Intraoperative Holographics Support Cardiac Procedures
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 08 Oct 2019 |
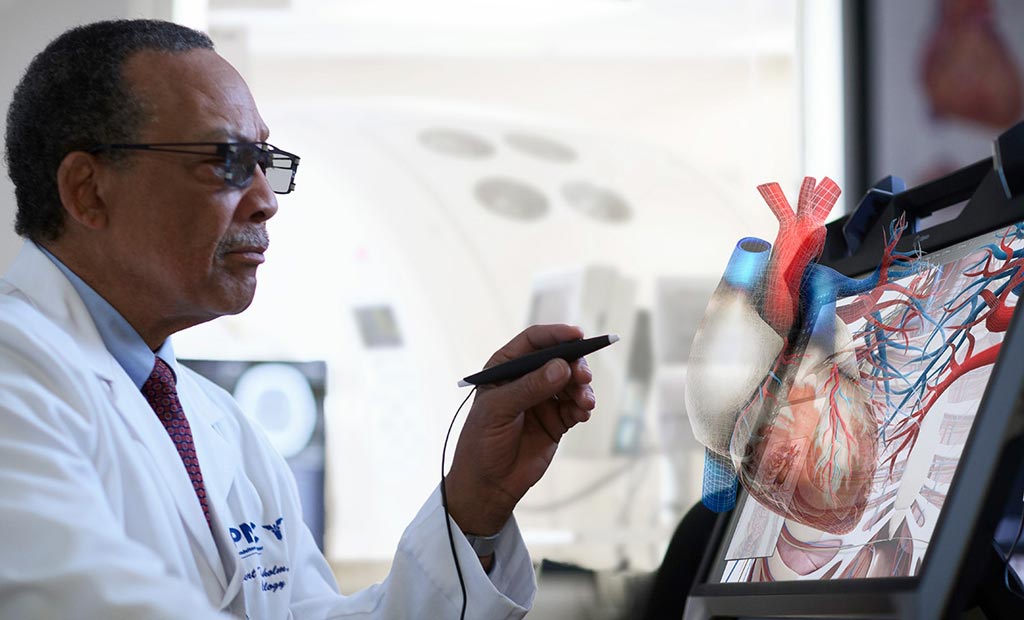
Image: VR glasses and an electronic scribe help manipulate a holographic heart (Photo courtesy of EchoPixel).
A novel intraoperative software suite provides naked-eye, touchless, and interactive three-dimensional (3D) anatomical imaging to enhance structural heart procedures.
The EchoPixel (Santa Clara, CA, USA) True3D anatomical imaging tools are designed to provide clinicians with a holographic experience by using special virtual reality (VR) glasses that help them visualize and interact with patient-specific organs and tissue, just as they would with physical objects in the real world. This allows for enhanced pre-operative planning, improved patient selection, increased patient engagement, and the completion of increasingly complex structural heart and congenital heart disease procedures in both adults and pediatric patients in shorter timeframes.
The interactive VR software leverages computerized tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), C-Arm fluoroscopy images, and echocardiography to create life-size holographic versions of organs, blood vessels, and other structures. This allows physicians to interact with a digital twin of the patient specific anatomy to identify optimal treatment target, approach, and catheter position, capture accurate measurements, distances, and angles, and virtually try in and fit implants and cardiac devices. The enhanced visualization of anatomical structures and spatial relationships also facilitate completion of procedures with reproducible, reliable outcomes.
“Building on the success of our existing technology in pediatric congenital heart procedures, EchoPixel is committed to enabling digital surgery, providing and continuously improving transformative technology designed to help clinicians improve and personalize delivery of minimally invasive therapies,” said Sergio Aguirre, CEO of EchoPixel. “Going forward, our vision for the OR of the future involves expanding our mixed reality True3D software platform to integrate AI and robotics to enable the completion of more precise and personalized procedures.”
“EchoPixel's technology lets you effortlessly interact with 3D images to better understand complex cardiac anatomy and the anatomic variability that is commonly seen in structural heart disease patients,” said Saurabh Sanon, MD, of Florida Atlantic University (Boca Raton, USA). “We are currently working on a research study comparing procedure times with and without the technology, and the initial results are promising in terms of reducing procedure times and device waste.”
