AI Tool Combined with Radiologists Identifies Breast Cancer with 90% Accuracy
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 04 Nov 2019 |
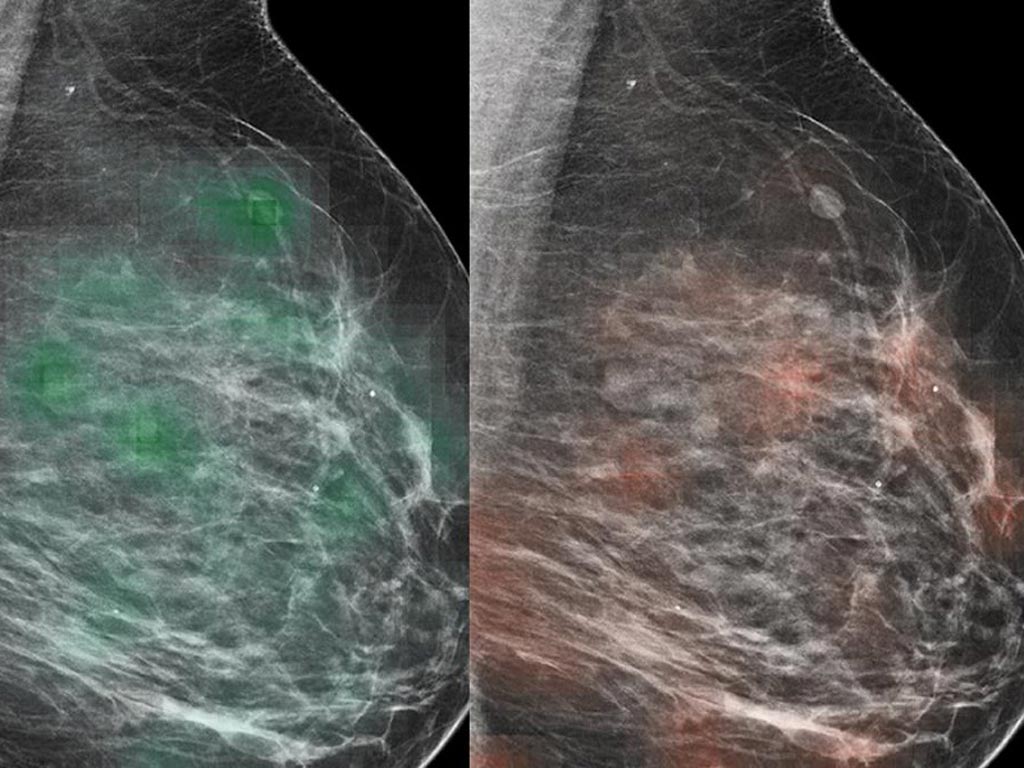
Image: An AI tool-radiologist combo can identify breast cancer with approximately 90% accuracy (Photo courtesy of MDN).
An artificial intelligence (AI) tool trained by researchers on approximately one million screening mammography images has identified breast cancer with approximately 90% accuracy when combined with analysis by radiologists in a new study. Researchers from the NYU School of Medicine (New York City, NY, USA) and the NYU Center for Data Science examined the ability of a type of AI to add value to the diagnoses reached by a group of 14 radiologists as they reviewed 720 mammogram images.
The researchers designed statistical techniques that let their program “learn” how to get better at a task without being told exactly how. They trained the AI tool on several images matched with the results of biopsies performed in the past with the aim of enabling it to help radiologists reduce the number biopsies needed. For training the AI tool, the researchers used an extraordinarily large dataset consisting of 229,426 digital screening mammography exams and 1,001,093 images. The neural network was trained by programming it to analyze images from the database for which cancer diagnoses had already been determined.
Additionally, the researchers designed the study AI model to first consider very small patches of the full resolution image separately in order to create a heat map, a statistical picture of the disease likelihood. Then the program was taught to consider the entire breast for structural features linked to cancer, paying closer attention to the areas flagged in the pixel-level heat map. Instead of the researchers identifying the image features for their AI to search for, the tool is discovering which image features increase prediction accuracy all by itself. Going forward, the team plans to further increase the tool’s accuracy by training the AI program on more data, even identify changes in breast tissue that are not yet cancerous but have the potential to be.
“Our study found that AI identified cancer-related patterns in the data that radiologists could not, and vice versa,” said senior study author Krzysztof Geras, assistant professor in the Department of Radiology at NYU Langone. “AI detected pixel-level changes in tissue invisible to the human eye, while humans used forms of reasoning not available to AI. The ultimate goal of our work is to augment, not replace, human radiologists.”
“The transition to AI support in diagnostic radiology should proceed like the adoption of self-driving cars—slowly and carefully, building trust, and improving systems along the way with a focus on safety,” said first author Nan Wu, a doctoral candidate at the NYU Center for Data Science.
Related Links:
NYU School of Medicine
The researchers designed statistical techniques that let their program “learn” how to get better at a task without being told exactly how. They trained the AI tool on several images matched with the results of biopsies performed in the past with the aim of enabling it to help radiologists reduce the number biopsies needed. For training the AI tool, the researchers used an extraordinarily large dataset consisting of 229,426 digital screening mammography exams and 1,001,093 images. The neural network was trained by programming it to analyze images from the database for which cancer diagnoses had already been determined.
