New AI Algorithm Enhances Polyp Detection in Colonoscopy Procedures
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 23 Nov 2018 |
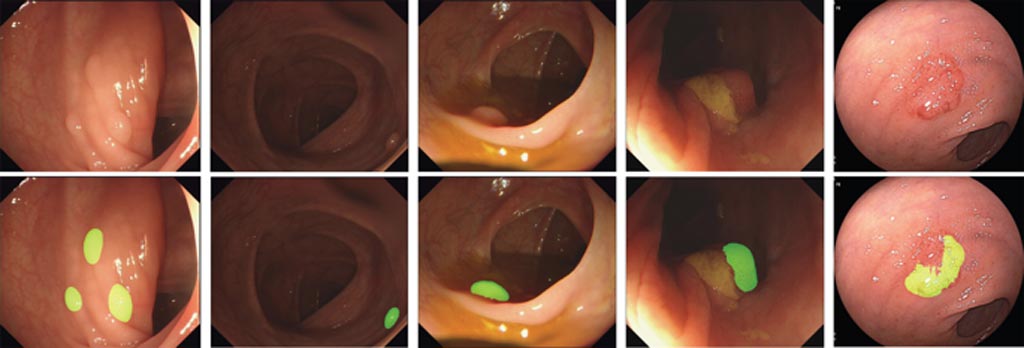
Image: The Wision AI algorithm highlights polyps on the monitor, enhancing detection (bottom) (Photo courtesy of Shanghai Wision AI).
Researchers at Shanghai Wision AI Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China), a developer of computer-aided diagnostic algorithms and systems to improve the accuracy and effectiveness of diagnostic imaging, have announced results of a study validating a novel machine-learning algorithm that improves detection of adenomatous polyps during colonoscopy. The AI algorithm is built on the same network architecture that is used to develop self-driving cars and is designed to enable “self-driving” in colonoscopy procedures.
The Wision AI algorithm was validated on large, prospectively developed datasets collected independently from the training dataset that were several-fold larger than the training dataset. This more rigorous validation approach utilized by Wision AI is meant to increase the performance of the algorithm in real-world clinical settings.
The algorithm was developed using 5,545 images (65.5% containing polyps and 34.5% without polyps) from the colonoscopy reports of 1,290 patients. Experienced endoscopists annotated the presence of polyps in all images used in the development dataset, and the algorithm was then validated on four independent datasets: two sets for image analysis (A and B) and two sets for video analysis (C and D). According to the study’s key findings, validation on dataset A, which included 27,113 images from patients undergoing colonoscopy at the Endoscopy Center of Sichuan Provincial People’s Hospital, found a per-image-sensitivity of 94.4% and a per-image-specificity of 95.9%. The per-image-sensitivity in a subset of 1,280 images with polyps that are typically hard to detect was 91.7%.
Validation on dataset B, based on a public database of 612 colonoscopy images acquired from the Hospital Clinic of Barcelona, found a per-image-sensitivity of 88.2%. The use of this dataset allowed for generalization of the validation data to a broader patient population. Validation on dataset C included a series of colonoscopy videos containing 138 polyps, found a per-image sensitivity of 91.6% among 60,914 frames of video, and a per-polyp sensitivity of 100%. Validation on dataset D, which contained 54 colonoscopy videos without any polyps, found a per-image-specificity of 95.4% among 1,072,483 frames. The total processing time for each image frame was 76.8 milliseconds, including preprocessing and displaying times before and after execution of the deep-learning algorithm. Implementation in a real-time system resulted in a processing rate of 30 frames per second with Nvidia Titan X GPUs.
Based on these findings, the researchers concluded that the automatic polyp-detection system based on deep learning has a high overall performance in both colonoscopy images and real-time videos.
“The results of this study demonstrate the power of our rigorous approach to developing deep-learning algorithms, which utilizes distinct datasets for training and validation and results in high levels of specificity and sensitivity that have the potential to improve diagnostic screening methods that are known to reduce disease risk, improve health outcomes and save lives,” said JingJia Liu, CEO at Wision AI.
Related Links:
Shanghai Wision AI
The Wision AI algorithm was validated on large, prospectively developed datasets collected independently from the training dataset that were several-fold larger than the training dataset. This more rigorous validation approach utilized by Wision AI is meant to increase the performance of the algorithm in real-world clinical settings.
