Combined Use of MRI and Ultrasound Boosts Market Growth
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 13 Mar 2012 |
When combined, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and ultrasound imaging becomes more effective, and this trend is among the many factors mentioned by a new market research report for the growth in sales of both modalities.
In healthcare market research publisher Kalorama Information’s (New York, NY, USA) recent report, the firm noted that worldwide revenues for MRI and ultrasound systems grew at 6% and 4%, respectively, between 2010 and 2011.
One example of combination usage is in rotator cuff tears. Whereas ultrasound is typically seen as more cost effective, MRI is most frequently used to assess the rotator cuff. When performing a cost utility analysis, utilizing ultrasound as the first medical imaging test for a rotator cuff tear, in addition to a preoperative MRI to identify alternative and concurrent diagnoses, can be a very effective hybrid imaging approach.
“Ultrasound is a cheaper imaging modality, yet MRI can provide more depth,” said Joe Constance, Kalorama’s imaging analyst and the author of the report. “So it’s not a surprise to see ultrasound recommended for the initial medical imaging test and an MRI as a secondary test to find any alternate diagnosis and give the surgeon the needed anatomy.”
Another field where a combination of modalities is used, according to Kalorama, is in breast cancer. A second-look ultrasound of the breast, used in conjunction with MRI, allows radiologists to identify lesions not detected with conventional mammography and first-look ultrasound; in some cases, it allows radiologists to determine whether or not a lesion is malignant or benign. This was underscored in a study performed at the University of Rome La Sapienza (Rome, Italy), which included 182 patients who had mammography, ultrasound, and MRI. It has become accepted among some radiologists.
New research may find new combination uses. An experimental procedure developed by scientists at the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA; USA) fuses MRI with real-time three-dimensional (3D) ultrasound to obtain biopsy specimens from suspicious areas in the prostate. Patients first received MRI scans of the prostate that evaluated three components in detecting cancer: suspicious contrasts in tissue, abnormal cellular density, and unusual blood flow within the prostate.
Kalorama Information, a division of MarketResearch.com, supplies independent medical market research in diagnostics, biotech, pharmaceuticals, medical devices and healthcare, as well as custom research services.
Related Links:
Kalorama Information
In healthcare market research publisher Kalorama Information’s (New York, NY, USA) recent report, the firm noted that worldwide revenues for MRI and ultrasound systems grew at 6% and 4%, respectively, between 2010 and 2011.
One example of combination usage is in rotator cuff tears. Whereas ultrasound is typically seen as more cost effective, MRI is most frequently used to assess the rotator cuff. When performing a cost utility analysis, utilizing ultrasound as the first medical imaging test for a rotator cuff tear, in addition to a preoperative MRI to identify alternative and concurrent diagnoses, can be a very effective hybrid imaging approach.
“Ultrasound is a cheaper imaging modality, yet MRI can provide more depth,” said Joe Constance, Kalorama’s imaging analyst and the author of the report. “So it’s not a surprise to see ultrasound recommended for the initial medical imaging test and an MRI as a secondary test to find any alternate diagnosis and give the surgeon the needed anatomy.”
Another field where a combination of modalities is used, according to Kalorama, is in breast cancer. A second-look ultrasound of the breast, used in conjunction with MRI, allows radiologists to identify lesions not detected with conventional mammography and first-look ultrasound; in some cases, it allows radiologists to determine whether or not a lesion is malignant or benign. This was underscored in a study performed at the University of Rome La Sapienza (Rome, Italy), which included 182 patients who had mammography, ultrasound, and MRI. It has become accepted among some radiologists.
New research may find new combination uses. An experimental procedure developed by scientists at the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA; USA) fuses MRI with real-time three-dimensional (3D) ultrasound to obtain biopsy specimens from suspicious areas in the prostate. Patients first received MRI scans of the prostate that evaluated three components in detecting cancer: suspicious contrasts in tissue, abnormal cellular density, and unusual blood flow within the prostate.
Kalorama Information, a division of MarketResearch.com, supplies independent medical market research in diagnostics, biotech, pharmaceuticals, medical devices and healthcare, as well as custom research services.