Additionally, the researchers designed the study AI model to first consider very small patches of the full resolution image separately in order to create a heat map, a statistical picture of the disease likelihood. Then the program was taught to consider the entire breast for structural features linked to cancer, paying closer attention to the areas flagged in the pixel-level heat map. Instead of the researchers identifying the image features for their AI to search for, the tool is discovering which image features increase prediction accuracy all by itself. Going forward, the team plans to further increase the tool’s accuracy by training the AI program on more data, even identify changes in breast tissue that are not yet cancerous but have the potential to be.
“Our study found that AI identified cancer-related patterns in the data that radiologists could not, and vice versa,” said senior study author Krzysztof Geras, assistant professor in the Department of Radiology at NYU Langone. “AI detected pixel-level changes in tissue invisible to the human eye, while humans used forms of reasoning not available to AI. The ultimate goal of our work is to augment, not replace, human radiologists.”
“The transition to AI support in diagnostic radiology should proceed like the adoption of self-driving cars—slowly and carefully, building trust, and improving systems along the way with a focus on safety,” said first author Nan Wu, a doctoral candidate at the NYU Center for Data Science.
Related Links:
NYU School of Medicine
Latest Industry News News
- GE HealthCare and NVIDIA Collaboration to Reimagine Diagnostic Imaging
- Patient-Specific 3D-Printed Phantoms Transform CT Imaging
- Siemens and Sectra Collaborate on Enhancing Radiology Workflows
- Bracco Diagnostics and ColoWatch Partner to Expand Availability CRC Screening Tests Using Virtual Colonoscopy
- Mindray Partners with TeleRay to Streamline Ultrasound Delivery
- Philips and Medtronic Partner on Stroke Care
- Siemens and Medtronic Enter into Global Partnership for Advancing Spine Care Imaging Technologies
- RSNA 2024 Technical Exhibits to Showcase Latest Advances in Radiology
- Bracco Collaborates with Arrayus on Microbubble-Assisted Focused Ultrasound Therapy for Pancreatic Cancer
- Innovative Collaboration to Enhance Ischemic Stroke Detection and Elevate Standards in Diagnostic Imaging
- RSNA 2024 Registration Opens
- Microsoft collaborates with Leading Academic Medical Systems to Advance AI in Medical Imaging
- GE HealthCare Acquires Intelligent Ultrasound Group’s Clinical Artificial Intelligence Business
- Bayer and Rad AI Collaborate on Expanding Use of Cutting Edge AI Radiology Operational Solutions
- Polish Med-Tech Company BrainScan to Expand Extensively into Foreign Markets
- Hologic Acquires UK-Based Breast Surgical Guidance Company Endomagnetics Ltd.
Channels
Radiography
view channel
World's Largest Class Single Crystal Diamond Radiation Detector Opens New Possibilities for Diagnostic Imaging
Diamonds possess ideal physical properties for radiation detection, such as exceptional thermal and chemical stability along with a quick response time. Made of carbon with an atomic number of six, diamonds... Read more
AI-Powered Imaging Technique Shows Promise in Evaluating Patients for PCI
Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), also known as coronary angioplasty, is a minimally invasive procedure where small metal tubes called stents are inserted into partially blocked coronary arteries... Read moreMRI
view channel
AI Tool Predicts Relapse of Pediatric Brain Cancer from Brain MRI Scans
Many pediatric gliomas are treatable with surgery alone, but relapses can be catastrophic. Predicting which patients are at risk for recurrence remains challenging, leading to frequent follow-ups with... Read more
AI Tool Tracks Effectiveness of Multiple Sclerosis Treatments Using Brain MRI Scans
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a condition in which the immune system attacks the brain and spinal cord, leading to impairments in movement, sensation, and cognition. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) markers... Read more
Ultra-Powerful MRI Scans Enable Life-Changing Surgery in Treatment-Resistant Epileptic Patients
Approximately 360,000 individuals in the UK suffer from focal epilepsy, a condition in which seizures spread from one part of the brain. Around a third of these patients experience persistent seizures... Read moreUltrasound
view channel.jpeg)
AI-Powered Lung Ultrasound Outperforms Human Experts in Tuberculosis Diagnosis
Despite global declines in tuberculosis (TB) rates in previous years, the incidence of TB rose by 4.6% from 2020 to 2023. Early screening and rapid diagnosis are essential elements of the World Health... Read more
AI Identifies Heart Valve Disease from Common Imaging Test
Tricuspid regurgitation is a condition where the heart's tricuspid valve does not close completely during contraction, leading to backward blood flow, which can result in heart failure. A new artificial... Read moreNuclear Medicine
view channel
Novel Radiolabeled Antibody Improves Diagnosis and Treatment of Solid Tumors
Interleukin-13 receptor α-2 (IL13Rα2) is a cell surface receptor commonly found in solid tumors such as glioblastoma, melanoma, and breast cancer. It is minimally expressed in normal tissues, making it... Read more
Novel PET Imaging Approach Offers Never-Before-Seen View of Neuroinflammation
COX-2, an enzyme that plays a key role in brain inflammation, can be significantly upregulated by inflammatory stimuli and neuroexcitation. Researchers suggest that COX-2 density in the brain could serve... Read moreGeneral/Advanced Imaging
view channel
AI-Powered Imaging System Improves Lung Cancer Diagnosis
Given the need to detect lung cancer at earlier stages, there is an increasing need for a definitive diagnostic pathway for patients with suspicious pulmonary nodules. However, obtaining tissue samples... Read more
AI Model Significantly Enhances Low-Dose CT Capabilities
Lung cancer remains one of the most challenging diseases, making early diagnosis vital for effective treatment. Fortunately, advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) are revolutionizing lung cancer... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more






















