Novel Sonic Beam Therapy Liquefies Tumor Tissues 
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 01 Nov 2021 |
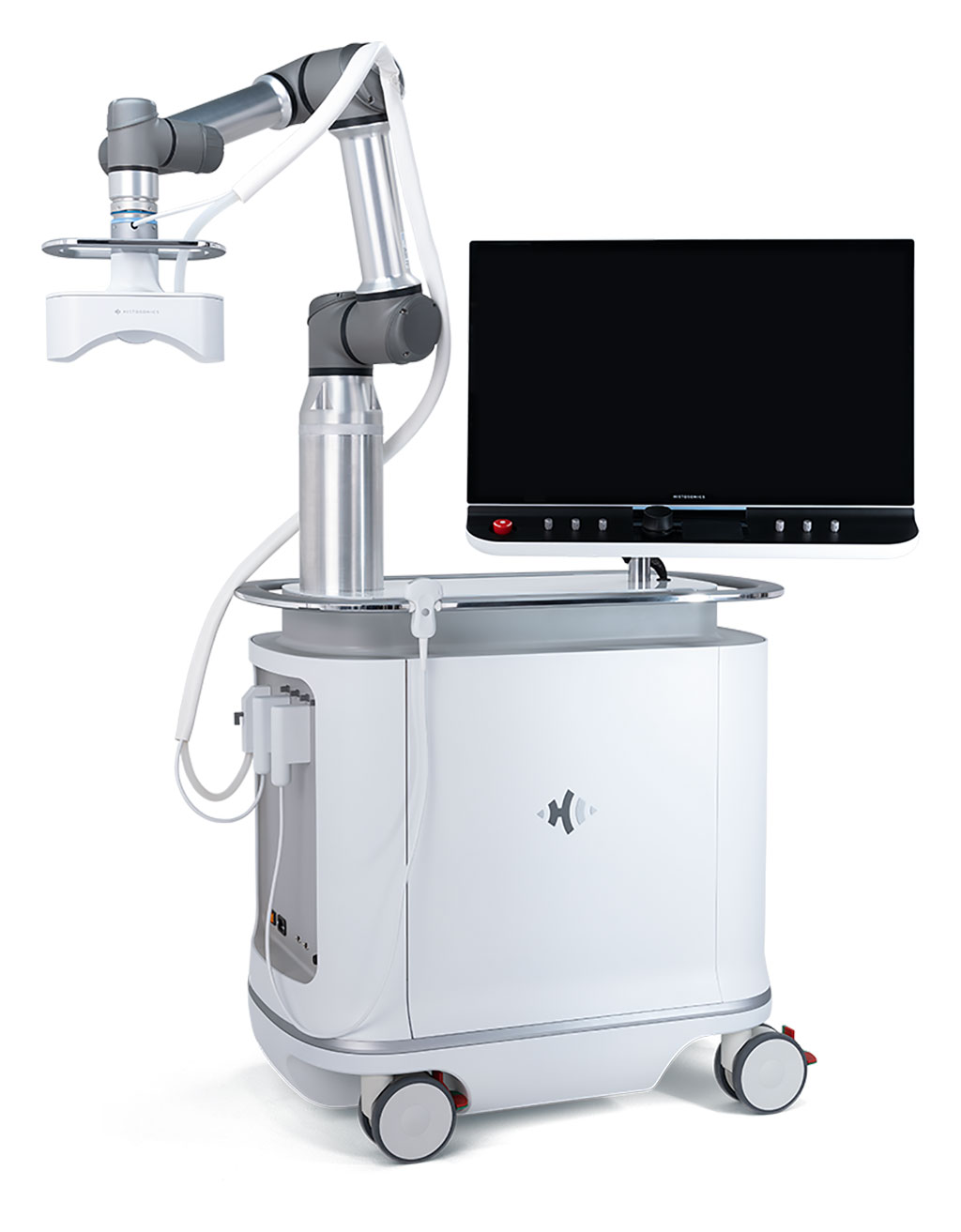
Image: The Edison histotripsy sonic beam platform (Photo courtesy of Histonics)
An automated external beam system uses acoustic energy to mechanically destroy tissue in the liver without incisions, ionizing radiation, or heat.