Related Links:
Kalorama Information
Latest Industry News News
- GE HealthCare and NVIDIA Collaboration to Reimagine Diagnostic Imaging
- Patient-Specific 3D-Printed Phantoms Transform CT Imaging
- Siemens and Sectra Collaborate on Enhancing Radiology Workflows
- Bracco Diagnostics and ColoWatch Partner to Expand Availability CRC Screening Tests Using Virtual Colonoscopy
- Mindray Partners with TeleRay to Streamline Ultrasound Delivery
- Philips and Medtronic Partner on Stroke Care
- Siemens and Medtronic Enter into Global Partnership for Advancing Spine Care Imaging Technologies
- RSNA 2024 Technical Exhibits to Showcase Latest Advances in Radiology
- Bracco Collaborates with Arrayus on Microbubble-Assisted Focused Ultrasound Therapy for Pancreatic Cancer
- Innovative Collaboration to Enhance Ischemic Stroke Detection and Elevate Standards in Diagnostic Imaging
- RSNA 2024 Registration Opens
- Microsoft collaborates with Leading Academic Medical Systems to Advance AI in Medical Imaging
- GE HealthCare Acquires Intelligent Ultrasound Group’s Clinical Artificial Intelligence Business
- Bayer and Rad AI Collaborate on Expanding Use of Cutting Edge AI Radiology Operational Solutions
- Polish Med-Tech Company BrainScan to Expand Extensively into Foreign Markets
- Hologic Acquires UK-Based Breast Surgical Guidance Company Endomagnetics Ltd.
Channels
Radiography
view channel
AI Improves Early Detection of Interval Breast Cancers
Interval breast cancers, which occur between routine screenings, are easier to treat when detected earlier. Early detection can reduce the need for aggressive treatments and improve the chances of better outcomes.... Read more
World's Largest Class Single Crystal Diamond Radiation Detector Opens New Possibilities for Diagnostic Imaging
Diamonds possess ideal physical properties for radiation detection, such as exceptional thermal and chemical stability along with a quick response time. Made of carbon with an atomic number of six, diamonds... Read moreMRI
view channel
Cutting-Edge MRI Technology to Revolutionize Diagnosis of Common Heart Problem
Aortic stenosis is a common and potentially life-threatening heart condition. It occurs when the aortic valve, which regulates blood flow from the heart to the rest of the body, becomes stiff and narrow.... Read more
New MRI Technique Reveals True Heart Age to Prevent Attacks and Strokes
Heart disease remains one of the leading causes of death worldwide. Individuals with conditions such as diabetes or obesity often experience accelerated aging of their hearts, sometimes by decades.... Read more
AI Tool Predicts Relapse of Pediatric Brain Cancer from Brain MRI Scans
Many pediatric gliomas are treatable with surgery alone, but relapses can be catastrophic. Predicting which patients are at risk for recurrence remains challenging, leading to frequent follow-ups with... Read more
AI Tool Tracks Effectiveness of Multiple Sclerosis Treatments Using Brain MRI Scans
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a condition in which the immune system attacks the brain and spinal cord, leading to impairments in movement, sensation, and cognition. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) markers... Read moreUltrasound
view channel.jpeg)
AI-Powered Lung Ultrasound Outperforms Human Experts in Tuberculosis Diagnosis
Despite global declines in tuberculosis (TB) rates in previous years, the incidence of TB rose by 4.6% from 2020 to 2023. Early screening and rapid diagnosis are essential elements of the World Health... Read more
AI Identifies Heart Valve Disease from Common Imaging Test
Tricuspid regurgitation is a condition where the heart's tricuspid valve does not close completely during contraction, leading to backward blood flow, which can result in heart failure. A new artificial... Read moreNuclear Medicine
view channel
Novel Radiolabeled Antibody Improves Diagnosis and Treatment of Solid Tumors
Interleukin-13 receptor α-2 (IL13Rα2) is a cell surface receptor commonly found in solid tumors such as glioblastoma, melanoma, and breast cancer. It is minimally expressed in normal tissues, making it... Read more
Novel PET Imaging Approach Offers Never-Before-Seen View of Neuroinflammation
COX-2, an enzyme that plays a key role in brain inflammation, can be significantly upregulated by inflammatory stimuli and neuroexcitation. Researchers suggest that COX-2 density in the brain could serve... Read moreGeneral/Advanced Imaging
view channel
AI-Based CT Scan Analysis Predicts Early-Stage Kidney Damage Due to Cancer Treatments
Radioligand therapy, a form of targeted nuclear medicine, has recently gained attention for its potential in treating specific types of tumors. However, one of the potential side effects of this therapy... Read more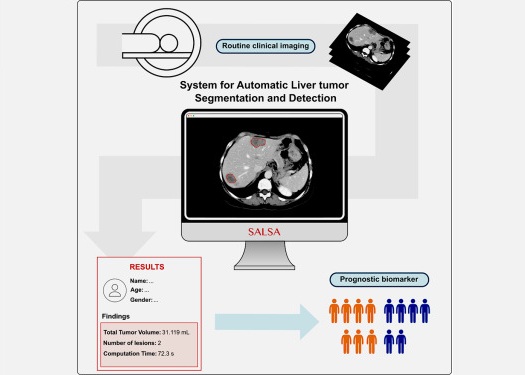
CT-Based Deep Learning-Driven Tool to Enhance Liver Cancer Diagnosis
Medical imaging, such as computed tomography (CT) scans, plays a crucial role in oncology, offering essential data for cancer detection, treatment planning, and monitoring of response to therapies.... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more





