In order to successfully identify an area of interest from a 3D medical data set, as those produced by CT, MRI and other devices, doctors are required to mentally integrate a series of 2D images and cognitively extract the relevant relationships that define the tissue or organ of interest, as well as its neighboring anatomy. In complex cases, they must visually map multiple views of the same data to find appropriate correspondences of one view with another view to produce a match, and determine if what they see is the tissue they want to evaluate.
Related Links:
EchoPixel
Florida Atlantic University
The EchoPixel (Santa Clara, CA, USA) True3D anatomical imaging tools are designed to provide clinicians with a holographic experience by using special virtual reality (VR) glasses that help them visualize and interact with patient-specific organs and tissue, just as they would with physical objects in the real world. This allows for enhanced pre-operative planning, improved patient selection, increased patient engagement, and the completion of increasingly complex structural heart and congenital heart disease procedures in both adults and pediatric patients in shorter timeframes.
The interactive VR software leverages computerized tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), C-Arm fluoroscopy images, and echocardiography to create life-size holographic versions of organs, blood vessels, and other structures. This allows physicians to interact with a digital twin of the patient specific anatomy to identify optimal treatment target, approach, and catheter position, capture accurate measurements, distances, and angles, and virtually try in and fit implants and cardiac devices. The enhanced visualization of anatomical structures and spatial relationships also facilitate completion of procedures with reproducible, reliable outcomes.
“Building on the success of our existing technology in pediatric congenital heart procedures, EchoPixel is committed to enabling digital surgery, providing and continuously improving transformative technology designed to help clinicians improve and personalize delivery of minimally invasive therapies,” said Sergio Aguirre, CEO of EchoPixel. “Going forward, our vision for the OR of the future involves expanding our mixed reality True3D software platform to integrate AI and robotics to enable the completion of more precise and personalized procedures.”
“EchoPixel's technology lets you effortlessly interact with 3D images to better understand complex cardiac anatomy and the anatomic variability that is commonly seen in structural heart disease patients,” said Saurabh Sanon, MD, of Florida Atlantic University (Boca Raton, USA). “We are currently working on a research study comparing procedure times with and without the technology, and the initial results are promising in terms of reducing procedure times and device waste.”
In order to successfully identify an area of interest from a 3D medical data set, as those produced by CT, MRI and other devices, doctors are required to mentally integrate a series of 2D images and cognitively extract the relevant relationships that define the tissue or organ of interest, as well as its neighboring anatomy. In complex cases, they must visually map multiple views of the same data to find appropriate correspondences of one view with another view to produce a match, and determine if what they see is the tissue they want to evaluate.
Related Links:
EchoPixel
Florida Atlantic University
Latest General/Advanced Imaging News
- AI-Powered Imaging System Improves Lung Cancer Diagnosis
- AI Model Significantly Enhances Low-Dose CT Capabilities
- Ultra-Low Dose CT Aids Pneumonia Diagnosis in Immunocompromised Patients
- AI Reduces CT Lung Cancer Screening Workload by Almost 80%
- Cutting-Edge Technology Combines Light and Sound for Real-Time Stroke Monitoring
- AI System Detects Subtle Changes in Series of Medical Images Over Time
- New CT Scan Technique to Improve Prognosis and Treatments for Head and Neck Cancers
- World’s First Mobile Whole-Body CT Scanner to Provide Diagnostics at POC
- Comprehensive CT Scans Could Identify Atherosclerosis Among Lung Cancer Patients
- AI Improves Detection of Colorectal Cancer on Routine Abdominopelvic CT Scans
- Super-Resolution Technology Enhances Clinical Bone Imaging to Predict Osteoporotic Fracture Risk
- AI-Powered Abdomen Map Enables Early Cancer Detection
- Deep Learning Model Detects Lung Tumors on CT
- AI Predicts Cardiovascular Risk from CT Scans
- Deep Learning Based Algorithms Improve Tumor Detection in PET/CT Scans
- New Technology Provides Coronary Artery Calcification Scoring on Ungated Chest CT Scans
Channels
Radiography
view channel
World's Largest Class Single Crystal Diamond Radiation Detector Opens New Possibilities for Diagnostic Imaging
