Twin Robotic X-Ray System Combines Care and Productivity
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 11 Nov 2015 |
The world’s first twin robotic X-ray scanner delivers a combination of high asset utilization, new clinical insights, and less patient positioning and transfers.
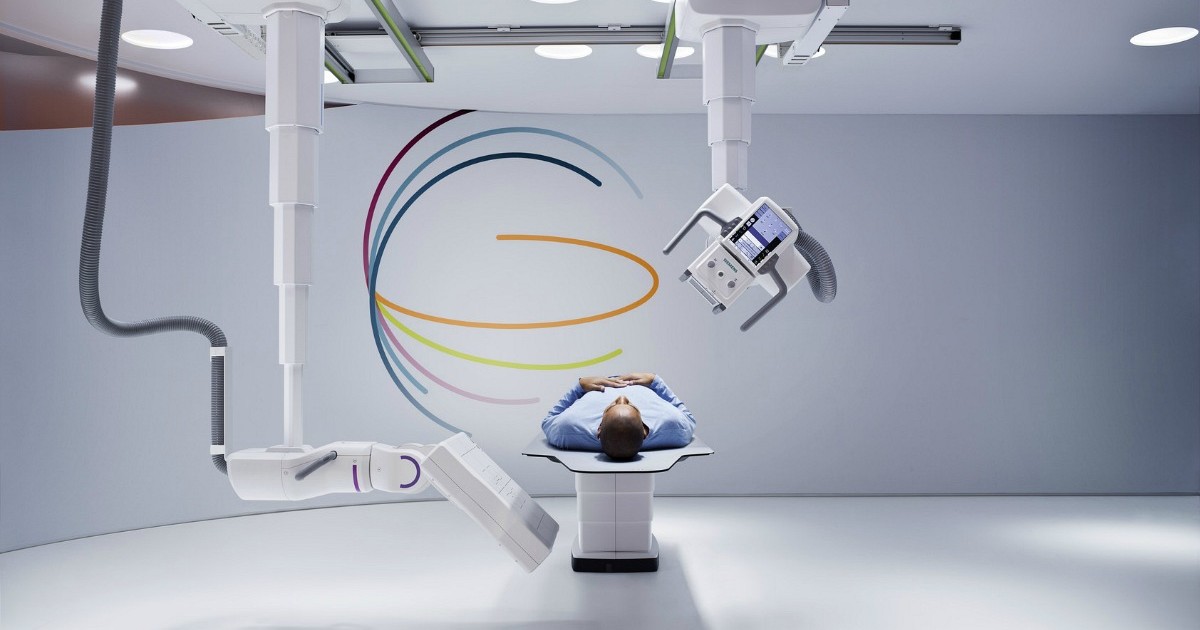
The Siemens Healthcare (Erlangen, Germany) Multitom Robotic Advanced X-ray (Rax) offers radiology departments a comprehensive range of applications by integrating multiple X-ray capabilities in one room, thus improving asset utilization and saving on costs. Modalities include radiography, tomography, fluoroscopy, and angiography; multi-clinical options, including trauma, orthopedic, intervention, pain management, and more; static, dynamic, and three dimensional (3D) scanning; and multiple patient configurations.
The two ceiling-mounted arms of the Multitom Rax can be moved into position automatically using robotic technology, and they can also be moved manually (servo motor supported) when required, such as for fine adjustment. One arm moves the X-ray tube and the large touchscreen control, while the other carries a 43 x 43 cm flat panel detector. Consequently, there is no need to reposition the patient or to change rooms for further imaging procedures, which makes examinations less painful and less time-consuming.
Multitom Rax also offers Real 3D—the ability to perform X-ray examinations and diagnoses under natural weight-bearing conditions, such as in lying, sitting, and standing conditions, allowing comfortable patient positioning with an open design, while still maintaining low-dose protocols. Another comfort feature is that the scanner revolves around the patient utilizing an open, patient-centered design, resulting in less patient risks and pain due to fewer transfers and repositioning, especially important in pediatric, geriatric, bariatric, immobile, and trauma patients.
