Researchers Develop PET Probe to Assist Pulmonary Fibrosis Patients
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 12 Apr 2017 |
Researchers have developed a Positron Emission Tomography (PET) imaging probe that can help diagnose and stage pulmonary fibrosis.
Pulmonary fibrosis is a lung disease that may in part be caused by exposure of patients to pollutants, or from other diseases, and causes the buildup of scar tissue. This stiffens the lung tissue and restricts oxygen absorption and breathing. The condition can lead to death in patients between three and five years.
The researchers from the Massachusetts General Hospital published their results in the April 2017 issue of the journal Science Translational Medicine.
The collagen-targeting probe, called 68Ga-CBP8, was able to bind to the lung scar tissue of animal models indicating the extent of fibrosis. The researchers also showed how fibrosis could be reduced in animals using an anti-fibrotic drug. The researchers also used human lung tissue, and found that the probe could differentiate between stable pulmonary fibrosis and progressive fibrosis.
Experiments using another model showed that there was increased uptake of the probe in areas where there was more extensive fibrosis. This model was also able to track disease progression over time.
Co-corresponding author of the paper, Michael Lanuti, MD, from the MGH Division of Thoracic Surgery, said, "The ability of molecular PET imaging with this probe to detect early-stage fibrosis would allow us to begin treatment when it would be most effective. This probe may also be able to distinguish new, active fibrosis from stable disease, which would allow clinicians to better tailor therapy to individual patients. And since response to therapy is difficult to ascertain with high-resolution CT scanning, PET molecular imaging may be a more sensitive way to detect changes in active fibrosis."
Pulmonary fibrosis is a lung disease that may in part be caused by exposure of patients to pollutants, or from other diseases, and causes the buildup of scar tissue. This stiffens the lung tissue and restricts oxygen absorption and breathing. The condition can lead to death in patients between three and five years.
The researchers from the Massachusetts General Hospital published their results in the April 2017 issue of the journal Science Translational Medicine.
The collagen-targeting probe, called 68Ga-CBP8, was able to bind to the lung scar tissue of animal models indicating the extent of fibrosis. The researchers also showed how fibrosis could be reduced in animals using an anti-fibrotic drug. The researchers also used human lung tissue, and found that the probe could differentiate between stable pulmonary fibrosis and progressive fibrosis.
Experiments using another model showed that there was increased uptake of the probe in areas where there was more extensive fibrosis. This model was also able to track disease progression over time.
Co-corresponding author of the paper, Michael Lanuti, MD, from the MGH Division of Thoracic Surgery, said, "The ability of molecular PET imaging with this probe to detect early-stage fibrosis would allow us to begin treatment when it would be most effective. This probe may also be able to distinguish new, active fibrosis from stable disease, which would allow clinicians to better tailor therapy to individual patients. And since response to therapy is difficult to ascertain with high-resolution CT scanning, PET molecular imaging may be a more sensitive way to detect changes in active fibrosis."
Latest Nuclear Medicine News
- Novel PET Imaging Approach Offers Never-Before-Seen View of Neuroinflammation
- Novel Radiotracer Identifies Biomarker for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
- Innovative PET Imaging Technique to Help Diagnose Neurodegeneration
- New Molecular Imaging Test to Improve Lung Cancer Diagnosis
- Novel PET Technique Visualizes Spinal Cord Injuries to Predict Recovery
- Next-Gen Tau Radiotracers Outperform FDA-Approved Imaging Agents in Detecting Alzheimer’s
- Breakthrough Method Detects Inflammation in Body Using PET Imaging
- Advanced Imaging Reveals Hidden Metastases in High-Risk Prostate Cancer Patients
- Combining Advanced Imaging Technologies Offers Breakthrough in Glioblastoma Treatment
- New Molecular Imaging Agent Accurately Identifies Crucial Cancer Biomarker
- New Scans Light Up Aggressive Tumors for Better Treatment
- AI Stroke Brain Scan Readings Twice as Accurate as Current Method
- AI Analysis of PET/CT Images Predicts Side Effects of Immunotherapy in Lung Cancer
