NVIDIA Showcases Latest AI-driven Medical Imaging Advancements at RSNA 2019
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 02 Dec 2019 |
Image: NVIDIA Clara™ (Photo courtesy of NVIDIA)
NVIDIA (Santa Clara, CA, USA) demonstrated how GPU-accelerated artificial intelligence (AI) is driving innovation in radiology and transforming the healthcare landscape at the 2019 RSNA Annual Meeting held December 1–6 in Chicago, USA. Visitors to NVIDIA’s RSNA 2019 booth in the event’s AI Showcase saw its latest AI-driven medical imaging advancements and met the company’s deep learning experts about using AI to advance research and accelerate clinical workflows.
The medical imaging industry is being transformed. A decade ago, the earliest applications to take advantage of GPU computing were image & signal processing applications. Today, GPUs are found in almost all imaging modalities, including CT, MRI, X-ray, and ultrasound, bringing more computing capabilities to edge devices. Deep learning research in medical imaging is also booming with more efficient and improved approaches being developed to enable AI-assisted workflows. Today, most of this AI research is being done in isolation and with limited datasets which may lead to overly simplified models. Even when a fully validated model is available, it is a challenge to deploy the algorithm in a local environment.
By equipping the world’s leading institutions with advanced solutions, NVIDIA is enabling them to tackle interoperable data and meet the increasing demand for personalized medicine and next-generation clinics. NVIDIA Clara Medical Imaging is a collection of developer toolkits built on NVIDIA’s compute platform aimed at accelerating compute, AI, and advanced visualization. From automating workflows to improving processing speed and image quality, medical imaging developers are using NVIDIA Clara to harness AI to transform healthcare workloads. With the latest release of Clara AI for Medical Imaging now data scientists, researchers and software developers have the necessary tools, APIs and development framework to train and deploy AI workflows.
Related Links:
NVIDIA
The medical imaging industry is being transformed. A decade ago, the earliest applications to take advantage of GPU computing were image & signal processing applications. Today, GPUs are found in almost all imaging modalities, including CT, MRI, X-ray, and ultrasound, bringing more computing capabilities to edge devices. Deep learning research in medical imaging is also booming with more efficient and improved approaches being developed to enable AI-assisted workflows. Today, most of this AI research is being done in isolation and with limited datasets which may lead to overly simplified models. Even when a fully validated model is available, it is a challenge to deploy the algorithm in a local environment.
By equipping the world’s leading institutions with advanced solutions, NVIDIA is enabling them to tackle interoperable data and meet the increasing demand for personalized medicine and next-generation clinics. NVIDIA Clara Medical Imaging is a collection of developer toolkits built on NVIDIA’s compute platform aimed at accelerating compute, AI, and advanced visualization. From automating workflows to improving processing speed and image quality, medical imaging developers are using NVIDIA Clara to harness AI to transform healthcare workloads. With the latest release of Clara AI for Medical Imaging now data scientists, researchers and software developers have the necessary tools, APIs and development framework to train and deploy AI workflows.
Related Links:
NVIDIA