The algorithm was developed using 5,545 images (65.5% containing polyps and 34.5% without polyps) from the colonoscopy reports of 1,290 patients. Experienced endoscopists annotated the presence of polyps in all images used in the development dataset, and the algorithm was then validated on four independent datasets: two sets for image analysis (A and B) and two sets for video analysis (C and D). According to the study’s key findings, validation on dataset A, which included 27,113 images from patients undergoing colonoscopy at the Endoscopy Center of Sichuan Provincial People’s Hospital, found a per-image-sensitivity of 94.4% and a per-image-specificity of 95.9%. The per-image-sensitivity in a subset of 1,280 images with polyps that are typically hard to detect was 91.7%.
Validation on dataset B, based on a public database of 612 colonoscopy images acquired from the Hospital Clinic of Barcelona, found a per-image-sensitivity of 88.2%. The use of this dataset allowed for generalization of the validation data to a broader patient population. Validation on dataset C included a series of colonoscopy videos containing 138 polyps, found a per-image sensitivity of 91.6% among 60,914 frames of video, and a per-polyp sensitivity of 100%. Validation on dataset D, which contained 54 colonoscopy videos without any polyps, found a per-image-specificity of 95.4% among 1,072,483 frames. The total processing time for each image frame was 76.8 milliseconds, including preprocessing and displaying times before and after execution of the deep-learning algorithm. Implementation in a real-time system resulted in a processing rate of 30 frames per second with Nvidia Titan X GPUs.
Based on these findings, the researchers concluded that the automatic polyp-detection system based on deep learning has a high overall performance in both colonoscopy images and real-time videos.
“The results of this study demonstrate the power of our rigorous approach to developing deep-learning algorithms, which utilizes distinct datasets for training and validation and results in high levels of specificity and sensitivity that have the potential to improve diagnostic screening methods that are known to reduce disease risk, improve health outcomes and save lives,” said JingJia Liu, CEO at Wision AI.
Related Links:
Shanghai Wision AI
Latest Industry News News
- GE HealthCare and NVIDIA Collaboration to Reimagine Diagnostic Imaging
- Patient-Specific 3D-Printed Phantoms Transform CT Imaging
- Siemens and Sectra Collaborate on Enhancing Radiology Workflows
- Bracco Diagnostics and ColoWatch Partner to Expand Availability CRC Screening Tests Using Virtual Colonoscopy
- Mindray Partners with TeleRay to Streamline Ultrasound Delivery
- Philips and Medtronic Partner on Stroke Care
- Siemens and Medtronic Enter into Global Partnership for Advancing Spine Care Imaging Technologies
- RSNA 2024 Technical Exhibits to Showcase Latest Advances in Radiology
- Bracco Collaborates with Arrayus on Microbubble-Assisted Focused Ultrasound Therapy for Pancreatic Cancer
- Innovative Collaboration to Enhance Ischemic Stroke Detection and Elevate Standards in Diagnostic Imaging
- RSNA 2024 Registration Opens
- Microsoft collaborates with Leading Academic Medical Systems to Advance AI in Medical Imaging
- GE HealthCare Acquires Intelligent Ultrasound Group’s Clinical Artificial Intelligence Business
- Bayer and Rad AI Collaborate on Expanding Use of Cutting Edge AI Radiology Operational Solutions
- Polish Med-Tech Company BrainScan to Expand Extensively into Foreign Markets
- Hologic Acquires UK-Based Breast Surgical Guidance Company Endomagnetics Ltd.