“The robotic technology ensures a new level of precision and automation, enabling a new level of standardization and throughput,” said Francois Nolte, head of the X-ray products business line at Siemens Healthcare. “The precise positioning of the arms in all three planes makes the examinations so much easier: regardless of whether the patient is standing, sitting or lying down, the robotic arms move with perfect accuracy using robotic technology. Our strategy is based on the principle that the system moves, not the patient, which reduces risk of additional injuries and pain.”
The Siemens Multitom Robotic Advanced X-ray (Rax) also offers optional wireless, portable, detectors in two different sizes that can be positioned directly between a wheelchair or mattress and the patient's back, which avoids the need to sit the patient up. Preprogrammed safety zones, an automatic stop in response to contact, and automatic control of the robotic arms that ensures that they will always take the shortest and safest route to reach the next programmed position also improve safety.
Related Links:
Siemens Healthcare
The Siemens Healthcare (Erlangen, Germany) Multitom Robotic Advanced X-ray (Rax) offers radiology departments a comprehensive range of applications by integrating multiple X-ray capabilities in one room, thus improving asset utilization and saving on costs. Modalities include radiography, tomography, fluoroscopy, and angiography; multi-clinical options, including trauma, orthopedic, intervention, pain management, and more; static, dynamic, and three dimensional (3D) scanning; and multiple patient configurations.
The two ceiling-mounted arms of the Multitom Rax can be moved into position automatically using robotic technology, and they can also be moved manually (servo motor supported) when required, such as for fine adjustment. One arm moves the X-ray tube and the large touchscreen control, while the other carries a 43 x 43 cm flat panel detector. Consequently, there is no need to reposition the patient or to change rooms for further imaging procedures, which makes examinations less painful and less time-consuming.
Multitom Rax also offers Real 3D—the ability to perform X-ray examinations and diagnoses under natural weight-bearing conditions, such as in lying, sitting, and standing conditions, allowing comfortable patient positioning with an open design, while still maintaining low-dose protocols. Another comfort feature is that the scanner revolves around the patient utilizing an open, patient-centered design, resulting in less patient risks and pain due to fewer transfers and repositioning, especially important in pediatric, geriatric, bariatric, immobile, and trauma patients.
“The robotic technology ensures a new level of precision and automation, enabling a new level of standardization and throughput,” said Francois Nolte, head of the X-ray products business line at Siemens Healthcare. “The precise positioning of the arms in all three planes makes the examinations so much easier: regardless of whether the patient is standing, sitting or lying down, the robotic arms move with perfect accuracy using robotic technology. Our strategy is based on the principle that the system moves, not the patient, which reduces risk of additional injuries and pain.”
The Siemens Multitom Robotic Advanced X-ray (Rax) also offers optional wireless, portable, detectors in two different sizes that can be positioned directly between a wheelchair or mattress and the patient's back, which avoids the need to sit the patient up. Preprogrammed safety zones, an automatic stop in response to contact, and automatic control of the robotic arms that ensures that they will always take the shortest and safest route to reach the next programmed position also improve safety.
Related Links:
Siemens Healthcare
Read the full article by registering today, it's FREE! 

Register now for FREE to MedImaging.net and get access to news and events that shape the world of Radiology. 
- Free digital version edition of Medical Imaging International sent by email on regular basis
- Free print version of Medical Imaging International magazine (available only outside USA and Canada).
- Free and unlimited access to back issues of Medical Imaging International in digital format
- Free Medical Imaging International Newsletter sent every week containing the latest news
- Free breaking news sent via email
- Free access to Events Calendar
- Free access to LinkXpress new product services
- REGISTRATION IS FREE AND EASY!