- New Imaging Agent to Drive Step-Change for Brain Cancer Imaging
- Portable PET Scanner to Detect Earliest Stages of Alzheimer’s Disease
- New Immuno-PET Imaging Technique Identifies Glioblastoma Patients Who Would Benefit from Immunotherapy
Channels
Radiography
view channel
World's Largest Class Single Crystal Diamond Radiation Detector Opens New Possibilities for Diagnostic Imaging
Diamonds possess ideal physical properties for radiation detection, such as exceptional thermal and chemical stability along with a quick response time. Made of carbon with an atomic number of six, diamonds... Read more
AI-Powered Imaging Technique Shows Promise in Evaluating Patients for PCI
Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), also known as coronary angioplasty, is a minimally invasive procedure where small metal tubes called stents are inserted into partially blocked coronary arteries... Read moreMRI
view channel
Ultra-Powerful MRI Scans Enable Life-Changing Surgery in Treatment-Resistant Epileptic Patients
Approximately 360,000 individuals in the UK suffer from focal epilepsy, a condition in which seizures spread from one part of the brain. Around a third of these patients experience persistent seizures... Read more
AI-Powered MRI Technology Improves Parkinson’s Diagnoses
Current research shows that the accuracy of diagnosing Parkinson’s disease typically ranges from 55% to 78% within the first five years of assessment. This is partly due to the similarities shared by Parkinson’s... Read more
Biparametric MRI Combined with AI Enhances Detection of Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer
Artificial intelligence (AI) technologies are transforming the way medical images are analyzed, offering unprecedented capabilities in quantitatively extracting features that go beyond traditional visual... Read more
First-Of-Its-Kind AI-Driven Brain Imaging Platform to Better Guide Stroke Treatment Options
Each year, approximately 800,000 people in the U.S. experience strokes, with marginalized and minoritized groups being disproportionately affected. Strokes vary in terms of size and location within the... Read moreUltrasound
view channel
Ultrasound-Based Microscopy Technique to Help Diagnose Small Vessel Diseases
Clinical ultrasound, commonly used in pregnancy scans, provides real-time images of body structures. It is one of the most widely used imaging techniques in medicine, but until recently, it had little... Read more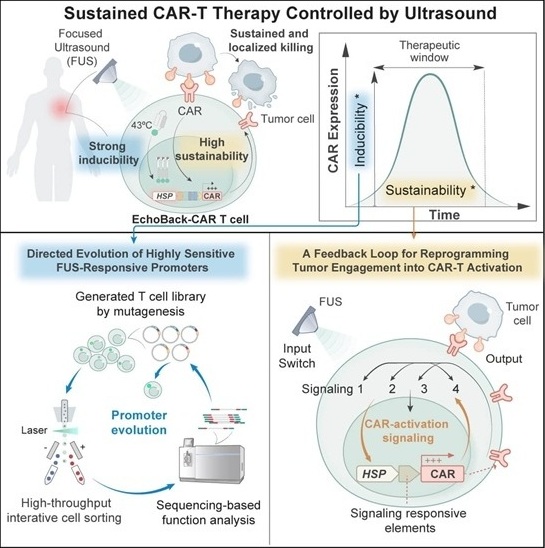
Smart Ultrasound-Activated Immune Cells Destroy Cancer Cells for Extended Periods
Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy has emerged as a highly promising cancer treatment, especially for bloodborne cancers like leukemia. This highly personalized therapy involves extracting... Read moreGeneral/Advanced Imaging
view channel
AI-Powered Imaging System Improves Lung Cancer Diagnosis
Given the need to detect lung cancer at earlier stages, there is an increasing need for a definitive diagnostic pathway for patients with suspicious pulmonary nodules. However, obtaining tissue samples... Read more
AI Model Significantly Enhances Low-Dose CT Capabilities
Lung cancer remains one of the most challenging diseases, making early diagnosis vital for effective treatment. Fortunately, advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) are revolutionizing lung cancer... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more
Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in medical diagnostics market is expanding with early disease detection being one of its key applications and image recognition becoming a compelling consumer proposition... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
GE HealthCare and NVIDIA Collaboration to Reimagine Diagnostic Imaging
GE HealthCare (Chicago, IL, USA) has entered into a collaboration with NVIDIA (Santa Clara, CA, USA), expanding the existing relationship between the two companies to focus on pioneering innovation in... Read more
Patient-Specific 3D-Printed Phantoms Transform CT Imaging
New research has highlighted how anatomically precise, patient-specific 3D-printed phantoms are proving to be scalable, cost-effective, and efficient tools in the development of new CT scan algorithms... Read more
Siemens and Sectra Collaborate on Enhancing Radiology Workflows
Siemens Healthineers (Forchheim, Germany) and Sectra (Linköping, Sweden) have entered into a collaboration aimed at enhancing radiologists' diagnostic capabilities and, in turn, improving patient care... Read more