CT Imaging-Based Assessment of Thoracic Aortic Diameter Useful for Predicting Heart Attacks
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 13 Apr 2022 |

The aorta is a large artery that carries oxygenated blood to the heart and other parts of the body. The portion that passes through the chest, known as the thoracic aorta, is divided into an ascending aorta that rises from the left ventricle of the heart and a descending aorta in the back of the chest. The thoracic aorta grows as we age, but changes of vessel size and structure, a phenomenon known as vascular remodeling, have a systemic nature involving hemodynamic -basic measures of cardiovascular function and blood circulation - and biological processes that are also linked to cardiovascular disease. Now, a new study has revealed that the diameter of the thoracic aorta is a biomarker for heart attacks and other adverse cardiovascular events in women and men.
In the study, researchers at the Erasmus University Medical Center (Rotterdam, the Netherlands) assessed these associations in 2,178 participants from the population-based Rotterdam Study. Participants underwent multi-detector CT scans between 2003 and 2006 and were followed for nine years, on average. Thoracic aorta diameters were indexed for body mass index (BMI). Larger BMI-indexed ascending and descending thoracic aortic diameters were significantly associated with increased risk of adverse cardiovascular outcomes like stroke and death in both women and men. In women, greater ascending aortic diameter was associated with 33% higher cardiovascular mortality risk. Remodeling of the aging aorta seems to be different between women and men with faster deterioration in women.
The study findings suggest that cardiovascular risk assessment associated with thoracic aortic size among asymptomatic women and men could lead to effective, sex-specific prevention strategies. Thoracic aorta size assessment could easily be added to existing screening methods, the researchers said. The cardiac CT scans deployed in the study are already commonly used to assess coronary calcium. Thoracic aortic diameter could also be measured routinely, for example as part of CT-based lung cancer screening. The current study was based on a single CT-based assessment of thoracic aorta among a large group of participants from the general population, followed up for nine years for incidence of cardiovascular outcomes and mortality. The researchers have recently repeated the CT-based assessment of thoracic aorta among these participants after a median of 14 years.
"While enlargement of the thoracic aorta is a frequent finding in clinical practice, few longitudinal data regarding its long-term prognosis for major cardiovascular disease outcomes at the population level exist," said study senior author Maryam Kavousi M.D., Ph.D., from the Department of Epidemiology at Erasmus MC. "Our results suggest that imaging-based assessment of diameter of thoracic aorta can be considered as a risk marker for future cardiovascular disease. As the aortic diameter is significantly related to body size, use of aortic diameters indexed for body measurements could improve its prognostic value for cardiovascular outcomes."
Related Links:
Erasmus University Medical Center
Latest General/Advanced Imaging News
- Extending CT Imaging Detects Hidden Blood Clots in Stroke Patients
- Groundbreaking AI Model Accurately Segments Liver Tumors from CT Scans
- New CT-Based Indicator Helps Predict Life-Threatening Postpartum Bleeding Cases
- CT Colonography Beats Stool DNA Testing for Colon Cancer Screening
- First-Of-Its-Kind Wearable Device Offers Revolutionary Alternative to CT Scans
- AI-Based CT Scan Analysis Predicts Early-Stage Kidney Damage Due to Cancer Treatments
- CT-Based Deep Learning-Driven Tool to Enhance Liver Cancer Diagnosis
- AI-Powered Imaging System Improves Lung Cancer Diagnosis
- AI Model Significantly Enhances Low-Dose CT Capabilities
- Ultra-Low Dose CT Aids Pneumonia Diagnosis in Immunocompromised Patients
- AI Reduces CT Lung Cancer Screening Workload by Almost 80%