Latest RSNA 2019 News
- Carestream Introduces Three-Dimensional Extension of General Radiography Through Its Digital Tomosynthesis Functionality
- Lunit Demonstrates Latest Updated AI Solutions for Chest and Breast Radiology at RSNA 2019
- Bracco Diagnostics Unveils Contrast Media and Device Offerings at RSNA 2019
- Guerbet Showcases New Dose&Care and Other Digital Solutions with Diagnostic and Interventional Imaging Offerings
- Canon Introduces New Wireless Detectors and Digital PET/CT Scanner at RSNA 2019
- Siemens Healthineers Introduces SOMATOM On.site Mobile Head CT Scanner and AI-based MRI Assistants at RSNA
- Hologic Launches Unifi Workspace, Comprehensive Reading Solution for Breast Health Diagnostics
- Agfa Launches New Groundbreaking Digital Radiography Unit at RSNA 2019
- Fujifilm SonoSite Exhibits Complete Point-of-Care Ultrasound Portfolio at RSNA 2019
- Fujifilm Previews World's First Glass-Free Digital Radiography Detector at RSNA 2019 Image
- Philips Healthcare Demonstrates How AI Breast Software Brings Intelligence and Automation to Breast Ultrasound
- Siemens Healthineers Focuses on Digital Transformation of Imaging and Therapy at RSNA 2019
Channels
Radiography
view channel
AI-Powered Mammograms Predict Cardiovascular Risk
The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends that women in middle age and older undergo a mammogram, which is an X-ray of the breast, every one or two years to screen for breast cancer.... Read more
Generative AI Model Significantly Reduces Chest X-Ray Reading Time
The prompt and accurate interpretation of radiologic images is critical due to its significant impact on patient outcomes, as errors in interpretation can lead to changes in clinical management.... Read moreMRI
view channel
Ultra-Powerful MRI Scans Enable Life-Changing Surgery in Treatment-Resistant Epileptic Patients
Approximately 360,000 individuals in the UK suffer from focal epilepsy, a condition in which seizures spread from one part of the brain. Around a third of these patients experience persistent seizures... Read more
AI-Powered MRI Technology Improves Parkinson’s Diagnoses
Current research shows that the accuracy of diagnosing Parkinson’s disease typically ranges from 55% to 78% within the first five years of assessment. This is partly due to the similarities shared by Parkinson’s... Read more
Biparametric MRI Combined with AI Enhances Detection of Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer
Artificial intelligence (AI) technologies are transforming the way medical images are analyzed, offering unprecedented capabilities in quantitatively extracting features that go beyond traditional visual... Read more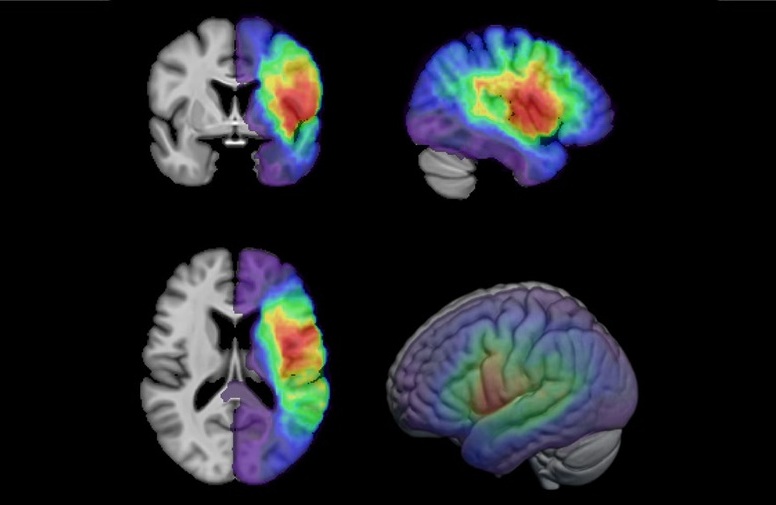
First-Of-Its-Kind AI-Driven Brain Imaging Platform to Better Guide Stroke Treatment Options
Each year, approximately 800,000 people in the U.S. experience strokes, with marginalized and minoritized groups being disproportionately affected. Strokes vary in terms of size and location within the... Read moreUltrasound
view channel
High Resolution Ultrasound Speeds Up Prostate Cancer Diagnosis
Each year, approximately one million prostate cancer biopsies are conducted across Europe, with similar numbers in the USA and around 100,000 in Canada. Most of these biopsies are performed using MRI images... Read more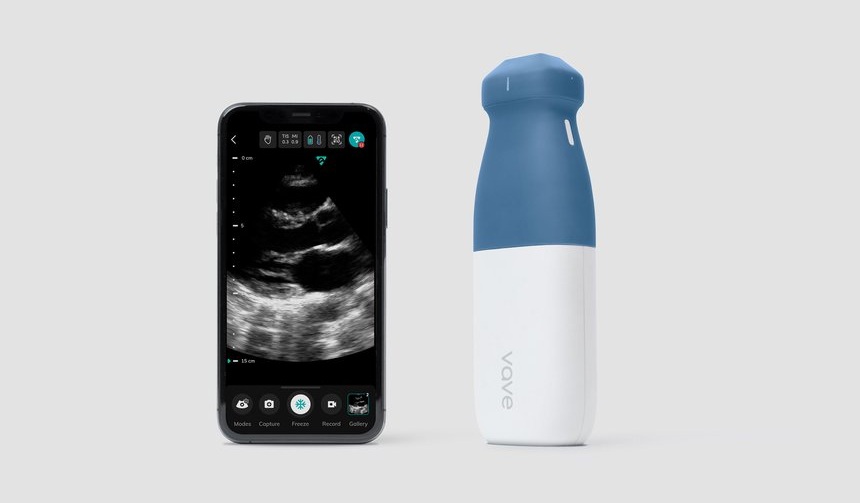
World's First Wireless, Handheld, Whole-Body Ultrasound with Single PZT Transducer Makes Imaging More Accessible
Ultrasound devices play a vital role in the medical field, routinely used to examine the body's internal tissues and structures. While advancements have steadily improved ultrasound image quality and processing... Read more
