Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy Relieves RT Side Effects
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 30 Oct 2019 |

Image: The HBOT chamber at Sahlgrenska Academy (Photo courtesy of Sahlgrenska Academy).
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) reduces the self-reported symptoms and side effects of cancer radiotherapy (RT) in the pelvic region, according to a new study.
Researchers at Angereds Hospital (Sweden), Sahlgrenska Academy (SA; Göteborg, Sweden), Haukeland University Hospital (Bergen, Norway), and other institutions conducted a randomized, controlled trial at five Nordic hospitals involving 87 patients (18–80 years of age) with pelvic RT who were referred to a HBOT clinic due to symptoms of late radiation cystitis. Patients were randomly assigned to either HBOT (42 patients) or to standard care with no restrictions for other medications or interventions (45 patients).
The HBOT patients received 30–40 sessions of 100% oxygen breathed at a pressure of 240–250 kPa, for 80–90 min daily. The primary outcome was change in patient-perceived urinary symptoms assessed with the expanded prostate index composite score (EPIC), from inclusion to follow-up at visit four, held six to eight months later. The results revealed a change in EPIC urinary total score at visit 4 of 10.1 points in the HBOT group, compared to 7.7 points in the standard care group. In all, 41% of the HBOT patients experienced transient adverse events related to sight and hearing during the treatment period. The study was published on September 17, 2019, in The Lancet Oncology.
“In the patients in the study, general health was greatly impaired before treatment, sometimes after long periods of discomfort,” said lead author Nicklas Oscarsson, MD, of Angered Hospital, and a doctoral student in anesthesiology and intensive care at Sahlgrenska Academy. “If a patient no longer needed morphine for pain, or was able to go to the toilet once a night instead of five times, it was a clear improvement. It's a great pleasure to hear patients tell us how they feel they're returning to a normal human life. This also applies to those who get better, but perhaps aren't entirely well.”
RT is part of many treatment protocols of cancer in organs such as the prostate, cervix, ovaries, and colon. One side effect of RT in the lower abdomen is damage of nearby, healthy tissue such as the urinary tract, bladder, vagina or rectum. Symptoms such as a frequent urge to urinate, incontinence, bleeding, and severe abdominal pain may arise immediately following or even several years after RT, causing chronic and often increasing discomfort.
Related Links:
Angereds Hospital
Sahlgrenska Academy
Haukeland University Hospital
Researchers at Angereds Hospital (Sweden), Sahlgrenska Academy (SA; Göteborg, Sweden), Haukeland University Hospital (Bergen, Norway), and other institutions conducted a randomized, controlled trial at five Nordic hospitals involving 87 patients (18–80 years of age) with pelvic RT who were referred to a HBOT clinic due to symptoms of late radiation cystitis. Patients were randomly assigned to either HBOT (42 patients) or to standard care with no restrictions for other medications or interventions (45 patients).
The HBOT patients received 30–40 sessions of 100% oxygen breathed at a pressure of 240–250 kPa, for 80–90 min daily. The primary outcome was change in patient-perceived urinary symptoms assessed with the expanded prostate index composite score (EPIC), from inclusion to follow-up at visit four, held six to eight months later. The results revealed a change in EPIC urinary total score at visit 4 of 10.1 points in the HBOT group, compared to 7.7 points in the standard care group. In all, 41% of the HBOT patients experienced transient adverse events related to sight and hearing during the treatment period. The study was published on September 17, 2019, in The Lancet Oncology.
“In the patients in the study, general health was greatly impaired before treatment, sometimes after long periods of discomfort,” said lead author Nicklas Oscarsson, MD, of Angered Hospital, and a doctoral student in anesthesiology and intensive care at Sahlgrenska Academy. “If a patient no longer needed morphine for pain, or was able to go to the toilet once a night instead of five times, it was a clear improvement. It's a great pleasure to hear patients tell us how they feel they're returning to a normal human life. This also applies to those who get better, but perhaps aren't entirely well.”
RT is part of many treatment protocols of cancer in organs such as the prostate, cervix, ovaries, and colon. One side effect of RT in the lower abdomen is damage of nearby, healthy tissue such as the urinary tract, bladder, vagina or rectum. Symptoms such as a frequent urge to urinate, incontinence, bleeding, and severe abdominal pain may arise immediately following or even several years after RT, causing chronic and often increasing discomfort.
