Single Room System Advances Proton Therapy Accessibility
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 17 Oct 2019 |
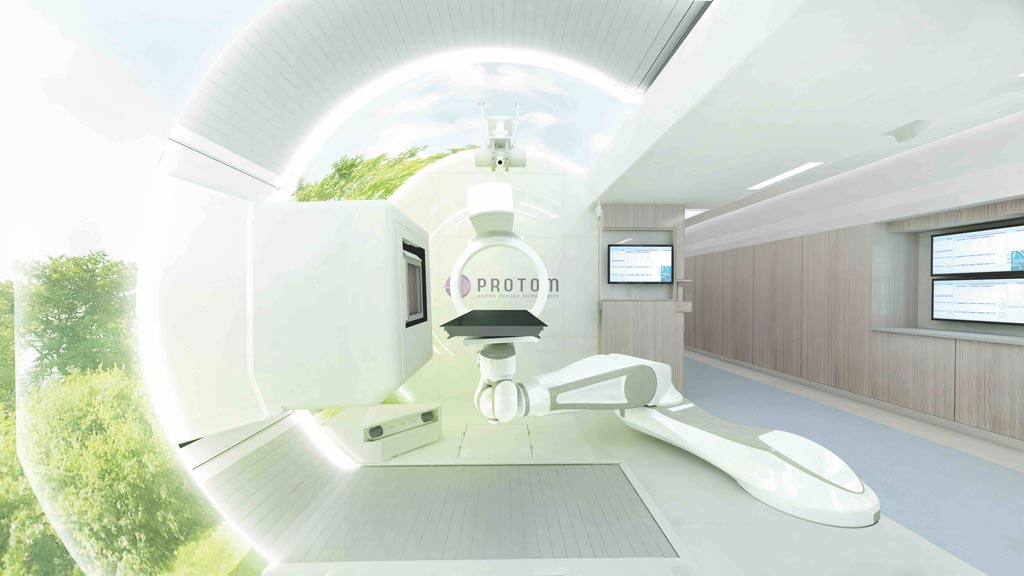
Image: The Radiance330 proton therapy system treatment room (Photo courtesy of ProTom International).
A compact proton therapy (PT) system equipped with advanced pencil beam scanning and integrated imaging and control systems expand the accessibility of PT.
The ProTom International (Wakefield, MA, USA) Radiance 330 proton therapy system boasts a compact synchrotron that serves as the source of the proton beam, composed of an injector that generates the proton beam and the synchrotron, which accumulates, accelerates, and extracts the proton beam. Depending on the configuration required, the transport and delivery sub-systems control the guidance, irradiation dose, and shape of the proton beam, and direct the beam appropriately. The Radiance 330 is installed at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH; Boston, USA).
The Radiance 330 is designed to interface with a range of in-room imaging solutions, such as computed tomography (CT) or cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT), and its 330 MeV capacity also allows for proton imaging of any anatomical area. An additional feature is orthogonal imaging, including image-registration software, which generates a six-degree of freedom patient-alignment correction vector. The compact system can be installed within an interior accelerator vault space of just 6 x 9 meters, and requires up to 40% less radiation shielding.
“ProTom is a company devoted to proton therapy as its sole mission; this is all we do. We thank our customers, partners, and suppliers for their confidence and support throughout this process,” said Steve Spotts, CEO and co-founder of ProTom International, upon receipt of U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) clearance. “This achievement accelerates ProTom's single and relentless mission to place this highly sophisticated and targeted cancer-fighting tool within reach of many more physicians.”
Photon radiation typically uses multiple X-ray beams to attack a tumor target, but unavoidably deposits radiation in the normal tissues beyond the target, potentially damaging those tissues as the beam exits the body. Proton therapy, an alternative radiation, works differently, by directing positively charged protons at the tumor target, where they deposit the bulk of the radiation dose, with minimal residual radiation delivered beyond the target, potentially reducing side effects and damage to surrounding tissue.
Related Links:
ProTom International
The ProTom International (Wakefield, MA, USA) Radiance 330 proton therapy system boasts a compact synchrotron that serves as the source of the proton beam, composed of an injector that generates the proton beam and the synchrotron, which accumulates, accelerates, and extracts the proton beam. Depending on the configuration required, the transport and delivery sub-systems control the guidance, irradiation dose, and shape of the proton beam, and direct the beam appropriately. The Radiance 330 is installed at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH; Boston, USA).
