trying to assess second-line chemotherapy treatments. Now, an advanced form of cardiac MRI has for the first-time enabled clinicians to measure the effectiveness of chemotherapy in patients with ‘stiff heart syndrome’.
Researchers at University College London (London, UK) have, for 10 years, been developing and refining Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance (CMR) Extracellular Volume Mapping (ECV) for amyloid. This non-invasive technique enables clinicians to measure both the presence and amount of amyloid protein using MRI. Now for the first time they have used the technology to evaluate the success of chemotherapy treatment, by assessing cardiac amyloid regression or progression.
For the study 176 patients with light-chain cardiac amyloidosis had Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance with Extracellular Volume Mapping. CMR scans with ECV mapping were done at diagnosis, and then at six, 12 and 24 months after starting chemotherapy. The advanced MRI technique allowed researchers to accurately measure the amount of amyloid protein in hearts, and, for the first-time ever, to measure the changes in response to chemotherapy on repeat scans. By measuring the changes they could detect which patients would have a better or worse prognosis. Further, combining the results with blood tests for the disease, it was found almost 40% of patients had a substantial improvement (reduction) in amyloid deposition, something that was not thought to be possible before – showing how effective chemotherapy can be. The researchers believe that the MRI technique should now be used immediately to diagnose and assess all cases of light-chain cardiac amyloidosis.
“Since MRI scans are widely available, by developing the use of ECV mapping in a machine that already is used for these patients, we hope that its use can be made available to more patients to help improve their care,” said Professor Marianna Fontana (UCL Division of Medicine), senior author and a British Heart Foundation (BHF) Clinical Fellow. “The aim would be to use these scans routinely for all patients with the disease to help doctors monitor the response to chemotherapy to help improve patient survival, which is very poor in patients who do not respond to treatment.”
Related Links:
University College London
Latest MRI News
- MRI Scans Reveal Signature Patterns of Brain Activity to Predict Recovery from TBI
- Novel Imaging Approach to Improve Treatment for Spinal Cord Injuries
- AI-Assisted Model Enhances MRI Heart Scans
- AI Model Outperforms Doctors at Identifying Patients Most At-Risk of Cardiac Arrest
- New MRI Technique Reveals Hidden Heart Issues
- Shorter MRI Exam Effectively Detects Cancer in Dense Breasts
- MRI to Replace Painful Spinal Tap for Faster MS Diagnosis
- MRI Scans Can Identify Cardiovascular Disease Ten Years in Advance
- Simple Brain Scan Diagnoses Parkinson's Disease Years Before It Becomes Untreatable
- Cutting-Edge MRI Technology to Revolutionize Diagnosis of Common Heart Problem
- New MRI Technique Reveals True Heart Age to Prevent Attacks and Strokes
- AI Tool Predicts Relapse of Pediatric Brain Cancer from Brain MRI Scans
- AI Tool Tracks Effectiveness of Multiple Sclerosis Treatments Using Brain MRI Scans
- Ultra-Powerful MRI Scans Enable Life-Changing Surgery in Treatment-Resistant Epileptic Patients
- AI-Powered MRI Technology Improves Parkinson’s Diagnoses
- Biparametric MRI Combined with AI Enhances Detection of Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer
Channels
Radiography
view channel
Routine Mammograms Could Predict Future Cardiovascular Disease in Women
Mammograms are widely used to screen for breast cancer, but they may also contain overlooked clues about cardiovascular health. Calcium deposits in the arteries of the breast signal stiffening blood vessels,... Read more
AI Detects Early Signs of Aging from Chest X-Rays
Chronological age does not always reflect how fast the body is truly aging, and current biological age tests often rely on DNA-based markers that may miss early organ-level decline. Detecting subtle, age-related... Read moreUltrasound
view channel
Wearable Ultrasound Imaging System to Enable Real-Time Disease Monitoring
Chronic conditions such as hypertension and heart failure require close monitoring, yet today’s ultrasound imaging is largely confined to hospitals and short, episodic scans. This reactive model limits... Read more
Ultrasound Technique Visualizes Deep Blood Vessels in 3D Without Contrast Agents
Producing clear 3D images of deep blood vessels has long been difficult without relying on contrast agents, CT scans, or MRI. Standard ultrasound typically provides only 2D cross-sections, limiting clinicians’... Read moreNuclear Medicine
view channel
Radiopharmaceutical Molecule Marker to Improve Choice of Bladder Cancer Therapies
Targeted cancer therapies only work when tumor cells express the specific molecular structures they are designed to attack. In urothelial carcinoma, a common form of bladder cancer, the cell surface protein... Read more
Cancer “Flashlight” Shows Who Can Benefit from Targeted Treatments
Targeted cancer therapies can be highly effective, but only when a patient’s tumor expresses the specific protein the treatment is designed to attack. Determining this usually requires biopsies or advanced... Read moreGeneral/Advanced Imaging
view channel
New 3D Imaging System Addresses MRI, CT and Ultrasound Limitations
Medical imaging is central to diagnosing and managing injuries, cancer, infections, and chronic diseases, yet existing tools each come with trade-offs. Ultrasound, X-ray, CT, and MRI can be costly, time-consuming,... Read more
AI-Based Tool Predicts Future Cardiovascular Events in Angina Patients
Stable coronary artery disease is a common cause of chest pain, yet accurately identifying patients at the highest risk of future heart attacks or death remains difficult. Standard coronary CT scans show... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more
Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in medical diagnostics market is expanding with early disease detection being one of its key applications and image recognition becoming a compelling consumer proposition... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
GE HealthCare and NVIDIA Collaboration to Reimagine Diagnostic Imaging
GE HealthCare (Chicago, IL, USA) has entered into a collaboration with NVIDIA (Santa Clara, CA, USA), expanding the existing relationship between the two companies to focus on pioneering innovation in... Read more
Patient-Specific 3D-Printed Phantoms Transform CT Imaging
New research has highlighted how anatomically precise, patient-specific 3D-printed phantoms are proving to be scalable, cost-effective, and efficient tools in the development of new CT scan algorithms... Read more
Siemens and Sectra Collaborate on Enhancing Radiology Workflows
Siemens Healthineers (Forchheim, Germany) and Sectra (Linköping, Sweden) have entered into a collaboration aimed at enhancing radiologists' diagnostic capabilities and, in turn, improving patient care... Read more