Post-Mortem CT Angiography Increases Forensic Accuracy
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 04 Jul 2018 |
Image: A new study suggests post-mortem CT angiography helps uncover causes of death (Photo courtesy of Royal Preston Hospital).
A new study suggests that post-mortem CT angiography (PMCTA) can detect 90% of incidental findings, while autopsy finds only 61%.
Researchers at the University Center of Legal Medicine Lausanne-Geneva (CURML; Switzerland), the University of Leipzig (Germany), and other institutions conducted an autopsy study on 500 human corpses to determine if computed tomography (CT) and PMCTA could help to detect more lesions than autopsy alone, to evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of each method, and to define their indications. All images were read by an experienced team including one forensic pathologist and one radiologist blinded to the autopsy results.
The results revealed that among 18,654 findings, autopsies identified 61.3%, postmortem CT helped to identify 76%, and PMCTA helped identify 89.9%. PMCTA was superior to autopsy, especially at helping to identify essential skeletal and vascular lesions. Among the forensically essential findings, 23.4% were not detected at autopsy, while only 9.7% were missed at PMCTA. The best results were obtained when PMCTA was combined with autopsy. The study was published on May 1, 2018, in Radiology.
“The idea of the PMCTA is to simulate a post-mortem circulation. The heart is ‘replaced’ by a perfusion device, similar to the heart-lung machine that replaces the heart during heart surgery,” said lead author Silke Grabherr, MD, PhD, of CURML. “This method could, in many cases, be an alternative to invasive autopsy if such an opening of the body is not possible. This offers new investigation possibilities, for example, in countries where a conventional autopsy is not accepted or in cases where family members can refuse it.”
“The combination of bone lesions and vascular lesions is especially seen in cases of traumatic death, such as falls from height, traffic accidents, ballistic trauma, and sharp trauma in homicides and suicides,” concluded Dr. Grabherr. “This means that PMCTA is an excellent choice to investigate such cases, and can be used combined with or even independently of conventional autopsy for investigating in these cases.”
Compared with conventional autopsy, postmortem CT has several advantages, but the main reported weakness is relatively low soft-tissue contrast, especially in organ parenchyma, and poor ability to view the vascular system. This limitation can be overcome by using a scanning protocol and specific perfusion devices, with an intravenous oil-based contrast agent of specific viscosity. The most widespread single approach for postmortem angiography today is multiphase PMCTA.
Related Links:
University Center of Legal Medicine Lausanne-Geneva
University of Leipzig
Researchers at the University Center of Legal Medicine Lausanne-Geneva (CURML; Switzerland), the University of Leipzig (Germany), and other institutions conducted an autopsy study on 500 human corpses to determine if computed tomography (CT) and PMCTA could help to detect more lesions than autopsy alone, to evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of each method, and to define their indications. All images were read by an experienced team including one forensic pathologist and one radiologist blinded to the autopsy results.
The results revealed that among 18,654 findings, autopsies identified 61.3%, postmortem CT helped to identify 76%, and PMCTA helped identify 89.9%. PMCTA was superior to autopsy, especially at helping to identify essential skeletal and vascular lesions. Among the forensically essential findings, 23.4% were not detected at autopsy, while only 9.7% were missed at PMCTA. The best results were obtained when PMCTA was combined with autopsy. The study was published on May 1, 2018, in Radiology.
“The idea of the PMCTA is to simulate a post-mortem circulation. The heart is ‘replaced’ by a perfusion device, similar to the heart-lung machine that replaces the heart during heart surgery,” said lead author Silke Grabherr, MD, PhD, of CURML. “This method could, in many cases, be an alternative to invasive autopsy if such an opening of the body is not possible. This offers new investigation possibilities, for example, in countries where a conventional autopsy is not accepted or in cases where family members can refuse it.”
“The combination of bone lesions and vascular lesions is especially seen in cases of traumatic death, such as falls from height, traffic accidents, ballistic trauma, and sharp trauma in homicides and suicides,” concluded Dr. Grabherr. “This means that PMCTA is an excellent choice to investigate such cases, and can be used combined with or even independently of conventional autopsy for investigating in these cases.”
Compared with conventional autopsy, postmortem CT has several advantages, but the main reported weakness is relatively low soft-tissue contrast, especially in organ parenchyma, and poor ability to view the vascular system. This limitation can be overcome by using a scanning protocol and specific perfusion devices, with an intravenous oil-based contrast agent of specific viscosity. The most widespread single approach for postmortem angiography today is multiphase PMCTA.