Artificial Intelligence Detects Undiagnosed Liver Disease from Echocardiograms
Echocardiography is a diagnostic procedure that uses ultrasound to visualize the heart and its associated structures. This imaging test is commonly used as an early screening method when doctors suspect... Read more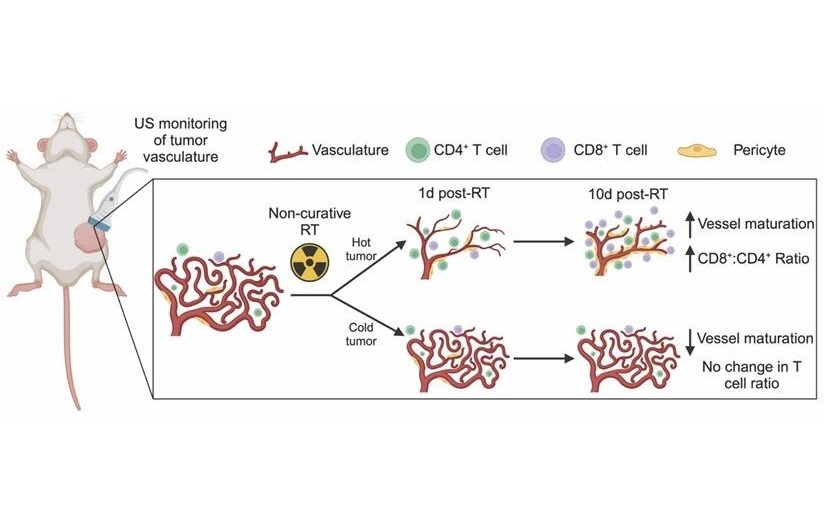
Ultrasound Imaging Non-Invasively Tracks Tumor Response to Radiation and Immunotherapy
While immunotherapy holds promise in the fight against triple-negative breast cancer, many patients fail to respond to current treatments. A major challenge has been predicting and monitoring how individual... Read moreNuclear Medicine
view channel
Novel Radiotracer Identifies Biomarker for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC), which represents 15-20% of all breast cancer cases, is one of the most aggressive subtypes, with a five-year survival rate of about 40%. Due to its significant heterogeneity... Read more
Innovative PET Imaging Technique to Help Diagnose Neurodegeneration
Neurodegenerative diseases, such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and Alzheimer’s disease, are often diagnosed only after physical symptoms appear, by which time treatment may no longer be effective.... Read moreGeneral/Advanced Imaging
view channel
Ultra-Low Dose CT Aids Pneumonia Diagnosis in Immunocompromised Patients
Lung infections can be life-threatening for patients with weakened immune systems, making timely diagnosis crucial. While CT scans are considered the gold standard for detecting pneumonia, repeated scans... Read more
AI Reduces CT Lung Cancer Screening Workload by Almost 80%
Lung cancer impacts over 48,000 individuals in the UK annually, and early detection is key to improving survival rates. The UK Lung Cancer Screening (UKLS) trial has already shown that low-dose CT (LDCT)... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more
Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in medical diagnostics market is expanding with early disease detection being one of its key applications and image recognition becoming a compelling consumer proposition... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
GE HealthCare and NVIDIA Collaboration to Reimagine Diagnostic Imaging
GE HealthCare (Chicago, IL, USA) has entered into a collaboration with NVIDIA (Santa Clara, CA, USA), expanding the existing relationship between the two companies to focus on pioneering innovation in... Read more
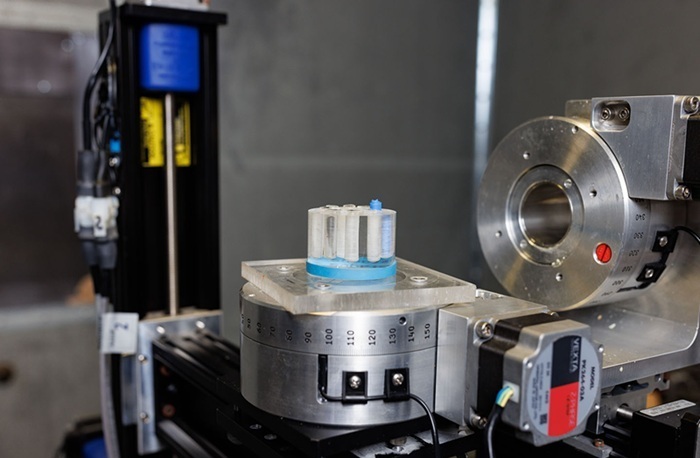
Patient-Specific 3D-Printed Phantoms Transform CT Imaging
New research has highlighted how anatomically precise, patient-specific 3D-printed phantoms are proving to be scalable, cost-effective, and efficient tools in the development of new CT scan algorithms... Read more
Siemens and Sectra Collaborate on Enhancing Radiology Workflows
Siemens Healthineers (Forchheim, Germany) and Sectra (Linköping, Sweden) have entered into a collaboration aimed at enhancing radiologists' diagnostic capabilities and, in turn, improving patient care... Read more













![Image: [18F]3F4AP in a human subject after mild incomplete spinal cord injury (Photo courtesy of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine, DOI:10.2967/jnumed.124.268242) Image: [18F]3F4AP in a human subject after mild incomplete spinal cord injury (Photo courtesy of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine, DOI:10.2967/jnumed.124.268242)](https://globetechcdn.com/mobile_medicalimaging/images/stories/articles/article_images/2025-02-24/Brugarolas_F8.large.jpg)