Channels
Radiography
view channel
AI-Powered Imaging Technique Shows Promise in Evaluating Patients for PCI
Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), also known as coronary angioplasty, is a minimally invasive procedure where small metal tubes called stents are inserted into partially blocked coronary arteries... Read more
Higher Chest X-Ray Usage Catches Lung Cancer Earlier and Improves Survival
Lung cancer continues to be the leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide. While advanced technologies like CT scanners play a crucial role in detecting lung cancer, more accessible and affordable... Read moreMRI
view channel
Ultra-Powerful MRI Scans Enable Life-Changing Surgery in Treatment-Resistant Epileptic Patients
Approximately 360,000 individuals in the UK suffer from focal epilepsy, a condition in which seizures spread from one part of the brain. Around a third of these patients experience persistent seizures... Read more
AI-Powered MRI Technology Improves Parkinson’s Diagnoses
Current research shows that the accuracy of diagnosing Parkinson’s disease typically ranges from 55% to 78% within the first five years of assessment. This is partly due to the similarities shared by Parkinson’s... Read more
Biparametric MRI Combined with AI Enhances Detection of Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer
Artificial intelligence (AI) technologies are transforming the way medical images are analyzed, offering unprecedented capabilities in quantitatively extracting features that go beyond traditional visual... Read more
First-Of-Its-Kind AI-Driven Brain Imaging Platform to Better Guide Stroke Treatment Options
Each year, approximately 800,000 people in the U.S. experience strokes, with marginalized and minoritized groups being disproportionately affected. Strokes vary in terms of size and location within the... Read moreUltrasound
view channel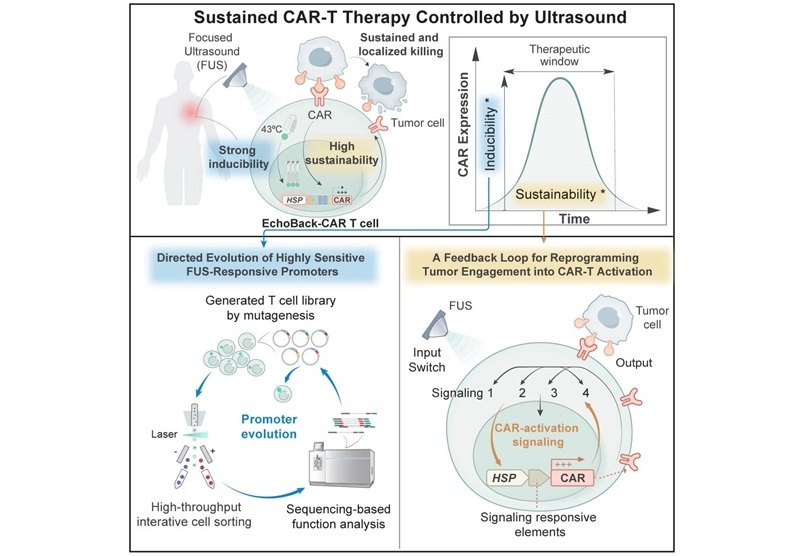
Smart Ultrasound-Activated Immune Cells Destroy Cancer Cells for Extended Periods
Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy has emerged as a highly promising cancer treatment, especially for bloodborne cancers like leukemia. This highly personalized therapy involves extracting... Read more
Tiny Magnetic Robot Takes 3D Scans from Deep Within Body
Colorectal cancer ranks as one of the leading causes of cancer-related mortality worldwide. However, when detected early, it is highly treatable. Now, a new minimally invasive technique could significantly... Read more
High Resolution Ultrasound Speeds Up Prostate Cancer Diagnosis
Each year, approximately one million prostate cancer biopsies are conducted across Europe, with similar numbers in the USA and around 100,000 in Canada. Most of these biopsies are performed using MRI images... Read more
World's First Wireless, Handheld, Whole-Body Ultrasound with Single PZT Transducer Makes Imaging More Accessible
Ultrasound devices play a vital role in the medical field, routinely used to examine the body's internal tissues and structures. While advancements have steadily improved ultrasound image quality and processing... Read moreNuclear Medicine
view channel
Novel PET Imaging Approach Offers Never-Before-Seen View of Neuroinflammation
COX-2, an enzyme that plays a key role in brain inflammation, can be significantly upregulated by inflammatory stimuli and neuroexcitation. Researchers suggest that COX-2 density in the brain could serve... Read more
Novel Radiotracer Identifies Biomarker for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC), which represents 15-20% of all breast cancer cases, is one of the most aggressive subtypes, with a five-year survival rate of about 40%. Due to its significant heterogeneity... Read moreGeneral/Advanced Imaging
view channel
AI-Powered Imaging System Improves Lung Cancer Diagnosis
Given the need to detect lung cancer at earlier stages, there is an increasing need for a definitive diagnostic pathway for patients with suspicious pulmonary nodules. However, obtaining tissue samples... Read more
AI Model Significantly Enhances Low-Dose CT Capabilities
Lung cancer remains one of the most challenging diseases, making early diagnosis vital for effective treatment. Fortunately, advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) are revolutionizing lung cancer... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more










 Guided Devices.jpg)