Related Links:
University Center of Legal Medicine Lausanne-Geneva
University of Leipzig
Latest General/Advanced Imaging News
- AI-Powered Imaging System Improves Lung Cancer Diagnosis
- AI Model Significantly Enhances Low-Dose CT Capabilities
- Ultra-Low Dose CT Aids Pneumonia Diagnosis in Immunocompromised Patients
- AI Reduces CT Lung Cancer Screening Workload by Almost 80%
- Cutting-Edge Technology Combines Light and Sound for Real-Time Stroke Monitoring
- AI System Detects Subtle Changes in Series of Medical Images Over Time
- New CT Scan Technique to Improve Prognosis and Treatments for Head and Neck Cancers
- World’s First Mobile Whole-Body CT Scanner to Provide Diagnostics at POC
- Comprehensive CT Scans Could Identify Atherosclerosis Among Lung Cancer Patients
- AI Improves Detection of Colorectal Cancer on Routine Abdominopelvic CT Scans
- Super-Resolution Technology Enhances Clinical Bone Imaging to Predict Osteoporotic Fracture Risk
- AI-Powered Abdomen Map Enables Early Cancer Detection
- Deep Learning Model Detects Lung Tumors on CT
- AI Predicts Cardiovascular Risk from CT Scans
- Deep Learning Based Algorithms Improve Tumor Detection in PET/CT Scans
- New Technology Provides Coronary Artery Calcification Scoring on Ungated Chest CT Scans
Channels
Radiography
view channel
World's Largest Class Single Crystal Diamond Radiation Detector Opens New Possibilities for Diagnostic Imaging
Diamonds possess ideal physical properties for radiation detection, such as exceptional thermal and chemical stability along with a quick response time. Made of carbon with an atomic number of six, diamonds... Read more
AI-Powered Imaging Technique Shows Promise in Evaluating Patients for PCI
Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), also known as coronary angioplasty, is a minimally invasive procedure where small metal tubes called stents are inserted into partially blocked coronary arteries... Read moreMRI
view channel
AI Tool Tracks Effectiveness of Multiple Sclerosis Treatments Using Brain MRI Scans
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a condition in which the immune system attacks the brain and spinal cord, leading to impairments in movement, sensation, and cognition. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) markers... Read more
Ultra-Powerful MRI Scans Enable Life-Changing Surgery in Treatment-Resistant Epileptic Patients
Approximately 360,000 individuals in the UK suffer from focal epilepsy, a condition in which seizures spread from one part of the brain. Around a third of these patients experience persistent seizures... Read more
AI-Powered MRI Technology Improves Parkinson’s Diagnoses
Current research shows that the accuracy of diagnosing Parkinson’s disease typically ranges from 55% to 78% within the first five years of assessment. This is partly due to the similarities shared by Parkinson’s... Read more
Biparametric MRI Combined with AI Enhances Detection of Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer
Artificial intelligence (AI) technologies are transforming the way medical images are analyzed, offering unprecedented capabilities in quantitatively extracting features that go beyond traditional visual... Read moreUltrasound
view channel
Ultrasound-Based Microscopy Technique to Help Diagnose Small Vessel Diseases
Clinical ultrasound, commonly used in pregnancy scans, provides real-time images of body structures. It is one of the most widely used imaging techniques in medicine, but until recently, it had little... Read more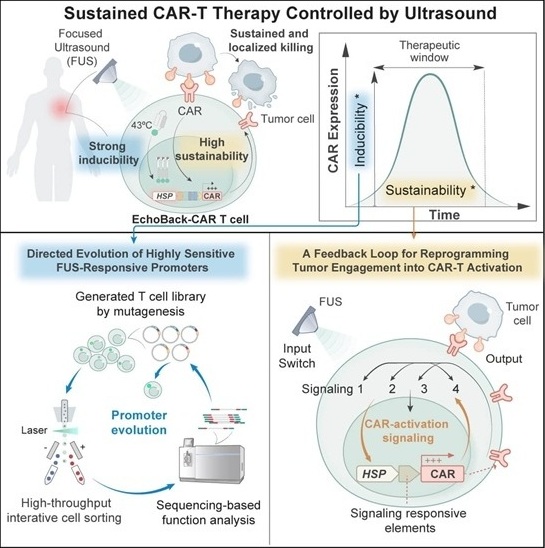
Smart Ultrasound-Activated Immune Cells Destroy Cancer Cells for Extended Periods
Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy has emerged as a highly promising cancer treatment, especially for bloodborne cancers like leukemia. This highly personalized therapy involves extracting... Read moreNuclear Medicine
view channel
Novel PET Imaging Approach Offers Never-Before-Seen View of Neuroinflammation
COX-2, an enzyme that plays a key role in brain inflammation, can be significantly upregulated by inflammatory stimuli and neuroexcitation. Researchers suggest that COX-2 density in the brain could serve... Read more
Novel Radiotracer Identifies Biomarker for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC), which represents 15-20% of all breast cancer cases, is one of the most aggressive subtypes, with a five-year survival rate of about 40%. Due to its significant heterogeneity... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more
Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in medical diagnostics market is expanding with early disease detection being one of its key applications and image recognition becoming a compelling consumer proposition... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
GE HealthCare and NVIDIA Collaboration to Reimagine Diagnostic Imaging
GE HealthCare (Chicago, IL, USA) has entered into a collaboration with NVIDIA (Santa Clara, CA, USA), expanding the existing relationship between the two companies to focus on pioneering innovation in... Read more
Patient-Specific 3D-Printed Phantoms Transform CT Imaging
New research has highlighted how anatomically precise, patient-specific 3D-printed phantoms are proving to be scalable, cost-effective, and efficient tools in the development of new CT scan algorithms... Read more
Siemens and Sectra Collaborate on Enhancing Radiology Workflows
Siemens Healthineers (Forchheim, Germany) and Sectra (Linköping, Sweden) have entered into a collaboration aimed at enhancing radiologists' diagnostic capabilities and, in turn, improving patient care... Read more