Sign in: Registered website members
Sign in: Registered magazine subscribers
Latest Radiography News
- World's Largest Class Single Crystal Diamond Radiation Detector Opens New Possibilities for Diagnostic Imaging
- AI-Powered Imaging Technique Shows Promise in Evaluating Patients for PCI
- Higher Chest X-Ray Usage Catches Lung Cancer Earlier and Improves Survival
- AI-Powered Mammograms Predict Cardiovascular Risk
- Generative AI Model Significantly Reduces Chest X-Ray Reading Time
- AI-Powered Mammography Screening Boosts Cancer Detection in Single-Reader Settings
- Photon Counting Detectors Promise Fast Color X-Ray Images
- AI Can Flag Mammograms for Supplemental MRI
- 3D CT Imaging from Single X-Ray Projection Reduces Radiation Exposure
- AI Method Accurately Predicts Breast Cancer Risk by Analyzing Multiple Mammograms
- Printable Organic X-Ray Sensors Could Transform Treatment for Cancer Patients
- Highly Sensitive, Foldable Detector to Make X-Rays Safer
- Novel Breast Cancer Screening Technology Could Offer Superior Alternative to Mammogram
- Artificial Intelligence Accurately Predicts Breast Cancer Years Before Diagnosis
- AI-Powered Chest X-Ray Detects Pulmonary Nodules Three Years Before Lung Cancer Symptoms
- AI Model Identifies Vertebral Compression Fractures in Chest Radiographs
Channels
MRI
view channel
AI Tool Tracks Effectiveness of Multiple Sclerosis Treatments Using Brain MRI Scans
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a condition in which the immune system attacks the brain and spinal cord, leading to impairments in movement, sensation, and cognition. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) markers... Read more
Ultra-Powerful MRI Scans Enable Life-Changing Surgery in Treatment-Resistant Epileptic Patients
Approximately 360,000 individuals in the UK suffer from focal epilepsy, a condition in which seizures spread from one part of the brain. Around a third of these patients experience persistent seizures... Read more
AI-Powered MRI Technology Improves Parkinson’s Diagnoses
Current research shows that the accuracy of diagnosing Parkinson’s disease typically ranges from 55% to 78% within the first five years of assessment. This is partly due to the similarities shared by Parkinson’s... Read more
Biparametric MRI Combined with AI Enhances Detection of Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer
Artificial intelligence (AI) technologies are transforming the way medical images are analyzed, offering unprecedented capabilities in quantitatively extracting features that go beyond traditional visual... Read moreUltrasound
view channel.jpeg)
AI-Powered Lung Ultrasound Outperforms Human Experts in Tuberculosis Diagnosis
Despite global declines in tuberculosis (TB) rates in previous years, the incidence of TB rose by 4.6% from 2020 to 2023. Early screening and rapid diagnosis are essential elements of the World Health... Read more
AI Identifies Heart Valve Disease from Common Imaging Test
Tricuspid regurgitation is a condition where the heart's tricuspid valve does not close completely during contraction, leading to backward blood flow, which can result in heart failure. A new artificial... Read moreNuclear Medicine
view channel
Novel PET Imaging Approach Offers Never-Before-Seen View of Neuroinflammation
COX-2, an enzyme that plays a key role in brain inflammation, can be significantly upregulated by inflammatory stimuli and neuroexcitation. Researchers suggest that COX-2 density in the brain could serve... Read more
Novel Radiotracer Identifies Biomarker for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC), which represents 15-20% of all breast cancer cases, is one of the most aggressive subtypes, with a five-year survival rate of about 40%. Due to its significant heterogeneity... Read moreGeneral/Advanced Imaging
view channel
AI-Powered Imaging System Improves Lung Cancer Diagnosis
Given the need to detect lung cancer at earlier stages, there is an increasing need for a definitive diagnostic pathway for patients with suspicious pulmonary nodules. However, obtaining tissue samples... Read more
AI Model Significantly Enhances Low-Dose CT Capabilities
Lung cancer remains one of the most challenging diseases, making early diagnosis vital for effective treatment. Fortunately, advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) are revolutionizing lung cancer... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more
Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in medical diagnostics market is expanding with early disease detection being one of its key applications and image recognition becoming a compelling consumer proposition... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
GE HealthCare and NVIDIA Collaboration to Reimagine Diagnostic Imaging
GE HealthCare (Chicago, IL, USA) has entered into a collaboration with NVIDIA (Santa Clara, CA, USA), expanding the existing relationship between the two companies to focus on pioneering innovation in... Read more
Patient-Specific 3D-Printed Phantoms Transform CT Imaging
New research has highlighted how anatomically precise, patient-specific 3D-printed phantoms are proving to be scalable, cost-effective, and efficient tools in the development of new CT scan algorithms... Read more
Siemens and Sectra Collaborate on Enhancing Radiology Workflows
Siemens Healthineers (Forchheim, Germany) and Sectra (Linköping, Sweden) have entered into a collaboration aimed at enhancing radiologists' diagnostic capabilities and, in turn, improving patient care... Read more