New Radiotracer Helps Diagnose Prostate Cancer Faster
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 17 Feb 2017 |
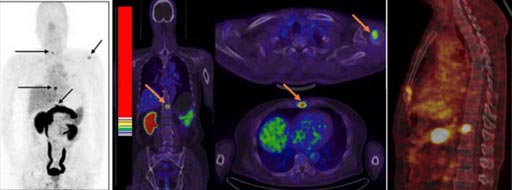
Image: The new tracer shows tumors in a 64-year-old man with PC (Photo courtesy of NIBIB).
A new study describes a radioactive tracer that targets two different biomarkers, gastrin-releasing peptide receptor (GRPR) and integrin αvβ3, which often indicate prostate cancer (PC).
Developed by researchers at Peking Union Medical College Hospital and the U.S. National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering, the new dual-receptor 68Ga-labeled heterodimeric peptide BBN-RGD radiotracer was designed to identify tumors at all PC stages by binding to the target receptors or biomarkers in primary tumors, metastatic lymph nodes, and metastatic bone lesions.
The radioactive atoms enable positron emission tomography (PET) or single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) scanners to image the areas where the tracers have collected in large numbers. In a Phase I clinical trial in 13 PC patients, the tracer was able to successfully identify three of four primary tumors, all 14 metastatic lymph nodes and, significantly, was also able to identity all 20 of the metastatic bone lesions. In contrast, only two of the primary tumors, five lymph nodes, and 12 bone lesions were positive using the 68Ga-BBN single receptor tracer. The study was published in the February 2017 issue of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine.
“We are far from finding one method to diagnose and monitor prostate cancer, but this is a step in that direction. Targeting multiple biomarkers could potentially allow us to identify prostate cancer at its early stages as well as after metastasis in one scan,” said senior author Xiaoyuan Chen, PhD, chief of the laboratory of molecular imaging and nanomedicine at NIBIB. “Dual-receptor targeting tracers could one day be the primary method for diagnosing and monitoring prostate cancer, reducing the amount of medical scans a patient would be forced to undergo and streamlining the diagnostic and therapeutic process.”
A variety of imaging techniques and tests are currently used to diagnose and monitor prostate cancer, including prostate specific antigen (PSA) blood tests, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), PET and SPECT, and computerized tomography (CT) scans. Each method has strengths and weaknesses, but there is no single method that is able to successfully identify and monitor primary tumors, metastatic lymph nodes, and bone lesions, which can cause the patient to undergo unnecessary treatments or painful biopsies.
Developed by researchers at Peking Union Medical College Hospital and the U.S. National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering, the new dual-receptor 68Ga-labeled heterodimeric peptide BBN-RGD radiotracer was designed to identify tumors at all PC stages by binding to the target receptors or biomarkers in primary tumors, metastatic lymph nodes, and metastatic bone lesions.
The radioactive atoms enable positron emission tomography (PET) or single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) scanners to image the areas where the tracers have collected in large numbers. In a Phase I clinical trial in 13 PC patients, the tracer was able to successfully identify three of four primary tumors, all 14 metastatic lymph nodes and, significantly, was also able to identity all 20 of the metastatic bone lesions. In contrast, only two of the primary tumors, five lymph nodes, and 12 bone lesions were positive using the 68Ga-BBN single receptor tracer. The study was published in the February 2017 issue of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine.
“We are far from finding one method to diagnose and monitor prostate cancer, but this is a step in that direction. Targeting multiple biomarkers could potentially allow us to identify prostate cancer at its early stages as well as after metastasis in one scan,” said senior author Xiaoyuan Chen, PhD, chief of the laboratory of molecular imaging and nanomedicine at NIBIB. “Dual-receptor targeting tracers could one day be the primary method for diagnosing and monitoring prostate cancer, reducing the amount of medical scans a patient would be forced to undergo and streamlining the diagnostic and therapeutic process.”
A variety of imaging techniques and tests are currently used to diagnose and monitor prostate cancer, including prostate specific antigen (PSA) blood tests, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), PET and SPECT, and computerized tomography (CT) scans. Each method has strengths and weaknesses, but there is no single method that is able to successfully identify and monitor primary tumors, metastatic lymph nodes, and bone lesions, which can cause the patient to undergo unnecessary treatments or painful biopsies.