The HistoSonics (Minneapolis, MN, USA) Edison is a sophisticated histotripsy sonic beam platform designed to deliver pulsed sound energy into the body, without any incisions or needles, that destroys tissue at the sub-cellular level. Physicians first contour and plan treatment according to shape and size of their target; once the energy required to initiate cellular destruction is determined, the acoustic pulses are delivered. Treatment is monitored in real-time, while the system automatically moves through the target area.
Histotripsy uses pulsed sound waves to induce microbubbles from gases that are naturally present in tissues. These “bubble clouds” form and collapse in microseconds, creating mechanical forces that are strong enough to destroy tissue in a non-invasive and non-thermal method. As only 20%-30% of patients with liver tumors are eligible for surgical resection, due to the presence of multiple tumors, underlying poor liver function, or general health issues, histotripsy may provide a solution. Edison has received breakthrough device designation from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
“The Breakthrough Device Designation is a significant milestone for our company and validates our belief that our platform offers significant advantages over existing approved or cleared alternatives,” said Mike Blue, President and CEO of HistoSonics. “Early and ongoing clinical results are promising and suggest that our ability to precisely destroy targeted liver tissue, completely non-invasively, and without the challenges associated with ionizing radiation or other locoregional therapies, provides advantages to patients and physicians that don't exist today.”
Primary liver tumors were the third leading cause of tumor related death worldwide in 2020, with approximately 906,000 new cases and 830,000 deaths globally, and 5-year survival rates less than 18%. Additionally, the liver is second only to lymph nodes as the most common site of metastatic tumors, and estimated to be present in up to 70% of patients with advanced disease from another site.
Related Links:
HistoSonics
The HistoSonics (Minneapolis, MN, USA) Edison is a sophisticated histotripsy sonic beam platform designed to deliver pulsed sound energy into the body, without any incisions or needles, that destroys tissue at the sub-cellular level. Physicians first contour and plan treatment according to shape and size of their target; once the energy required to initiate cellular destruction is determined, the acoustic pulses are delivered. Treatment is monitored in real-time, while the system automatically moves through the target area.
Histotripsy uses pulsed sound waves to induce microbubbles from gases that are naturally present in tissues. These “bubble clouds” form and collapse in microseconds, creating mechanical forces that are strong enough to destroy tissue in a non-invasive and non-thermal method. As only 20%-30% of patients with liver tumors are eligible for surgical resection, due to the presence of multiple tumors, underlying poor liver function, or general health issues, histotripsy may provide a solution. Edison has received breakthrough device designation from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
“The Breakthrough Device Designation is a significant milestone for our company and validates our belief that our platform offers significant advantages over existing approved or cleared alternatives,” said Mike Blue, President and CEO of HistoSonics. “Early and ongoing clinical results are promising and suggest that our ability to precisely destroy targeted liver tissue, completely non-invasively, and without the challenges associated with ionizing radiation or other locoregional therapies, provides advantages to patients and physicians that don't exist today.”
Primary liver tumors were the third leading cause of tumor related death worldwide in 2020, with approximately 906,000 new cases and 830,000 deaths globally, and 5-year survival rates less than 18%. Additionally, the liver is second only to lymph nodes as the most common site of metastatic tumors, and estimated to be present in up to 70% of patients with advanced disease from another site.