- Cutting-Edge Technology Combines Light and Sound for Real-Time Stroke Monitoring
- AI System Detects Subtle Changes in Series of Medical Images Over Time
- New CT Scan Technique to Improve Prognosis and Treatments for Head and Neck Cancers
- World’s First Mobile Whole-Body CT Scanner to Provide Diagnostics at POC
- Comprehensive CT Scans Could Identify Atherosclerosis Among Lung Cancer Patients
Channels
Radiography
view channel
AI Hybrid Strategy Improves Mammogram Interpretation
Breast cancer screening programs rely heavily on radiologists interpreting mammograms, a process that is time-intensive and subject to errors. While artificial intelligence (AI) models have shown strong... Read more
AI Technology Predicts Personalized Five-Year Risk of Developing Breast Cancer
Breast cancer remains one of the most common cancers among women, with about one in eight receiving a diagnosis in their lifetime. Despite widespread use of mammography, about 34% of patients in the U.... Read moreMRI
view channel
AI-Assisted Model Enhances MRI Heart Scans
A cardiac MRI can reveal critical information about the heart’s function and any abnormalities, but traditional scans take 30 to 90 minutes and often suffer from poor image quality due to patient movement.... Read more
AI Model Outperforms Doctors at Identifying Patients Most At-Risk of Cardiac Arrest
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is one of the most common inherited heart conditions and a leading cause of sudden cardiac death in young individuals and athletes. While many patients live normal lives, some... Read moreUltrasound
view channel
Non-Invasive Ultrasound-Based Tool Accurately Detects Infant Meningitis
Meningitis, an inflammation of the membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord, can be fatal in infants if not diagnosed and treated early. Even when treated, it may leave lasting damage, such as cognitive... Read more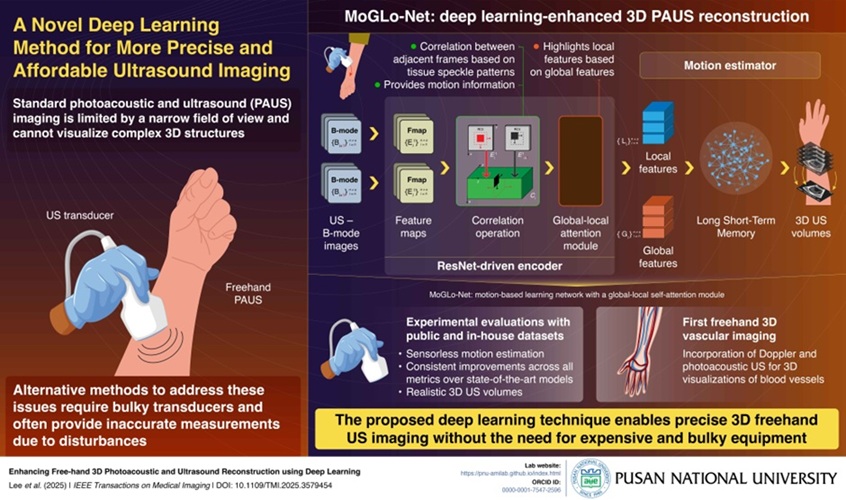
Breakthrough Deep Learning Model Enhances Handheld 3D Medical Imaging
Ultrasound imaging is a vital diagnostic technique used to visualize internal organs and tissues in real time and to guide procedures such as biopsies and injections. When paired with photoacoustic imaging... Read moreNuclear Medicine
view channel
New Camera Sees Inside Human Body for Enhanced Scanning and Diagnosis
Nuclear medicine scans like single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) allow doctors to observe heart function, track blood flow, and detect hidden diseases. However, current detectors are either... Read more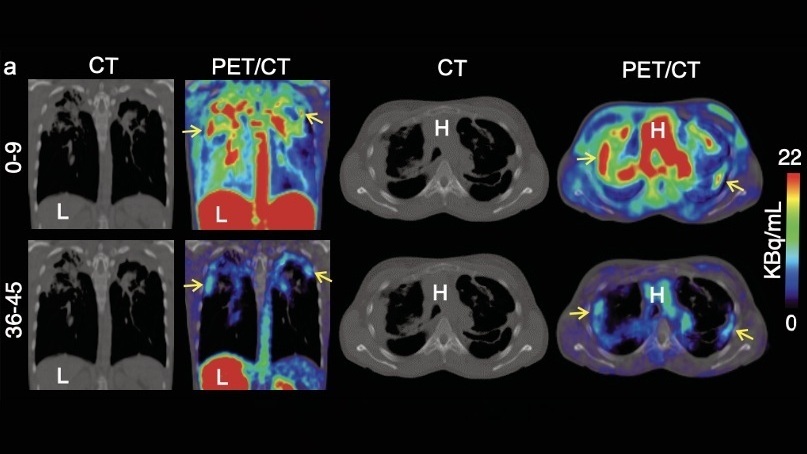
Novel Bacteria-Specific PET Imaging Approach Detects Hard-To-Diagnose Lung Infections
Mycobacteroides abscessus is a rapidly growing mycobacteria that primarily affects immunocompromised patients and those with underlying lung diseases, such as cystic fibrosis or chronic obstructive pulmonary... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more
Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in medical diagnostics market is expanding with early disease detection being one of its key applications and image recognition becoming a compelling consumer proposition... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
GE HealthCare and NVIDIA Collaboration to Reimagine Diagnostic Imaging
GE HealthCare (Chicago, IL, USA) has entered into a collaboration with NVIDIA (Santa Clara, CA, USA), expanding the existing relationship between the two companies to focus on pioneering innovation in... Read more
Patient-Specific 3D-Printed Phantoms Transform CT Imaging
New research has highlighted how anatomically precise, patient-specific 3D-printed phantoms are proving to be scalable, cost-effective, and efficient tools in the development of new CT scan algorithms... Read more
Siemens and Sectra Collaborate on Enhancing Radiology Workflows
Siemens Healthineers (Forchheim, Germany) and Sectra (Linköping, Sweden) have entered into a collaboration aimed at enhancing radiologists' diagnostic capabilities and, in turn, improving patient care... Read more




 Guided Devices.jpg)