Study Shows Accelerated Partial Breast Irradiation Can Be Used to Treat Early Stage Breast Cancer
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 01 Nov 2015 |
The results of a new prospective brachytherapy clinical study have been released at the annual meeting of the American Society for Therapeutic Radiation and Oncology (ASTRO; San Antonio, USA), October 18–21, 2015.
The randomized, multicenter phase III study evaluated 1,184 patients aged 40 years and older with a median age of 62, and compared treatment using Accelerated Partial Breast Irradiation (APBI) combined with interstitial multi-catheter brachytherapy to treatment using Whole Breast Irradiation (WBI). The study took place at 16 medical centers in six European countries—Austria, the Czech Republic, Germany, Hungary, Poland, Spain, and Switzerland.
The study results were announced by the Groupe Européen de Curiethérapie—European Society for Therapeutic Radiology and Oncology (GEC-ESTRO) and showed that overall survival, local and regional cancer control rates using APBI brachytherapy, after breast conserving surgery for those patients with early stage breast cancers, were equivalent to those using WBI.
The researchers randomized the patients either to a standardized treatment arm (WBI, n=551), or an investigational treatment arm (APBI, n=633). Follow-up exams were made for the patients every three months in the first 60 months, and then annually, with a median follow up of 6.6 years.
Nine patients were treated with APBI, and five patients with WBI. All had a local recurrence after five years, equivalent to cumulative recurrence rates of 1.44% and 0.92% (p=0.42) respectively. There was no significant difference in regional recurrence between the groups. The five-year overall survival was 97.27% for APBI and 95.55% for patients treated with WBI, with no observed difference in breast-cancer related deaths.
Prof. Vratislav Strnad, MD, PhD, Department of Radiation Oncology, University Hospital, Erlangen, Germany, said, "GEC-ESTRO is the most comprehensive clinical study to date evaluating the efficacy of APBI brachytherapy alone versus traditional external whole breast irradiation. APBI brachytherapy is an attractive treatment approach with a high level of precision, versatility and flexibility. The benefits of APBI brachytherapy include an at least four-fold reduction in total radiation exposure to healthy surrounding tissue and nearby structures including the chest wall, heart, lungs or skin; preservation of future treatment options; and a notably shorter course of therapy—four or five days, compared to three or up to seven weeks for whole breast irradiation."
Related Links:
University Hospital Erlangen
Cianni Medical
Elekta
The randomized, multicenter phase III study evaluated 1,184 patients aged 40 years and older with a median age of 62, and compared treatment using Accelerated Partial Breast Irradiation (APBI) combined with interstitial multi-catheter brachytherapy to treatment using Whole Breast Irradiation (WBI). The study took place at 16 medical centers in six European countries—Austria, the Czech Republic, Germany, Hungary, Poland, Spain, and Switzerland.
The study results were announced by the Groupe Européen de Curiethérapie—European Society for Therapeutic Radiology and Oncology (GEC-ESTRO) and showed that overall survival, local and regional cancer control rates using APBI brachytherapy, after breast conserving surgery for those patients with early stage breast cancers, were equivalent to those using WBI.
The researchers randomized the patients either to a standardized treatment arm (WBI, n=551), or an investigational treatment arm (APBI, n=633). Follow-up exams were made for the patients every three months in the first 60 months, and then annually, with a median follow up of 6.6 years.
Nine patients were treated with APBI, and five patients with WBI. All had a local recurrence after five years, equivalent to cumulative recurrence rates of 1.44% and 0.92% (p=0.42) respectively. There was no significant difference in regional recurrence between the groups. The five-year overall survival was 97.27% for APBI and 95.55% for patients treated with WBI, with no observed difference in breast-cancer related deaths.
Prof. Vratislav Strnad, MD, PhD, Department of Radiation Oncology, University Hospital, Erlangen, Germany, said, "GEC-ESTRO is the most comprehensive clinical study to date evaluating the efficacy of APBI brachytherapy alone versus traditional external whole breast irradiation. APBI brachytherapy is an attractive treatment approach with a high level of precision, versatility and flexibility. The benefits of APBI brachytherapy include an at least four-fold reduction in total radiation exposure to healthy surrounding tissue and nearby structures including the chest wall, heart, lungs or skin; preservation of future treatment options; and a notably shorter course of therapy—four or five days, compared to three or up to seven weeks for whole breast irradiation."