Related Links:
Angereds Hospital
Sahlgrenska Academy
Haukeland University Hospital
Latest Nuclear Medicine News
- New Camera Sees Inside Human Body for Enhanced Scanning and Diagnosis
- Novel Bacteria-Specific PET Imaging Approach Detects Hard-To-Diagnose Lung Infections
- New Imaging Approach Could Reduce Need for Biopsies to Monitor Prostate Cancer
- Novel Radiolabeled Antibody Improves Diagnosis and Treatment of Solid Tumors
- Novel PET Imaging Approach Offers Never-Before-Seen View of Neuroinflammation
- Novel Radiotracer Identifies Biomarker for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
- Innovative PET Imaging Technique to Help Diagnose Neurodegeneration
- New Molecular Imaging Test to Improve Lung Cancer Diagnosis
- Novel PET Technique Visualizes Spinal Cord Injuries to Predict Recovery
- Next-Gen Tau Radiotracers Outperform FDA-Approved Imaging Agents in Detecting Alzheimer’s
- Breakthrough Method Detects Inflammation in Body Using PET Imaging
- Advanced Imaging Reveals Hidden Metastases in High-Risk Prostate Cancer Patients
- Combining Advanced Imaging Technologies Offers Breakthrough in Glioblastoma Treatment
- New Molecular Imaging Agent Accurately Identifies Crucial Cancer Biomarker
- New Scans Light Up Aggressive Tumors for Better Treatment
- AI Stroke Brain Scan Readings Twice as Accurate as Current Method
Channels
Radiography
view channel
AI Hybrid Strategy Improves Mammogram Interpretation
Breast cancer screening programs rely heavily on radiologists interpreting mammograms, a process that is time-intensive and subject to errors. While artificial intelligence (AI) models have shown strong... Read more
AI Technology Predicts Personalized Five-Year Risk of Developing Breast Cancer
Breast cancer remains one of the most common cancers among women, with about one in eight receiving a diagnosis in their lifetime. Despite widespread use of mammography, about 34% of patients in the U.... Read moreMRI
view channel
AI-Assisted Model Enhances MRI Heart Scans
A cardiac MRI can reveal critical information about the heart’s function and any abnormalities, but traditional scans take 30 to 90 minutes and often suffer from poor image quality due to patient movement.... Read more
AI Model Outperforms Doctors at Identifying Patients Most At-Risk of Cardiac Arrest
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is one of the most common inherited heart conditions and a leading cause of sudden cardiac death in young individuals and athletes. While many patients live normal lives, some... Read moreUltrasound
view channel
Non-Invasive Ultrasound-Based Tool Accurately Detects Infant Meningitis
Meningitis, an inflammation of the membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord, can be fatal in infants if not diagnosed and treated early. Even when treated, it may leave lasting damage, such as cognitive... Read more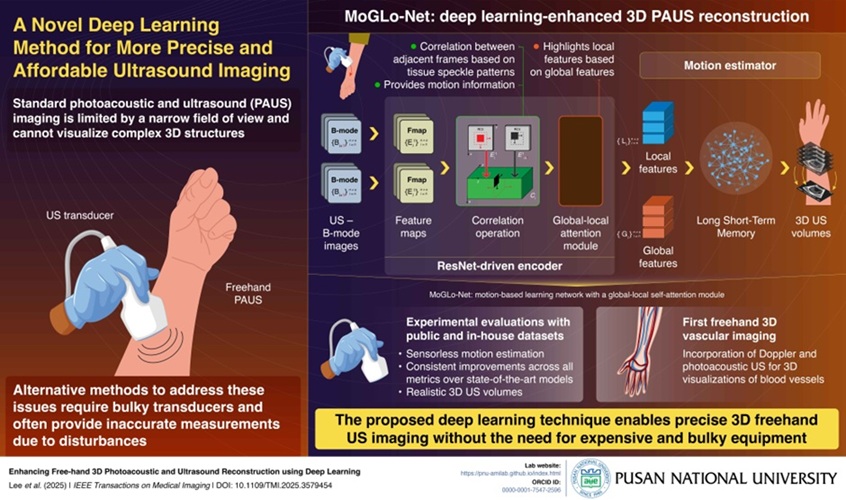
Breakthrough Deep Learning Model Enhances Handheld 3D Medical Imaging
Ultrasound imaging is a vital diagnostic technique used to visualize internal organs and tissues in real time and to guide procedures such as biopsies and injections. When paired with photoacoustic imaging... Read moreGeneral/Advanced Imaging
view channel
AI Algorithm Accurately Predicts Pancreatic Cancer Metastasis Using Routine CT Images
In pancreatic cancer, detecting whether the disease has spread to other organs is critical for determining whether surgery is appropriate. If metastasis is present, surgery is not recommended, yet current... Read more
Cutting-Edge Angio-CT Solution Offers New Therapeutic Possibilities
Maintaining accuracy and safety in interventional radiology is a constant challenge, especially as complex procedures require both high precision and efficiency. Traditional setups often involve multiple... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more
Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in medical diagnostics market is expanding with early disease detection being one of its key applications and image recognition becoming a compelling consumer proposition... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
GE HealthCare and NVIDIA Collaboration to Reimagine Diagnostic Imaging
GE HealthCare (Chicago, IL, USA) has entered into a collaboration with NVIDIA (Santa Clara, CA, USA), expanding the existing relationship between the two companies to focus on pioneering innovation in... Read more
Patient-Specific 3D-Printed Phantoms Transform CT Imaging
New research has highlighted how anatomically precise, patient-specific 3D-printed phantoms are proving to be scalable, cost-effective, and efficient tools in the development of new CT scan algorithms... Read more
Siemens and Sectra Collaborate on Enhancing Radiology Workflows
Siemens Healthineers (Forchheim, Germany) and Sectra (Linköping, Sweden) have entered into a collaboration aimed at enhancing radiologists' diagnostic capabilities and, in turn, improving patient care... Read more










 Guided Devices.jpg)