Latest Nuclear Medicine News
- Novel PET Imaging Approach Offers Never-Before-Seen View of Neuroinflammation
- Novel Radiotracer Identifies Biomarker for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
- Innovative PET Imaging Technique to Help Diagnose Neurodegeneration
- New Molecular Imaging Test to Improve Lung Cancer Diagnosis
- Novel PET Technique Visualizes Spinal Cord Injuries to Predict Recovery
- Next-Gen Tau Radiotracers Outperform FDA-Approved Imaging Agents in Detecting Alzheimer’s
- Breakthrough Method Detects Inflammation in Body Using PET Imaging
- Advanced Imaging Reveals Hidden Metastases in High-Risk Prostate Cancer Patients
- Combining Advanced Imaging Technologies Offers Breakthrough in Glioblastoma Treatment
- New Molecular Imaging Agent Accurately Identifies Crucial Cancer Biomarker
- New Scans Light Up Aggressive Tumors for Better Treatment
- AI Stroke Brain Scan Readings Twice as Accurate as Current Method
- AI Analysis of PET/CT Images Predicts Side Effects of Immunotherapy in Lung Cancer
- New Imaging Agent to Drive Step-Change for Brain Cancer Imaging
- Portable PET Scanner to Detect Earliest Stages of Alzheimer’s Disease
- New Immuno-PET Imaging Technique Identifies Glioblastoma Patients Who Would Benefit from Immunotherapy
Channels
Radiography
view channel
World's Largest Class Single Crystal Diamond Radiation Detector Opens New Possibilities for Diagnostic Imaging
Diamonds possess ideal physical properties for radiation detection, such as exceptional thermal and chemical stability along with a quick response time. Made of carbon with an atomic number of six, diamonds... Read more
AI-Powered Imaging Technique Shows Promise in Evaluating Patients for PCI
Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), also known as coronary angioplasty, is a minimally invasive procedure where small metal tubes called stents are inserted into partially blocked coronary arteries... Read moreMRI
view channel
AI Tool Tracks Effectiveness of Multiple Sclerosis Treatments Using Brain MRI Scans
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a condition in which the immune system attacks the brain and spinal cord, leading to impairments in movement, sensation, and cognition. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) markers... Read more
Ultra-Powerful MRI Scans Enable Life-Changing Surgery in Treatment-Resistant Epileptic Patients
Approximately 360,000 individuals in the UK suffer from focal epilepsy, a condition in which seizures spread from one part of the brain. Around a third of these patients experience persistent seizures... Read more
AI-Powered MRI Technology Improves Parkinson’s Diagnoses
Current research shows that the accuracy of diagnosing Parkinson’s disease typically ranges from 55% to 78% within the first five years of assessment. This is partly due to the similarities shared by Parkinson’s... Read more
Biparametric MRI Combined with AI Enhances Detection of Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer
Artificial intelligence (AI) technologies are transforming the way medical images are analyzed, offering unprecedented capabilities in quantitatively extracting features that go beyond traditional visual... Read moreUltrasound
view channel
Novel Imaging Method Enables Early Diagnosis and Treatment Monitoring of Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is recognized as an autoimmune inflammatory disease, where chronic inflammation leads to alterations in pancreatic islet microvasculature, a key factor in β-cell dysfunction.... Read more
Ultrasound-Based Microscopy Technique to Help Diagnose Small Vessel Diseases
Clinical ultrasound, commonly used in pregnancy scans, provides real-time images of body structures. It is one of the most widely used imaging techniques in medicine, but until recently, it had little... Read moreGeneral/Advanced Imaging
view channel
AI-Powered Imaging System Improves Lung Cancer Diagnosis
Given the need to detect lung cancer at earlier stages, there is an increasing need for a definitive diagnostic pathway for patients with suspicious pulmonary nodules. However, obtaining tissue samples... Read more
AI Model Significantly Enhances Low-Dose CT Capabilities
Lung cancer remains one of the most challenging diseases, making early diagnosis vital for effective treatment. Fortunately, advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) are revolutionizing lung cancer... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more
Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in medical diagnostics market is expanding with early disease detection being one of its key applications and image recognition becoming a compelling consumer proposition... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
GE HealthCare and NVIDIA Collaboration to Reimagine Diagnostic Imaging
GE HealthCare (Chicago, IL, USA) has entered into a collaboration with NVIDIA (Santa Clara, CA, USA), expanding the existing relationship between the two companies to focus on pioneering innovation in... Read more
Patient-Specific 3D-Printed Phantoms Transform CT Imaging
New research has highlighted how anatomically precise, patient-specific 3D-printed phantoms are proving to be scalable, cost-effective, and efficient tools in the development of new CT scan algorithms... Read more
Siemens and Sectra Collaborate on Enhancing Radiology Workflows
Siemens Healthineers (Forchheim, Germany) and Sectra (Linköping, Sweden) have entered into a collaboration aimed at enhancing radiologists' diagnostic capabilities and, in turn, improving patient care... Read more