Related Links:
University Hospital Erlangen
Cianni Medical
Elekta
Latest Radiography News
- AI-Powered Imaging Technique Shows Promise in Evaluating Patients for PCI
- Higher Chest X-Ray Usage Catches Lung Cancer Earlier and Improves Survival
- AI-Powered Mammograms Predict Cardiovascular Risk
- Generative AI Model Significantly Reduces Chest X-Ray Reading Time
- AI-Powered Mammography Screening Boosts Cancer Detection in Single-Reader Settings
- Photon Counting Detectors Promise Fast Color X-Ray Images
- AI Can Flag Mammograms for Supplemental MRI
- 3D CT Imaging from Single X-Ray Projection Reduces Radiation Exposure
- AI Method Accurately Predicts Breast Cancer Risk by Analyzing Multiple Mammograms
- Printable Organic X-Ray Sensors Could Transform Treatment for Cancer Patients
- Highly Sensitive, Foldable Detector to Make X-Rays Safer
- Novel Breast Cancer Screening Technology Could Offer Superior Alternative to Mammogram
- Artificial Intelligence Accurately Predicts Breast Cancer Years Before Diagnosis
- AI-Powered Chest X-Ray Detects Pulmonary Nodules Three Years Before Lung Cancer Symptoms
- AI Model Identifies Vertebral Compression Fractures in Chest Radiographs
- Advanced 3D Mammography Detects More Breast Cancers
Channels
MRI
view channel
Ultra-Powerful MRI Scans Enable Life-Changing Surgery in Treatment-Resistant Epileptic Patients
Approximately 360,000 individuals in the UK suffer from focal epilepsy, a condition in which seizures spread from one part of the brain. Around a third of these patients experience persistent seizures... Read more
AI-Powered MRI Technology Improves Parkinson’s Diagnoses
Current research shows that the accuracy of diagnosing Parkinson’s disease typically ranges from 55% to 78% within the first five years of assessment. This is partly due to the similarities shared by Parkinson’s... Read more
Biparametric MRI Combined with AI Enhances Detection of Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer
Artificial intelligence (AI) technologies are transforming the way medical images are analyzed, offering unprecedented capabilities in quantitatively extracting features that go beyond traditional visual... Read more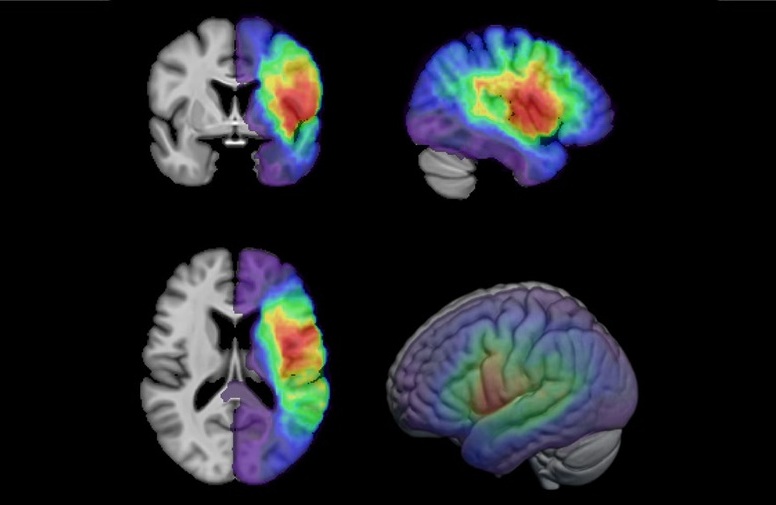
First-Of-Its-Kind AI-Driven Brain Imaging Platform to Better Guide Stroke Treatment Options
Each year, approximately 800,000 people in the U.S. experience strokes, with marginalized and minoritized groups being disproportionately affected. Strokes vary in terms of size and location within the... Read moreUltrasound
view channel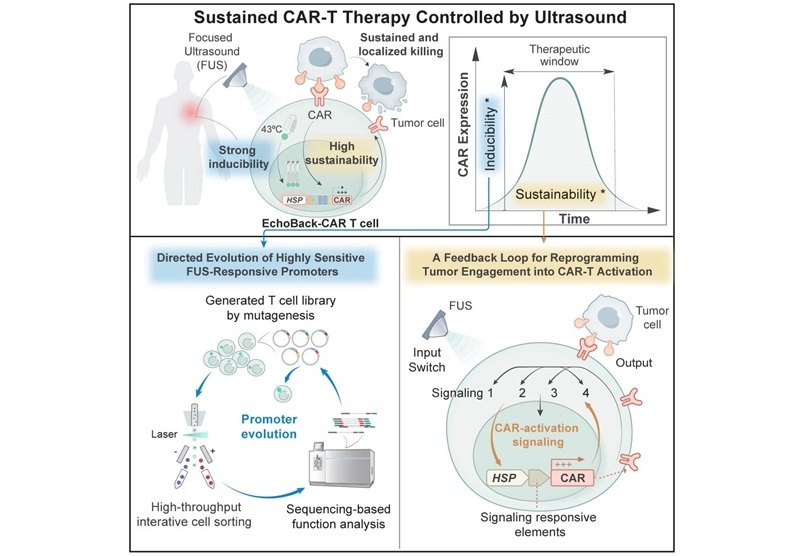
Smart Ultrasound-Activated Immune Cells Destroy Cancer Cells for Extended Periods
Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy has emerged as a highly promising cancer treatment, especially for bloodborne cancers like leukemia. This highly personalized therapy involves extracting... Read more
Tiny Magnetic Robot Takes 3D Scans from Deep Within Body
Colorectal cancer ranks as one of the leading causes of cancer-related mortality worldwide. However, when detected early, it is highly treatable. Now, a new minimally invasive technique could significantly... Read more