The Radiance 330 is designed to interface with a range of in-room imaging solutions, such as computed tomography (CT) or cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT), and its 330 MeV capacity also allows for proton imaging of any anatomical area. An additional feature is orthogonal imaging, including image-registration software, which generates a six-degree of freedom patient-alignment correction vector. The compact system can be installed within an interior accelerator vault space of just 6 x 9 meters, and requires up to 40% less radiation shielding.
“ProTom is a company devoted to proton therapy as its sole mission; this is all we do. We thank our customers, partners, and suppliers for their confidence and support throughout this process,” said Steve Spotts, CEO and co-founder of ProTom International, upon receipt of U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) clearance. “This achievement accelerates ProTom's single and relentless mission to place this highly sophisticated and targeted cancer-fighting tool within reach of many more physicians.”
Photon radiation typically uses multiple X-ray beams to attack a tumor target, but unavoidably deposits radiation in the normal tissues beyond the target, potentially damaging those tissues as the beam exits the body. Proton therapy, an alternative radiation, works differently, by directing positively charged protons at the tumor target, where they deposit the bulk of the radiation dose, with minimal residual radiation delivered beyond the target, potentially reducing side effects and damage to surrounding tissue.
Related Links:
ProTom International
Latest Nuclear Medicine News
- Radiopharmaceutical Molecule Marker to Improve Choice of Bladder Cancer Therapies
- Cancer “Flashlight” Shows Who Can Benefit from Targeted Treatments
- PET Imaging of Inflammation Predicts Recovery and Guides Therapy After Heart Attack
- Radiotheranostic Approach Detects, Kills and Reprograms Aggressive Cancers
- New Imaging Solution Improves Survival for Patients with Recurring Prostate Cancer
- PET Tracer Enables Same-Day Imaging of Triple-Negative Breast and Urothelial Cancers
- New Camera Sees Inside Human Body for Enhanced Scanning and Diagnosis
- Novel Bacteria-Specific PET Imaging Approach Detects Hard-To-Diagnose Lung Infections
- New Imaging Approach Could Reduce Need for Biopsies to Monitor Prostate Cancer
- Novel Radiolabeled Antibody Improves Diagnosis and Treatment of Solid Tumors
- Novel PET Imaging Approach Offers Never-Before-Seen View of Neuroinflammation
- Novel Radiotracer Identifies Biomarker for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
- Innovative PET Imaging Technique to Help Diagnose Neurodegeneration
- New Molecular Imaging Test to Improve Lung Cancer Diagnosis
- Novel PET Technique Visualizes Spinal Cord Injuries to Predict Recovery
- Next-Gen Tau Radiotracers Outperform FDA-Approved Imaging Agents in Detecting Alzheimer’s
Channels
Radiography
view channel
AI Tool Predicts Breast Cancer Risk Years Ahead Using Routine Mammograms
Breast cancer screening saves lives but still relies largely on uniform schedules despite wide differences in individual risk. This one-size-fits-all approach can miss cancers in higher-risk women while... Read more
Routine Mammograms Could Predict Future Cardiovascular Disease in Women