Diamonds possess ideal physical properties for radiation detection, such as exceptional thermal and chemical stability along with a quick response time. Made of carbon with an atomic number of six, diamonds... Read more
AI-Powered Imaging Technique Shows Promise in Evaluating Patients for PCI
Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), also known as coronary angioplasty, is a minimally invasive procedure where small metal tubes called stents are inserted into partially blocked coronary arteries... Read moreMRI
view channel
AI Tool Tracks Effectiveness of Multiple Sclerosis Treatments Using Brain MRI Scans
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a condition in which the immune system attacks the brain and spinal cord, leading to impairments in movement, sensation, and cognition. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) markers... Read more
Ultra-Powerful MRI Scans Enable Life-Changing Surgery in Treatment-Resistant Epileptic Patients
Approximately 360,000 individuals in the UK suffer from focal epilepsy, a condition in which seizures spread from one part of the brain. Around a third of these patients experience persistent seizures... Read more
AI-Powered MRI Technology Improves Parkinson’s Diagnoses
Current research shows that the accuracy of diagnosing Parkinson’s disease typically ranges from 55% to 78% within the first five years of assessment. This is partly due to the similarities shared by Parkinson’s... Read more
Biparametric MRI Combined with AI Enhances Detection of Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer
Artificial intelligence (AI) technologies are transforming the way medical images are analyzed, offering unprecedented capabilities in quantitatively extracting features that go beyond traditional visual... Read moreUltrasound
view channel.jpeg)
AI-Powered Lung Ultrasound Outperforms Human Experts in Tuberculosis Diagnosis
Despite global declines in tuberculosis (TB) rates in previous years, the incidence of TB rose by 4.6% from 2020 to 2023. Early screening and rapid diagnosis are essential elements of the World Health... Read more
AI Identifies Heart Valve Disease from Common Imaging Test
Tricuspid regurgitation is a condition where the heart's tricuspid valve does not close completely during contraction, leading to backward blood flow, which can result in heart failure. A new artificial... Read moreNuclear Medicine
view channel
Novel PET Imaging Approach Offers Never-Before-Seen View of Neuroinflammation
COX-2, an enzyme that plays a key role in brain inflammation, can be significantly upregulated by inflammatory stimuli and neuroexcitation. Researchers suggest that COX-2 density in the brain could serve... Read more
Novel Radiotracer Identifies Biomarker for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC), which represents 15-20% of all breast cancer cases, is one of the most aggressive subtypes, with a five-year survival rate of about 40%. Due to its significant heterogeneity... Read moreGeneral/Advanced Imaging
view channel
AI-Powered Imaging System Improves Lung Cancer Diagnosis
Given the need to detect lung cancer at earlier stages, there is an increasing need for a definitive diagnostic pathway for patients with suspicious pulmonary nodules. However, obtaining tissue samples... Read more
AI Model Significantly Enhances Low-Dose CT Capabilities
Lung cancer remains one of the most challenging diseases, making early diagnosis vital for effective treatment. Fortunately, advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) are revolutionizing lung cancer... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more
Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in medical diagnostics market is expanding with early disease detection being one of its key applications and image recognition becoming a compelling consumer proposition... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
GE HealthCare and NVIDIA Collaboration to Reimagine Diagnostic Imaging
GE HealthCare (Chicago, IL, USA) has entered into a collaboration with NVIDIA (Santa Clara, CA, USA), expanding the existing relationship between the two companies to focus on pioneering innovation in... Read more
Patient-Specific 3D-Printed Phantoms Transform CT Imaging
New research has highlighted how anatomically precise, patient-specific 3D-printed phantoms are proving to be scalable, cost-effective, and efficient tools in the development of new CT scan algorithms... Read more
Siemens and Sectra Collaborate on Enhancing Radiology Workflows
Siemens Healthineers (Forchheim, Germany) and Sectra (Linköping, Sweden) have entered into a collaboration aimed at enhancing radiologists' diagnostic capabilities and, in turn, improving patient care... Read more




