High Resolution Ultrasound Speeds Up Prostate Cancer Diagnosis
Each year, approximately one million prostate cancer biopsies are conducted across Europe, with similar numbers in the USA and around 100,000 in Canada. Most of these biopsies are performed using MRI images... Read more
World's First Wireless, Handheld, Whole-Body Ultrasound with Single PZT Transducer Makes Imaging More Accessible
Ultrasound devices play a vital role in the medical field, routinely used to examine the body's internal tissues and structures. While advancements have steadily improved ultrasound image quality and processing... Read moreNuclear Medicine
view channel
Novel PET Imaging Approach Offers Never-Before-Seen View of Neuroinflammation
COX-2, an enzyme that plays a key role in brain inflammation, can be significantly upregulated by inflammatory stimuli and neuroexcitation. Researchers suggest that COX-2 density in the brain could serve... Read more
Novel Radiotracer Identifies Biomarker for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC), which represents 15-20% of all breast cancer cases, is one of the most aggressive subtypes, with a five-year survival rate of about 40%. Due to its significant heterogeneity... Read moreGeneral/Advanced Imaging
view channel
AI-Powered Imaging System Improves Lung Cancer Diagnosis
Given the need to detect lung cancer at earlier stages, there is an increasing need for a definitive diagnostic pathway for patients with suspicious pulmonary nodules. However, obtaining tissue samples... Read more
AI Model Significantly Enhances Low-Dose CT Capabilities
Lung cancer remains one of the most challenging diseases, making early diagnosis vital for effective treatment. Fortunately, advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) are revolutionizing lung cancer... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more
Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in medical diagnostics market is expanding with early disease detection being one of its key applications and image recognition becoming a compelling consumer proposition... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
GE HealthCare and NVIDIA Collaboration to Reimagine Diagnostic Imaging
GE HealthCare (Chicago, IL, USA) has entered into a collaboration with NVIDIA (Santa Clara, CA, USA), expanding the existing relationship between the two companies to focus on pioneering innovation in... Read more
Patient-Specific 3D-Printed Phantoms Transform CT Imaging
New research has highlighted how anatomically precise, patient-specific 3D-printed phantoms are proving to be scalable, cost-effective, and efficient tools in the development of new CT scan algorithms... Read more
Siemens and Sectra Collaborate on Enhancing Radiology Workflows
Siemens Healthineers (Forchheim, Germany) and Sectra (Linköping, Sweden) have entered into a collaboration aimed at enhancing radiologists' diagnostic capabilities and, in turn, improving patient care... Read more
