Mammograms are widely used to screen for breast cancer, but they may also contain overlooked clues about cardiovascular health. Calcium deposits in the arteries of the breast signal stiffening blood vessels,... Read moreMRI
view channel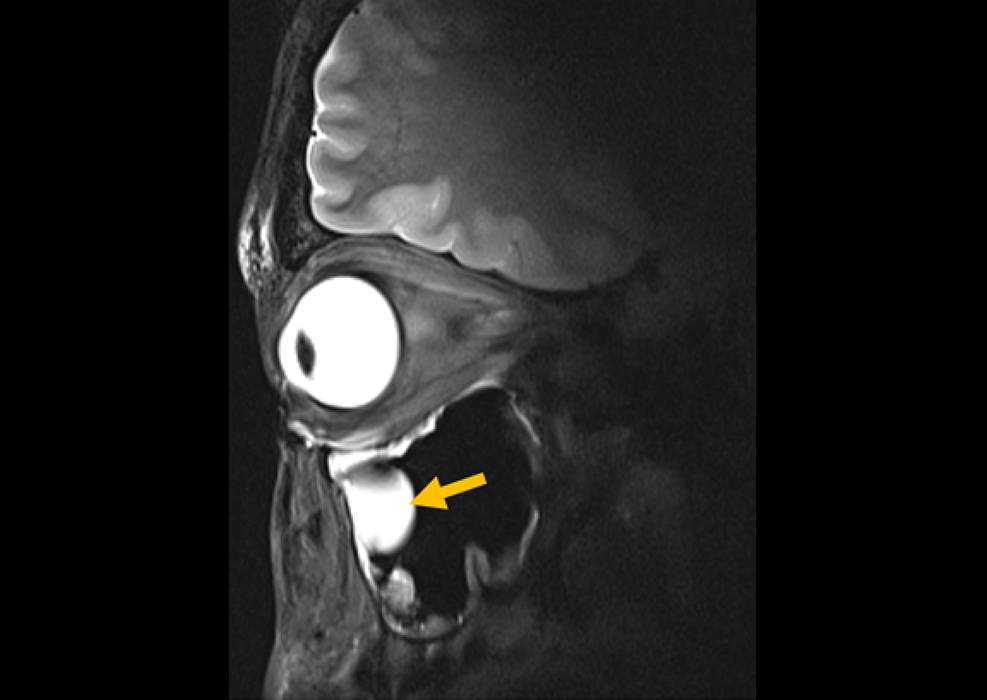
New Material Boosts MRI Image Quality
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a cornerstone of modern diagnostics, yet certain deep or anatomically complex tissues, including delicate structures of the eye and orbit, remain difficult to visualize clearly.... Read more
AI Model Reads and Diagnoses Brain MRI in Seconds
Brain MRI scans are critical for diagnosing strokes, hemorrhages, and other neurological disorders, but interpreting them can take hours or even days due to growing demand and limited specialist availability.... Read moreMRI Scan Breakthrough to Help Avoid Risky Invasive Tests for Heart Patients
Heart failure patients often require right heart catheterization to assess how severely their heart is struggling to pump blood, a procedure that involves inserting a tube into the heart to measure blood... Read more
MRI Scans Reveal Signature Patterns of Brain Activity to Predict Recovery from TBI
Recovery after traumatic brain injury (TBI) varies widely, with some patients regaining full function while others are left with lasting disabilities. Prognosis is especially difficult to assess in patients... Read moreUltrasound
view channel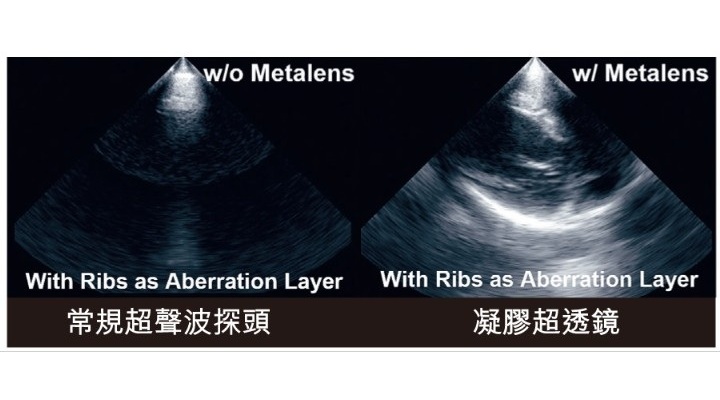
Groundbreaking Technology to Enhance Precision in Emergency and Critical Care
Rapid and accurate imaging is essential for diagnosing life-threatening conditions such as myocardial infarction, heart failure, and pulmonary embolism. However, conventional ultrasound imaging of the... Read more
Reusable Gel Pad Made from Tamarind Seed Could Transform Ultrasound Examinations
Ultrasound imaging depends on a conductive gel to eliminate air between the probe and the skin so sound waves can pass clearly into the body. While the imaging technology is fast, safe, and noninvasive,... Read moreGeneral/Advanced Imaging
view channel
AI Tool Predicts Side Effects from Lung Cancer Treatment
Radiation therapy is a central treatment for lung cancer, but even carefully targeted radiation can affect surrounding healthy tissue. Patients may develop side effects such as lung inflammation, coughing,... Read more
AI Tool Offers Prognosis for Patients with Head and Neck Cancer
Oropharyngeal cancer is a form of head and neck cancer that can spread through lymph nodes, significantly affecting survival and treatment decisions. Current therapies often involve combinations of surgery,... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more
Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in medical diagnostics market is expanding with early disease detection being one of its key applications and image recognition becoming a compelling consumer proposition... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
Nuclear Medicine Set for Continued Growth Driven by Demand for Precision Diagnostics
Clinical imaging services face rising demand for precise molecular diagnostics and targeted radiopharmaceutical therapy as cancer and chronic disease rates climb. A new market analysis projects rapid expansion... Read more




