Related Links:
HistoSonics
Latest Nuclear Medicine News
- Radiopharmaceutical Molecule Marker to Improve Choice of Bladder Cancer Therapies
- Cancer “Flashlight” Shows Who Can Benefit from Targeted Treatments
- PET Imaging of Inflammation Predicts Recovery and Guides Therapy After Heart Attack
- Radiotheranostic Approach Detects, Kills and Reprograms Aggressive Cancers
- New Imaging Solution Improves Survival for Patients with Recurring Prostate Cancer
- PET Tracer Enables Same-Day Imaging of Triple-Negative Breast and Urothelial Cancers
- New Camera Sees Inside Human Body for Enhanced Scanning and Diagnosis
- Novel Bacteria-Specific PET Imaging Approach Detects Hard-To-Diagnose Lung Infections
- New Imaging Approach Could Reduce Need for Biopsies to Monitor Prostate Cancer
- Novel Radiolabeled Antibody Improves Diagnosis and Treatment of Solid Tumors
- Novel PET Imaging Approach Offers Never-Before-Seen View of Neuroinflammation
- Novel Radiotracer Identifies Biomarker for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
- Innovative PET Imaging Technique to Help Diagnose Neurodegeneration
- New Molecular Imaging Test to Improve Lung Cancer Diagnosis
- Novel PET Technique Visualizes Spinal Cord Injuries to Predict Recovery
- Next-Gen Tau Radiotracers Outperform FDA-Approved Imaging Agents in Detecting Alzheimer’s
Channels
Radiography
view channel
Routine Mammograms Could Predict Future Cardiovascular Disease in Women
Mammograms are widely used to screen for breast cancer, but they may also contain overlooked clues about cardiovascular health. Calcium deposits in the arteries of the breast signal stiffening blood vessels,... Read more
AI Detects Early Signs of Aging from Chest X-Rays
Chronological age does not always reflect how fast the body is truly aging, and current biological age tests often rely on DNA-based markers that may miss early organ-level decline. Detecting subtle, age-related... Read moreMRI
view channel
MRI Scans Reveal Signature Patterns of Brain Activity to Predict Recovery from TBI
Recovery after traumatic brain injury (TBI) varies widely, with some patients regaining full function while others are left with lasting disabilities. Prognosis is especially difficult to assess in patients... Read more
Novel Imaging Approach to Improve Treatment for Spinal Cord Injuries
Vascular dysfunction in the spinal cord contributes to multiple neurological conditions, including traumatic injuries and degenerative cervical myelopathy, where reduced blood flow can lead to progressive... Read more
AI-Assisted Model Enhances MRI Heart Scans
A cardiac MRI can reveal critical information about the heart’s function and any abnormalities, but traditional scans take 30 to 90 minutes and often suffer from poor image quality due to patient movement.... Read more
AI Model Outperforms Doctors at Identifying Patients Most At-Risk of Cardiac Arrest
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is one of the most common inherited heart conditions and a leading cause of sudden cardiac death in young individuals and athletes. While many patients live normal lives, some... Read moreUltrasound
view channel
Portable Ultrasound Sensor to Enable Earlier Breast Cancer Detection
Breast cancer screening relies heavily on annual mammograms, but aggressive tumors can develop between scans, accounting for up to 30 percent of cases. These interval cancers are often diagnosed later,... Read more
Portable Imaging Scanner to Diagnose Lymphatic Disease in Real Time
Lymphatic disorders affect hundreds of millions of people worldwide and are linked to conditions ranging from limb swelling and organ dysfunction to birth defects and cancer-related complications.... Read more
Imaging Technique Generates Simultaneous 3D Color Images of Soft-Tissue Structure and Vasculature
Medical imaging tools often force clinicians to choose between speed, structural detail, and functional insight. Ultrasound is fast and affordable but typically limited to two-dimensional anatomy, while... Read moreGeneral/Advanced Imaging
view channel
AI Tool Offers Prognosis for Patients with Head and Neck Cancer
Oropharyngeal cancer is a form of head and neck cancer that can spread through lymph nodes, significantly affecting survival and treatment decisions. Current therapies often involve combinations of surgery,... Read more
New 3D Imaging System Addresses MRI, CT and Ultrasound Limitations
Medical imaging is central to diagnosing and managing injuries, cancer, infections, and chronic diseases, yet existing tools each come with trade-offs. Ultrasound, X-ray, CT, and MRI can be costly, time-consuming,... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more
Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in medical diagnostics market is expanding with early disease detection being one of its key applications and image recognition becoming a compelling consumer proposition... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
Nuclear Medicine Set for Continued Growth Driven by Demand for Precision Diagnostics
Clinical imaging services face rising demand for precise molecular diagnostics and targeted radiopharmaceutical therapy as cancer and chronic disease rates climb. A new market analysis projects rapid expansion... Read more




















