Targeted MRI to Transform Imaging Market
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 17 Nov 2010 |
Targeted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), a technology in development that would reveal specific disease indicators present in a patient to clinicians at the molecular level, would considerably improve demand for imaging procedures, according to recent healthcare market research.
In a recent report, Kalorama Information (New York, NY, USA), a publisher of healthcare market research, found that if the type of targeted agents now available for single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) training were applied to MRI and ultrasound in a clinical setting, the world market for contrast agents would see a dramatic increase.
"The development of targeted MRI contrast agents that are directed to specific molecular entities could dramatically expand the range of MRI market applications by combining the noninvasiveness and high spatial resolution of MRI with the specific localization of molecular targets,” said Joe Constance, Kalorama analyst and author of the report. "The technologies have the potential to make imaging definitive for a range of clinical applications such as the detection of tumors and heart disease.”
Targeted imaging involves adding special molecules to imaging agents that can attach directly to specific molecular entities. The application combines the effectiveness of a contrast agent with an adhesion molecule in order to target the contrast directly to the desired target. The imaging approach differs depending on whether the target is a single disease control point (a specific receptor or transport protein tied to the mechanistic activity of a drug) or a general disease control point applicable to a number of treatment paradigms (proliferation, angiogenesis, or inflammation).
Currently, there are no targeted MRI contrast agents available for specific imaging of tumor and cardiovascular diseases, but many MRI applications are under development, according to the report. However, several targeted SPECT imaging agents are available for clinical applications. Because of the fundamentally low sensitivity of MRI, in comparison with nuclear imaging, high concentrations of the contrast agent at the target site would be required, along with high affinity and specificity of cell recognition.
Scientists have successfully targeted MRI and nuclear medicine contrast agents to the alpha-V/beta 3 integrin, permitting noninvasive monitoring of angiogenesis.
In some instances, the targeted approach may require the use of less contrast. Differential contrast in soft tissues depends on endogenous differences in water content, relaxation times, or the diffusion characteristics of the tissue of interest. Gadolinium chelates, for example, have been successfully used for imaging hemodynamic parameters, including blood perfusion and vascular permeability.
Kalorama estimated the 2010 market for all contrast media at over US$7.5 billion. The firm sees realistic growth rates based on existing market conditions, but noted that a trend such as targeting agents could considerably increase revenue potential for companies in this industry.
Kalorama Information supplies independent market research in the life sciences, as well as a full range of custom research services.
Related Links:
Kalorama Information
In a recent report, Kalorama Information (New York, NY, USA), a publisher of healthcare market research, found that if the type of targeted agents now available for single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) training were applied to MRI and ultrasound in a clinical setting, the world market for contrast agents would see a dramatic increase.
"The development of targeted MRI contrast agents that are directed to specific molecular entities could dramatically expand the range of MRI market applications by combining the noninvasiveness and high spatial resolution of MRI with the specific localization of molecular targets,” said Joe Constance, Kalorama analyst and author of the report. "The technologies have the potential to make imaging definitive for a range of clinical applications such as the detection of tumors and heart disease.”
Targeted imaging involves adding special molecules to imaging agents that can attach directly to specific molecular entities. The application combines the effectiveness of a contrast agent with an adhesion molecule in order to target the contrast directly to the desired target. The imaging approach differs depending on whether the target is a single disease control point (a specific receptor or transport protein tied to the mechanistic activity of a drug) or a general disease control point applicable to a number of treatment paradigms (proliferation, angiogenesis, or inflammation).
Currently, there are no targeted MRI contrast agents available for specific imaging of tumor and cardiovascular diseases, but many MRI applications are under development, according to the report. However, several targeted SPECT imaging agents are available for clinical applications. Because of the fundamentally low sensitivity of MRI, in comparison with nuclear imaging, high concentrations of the contrast agent at the target site would be required, along with high affinity and specificity of cell recognition.
Scientists have successfully targeted MRI and nuclear medicine contrast agents to the alpha-V/beta 3 integrin, permitting noninvasive monitoring of angiogenesis.
In some instances, the targeted approach may require the use of less contrast. Differential contrast in soft tissues depends on endogenous differences in water content, relaxation times, or the diffusion characteristics of the tissue of interest. Gadolinium chelates, for example, have been successfully used for imaging hemodynamic parameters, including blood perfusion and vascular permeability.
Kalorama estimated the 2010 market for all contrast media at over US$7.5 billion. The firm sees realistic growth rates based on existing market conditions, but noted that a trend such as targeting agents could considerably increase revenue potential for companies in this industry.
Kalorama Information supplies independent market research in the life sciences, as well as a full range of custom research services.
Related Links:
Kalorama Information
Latest Industry News News
- GE HealthCare and NVIDIA Collaboration to Reimagine Diagnostic Imaging
- Patient-Specific 3D-Printed Phantoms Transform CT Imaging
- Siemens and Sectra Collaborate on Enhancing Radiology Workflows
- Bracco Diagnostics and ColoWatch Partner to Expand Availability CRC Screening Tests Using Virtual Colonoscopy
- Mindray Partners with TeleRay to Streamline Ultrasound Delivery
- Philips and Medtronic Partner on Stroke Care
- Siemens and Medtronic Enter into Global Partnership for Advancing Spine Care Imaging Technologies
- RSNA 2024 Technical Exhibits to Showcase Latest Advances in Radiology
- Bracco Collaborates with Arrayus on Microbubble-Assisted Focused Ultrasound Therapy for Pancreatic Cancer
- Innovative Collaboration to Enhance Ischemic Stroke Detection and Elevate Standards in Diagnostic Imaging
- RSNA 2024 Registration Opens
- Microsoft collaborates with Leading Academic Medical Systems to Advance AI in Medical Imaging
- GE HealthCare Acquires Intelligent Ultrasound Group’s Clinical Artificial Intelligence Business
- Bayer and Rad AI Collaborate on Expanding Use of Cutting Edge AI Radiology Operational Solutions
- Polish Med-Tech Company BrainScan to Expand Extensively into Foreign Markets
- Hologic Acquires UK-Based Breast Surgical Guidance Company Endomagnetics Ltd.
Channels
Radiography
view channel
AI Radiology Tool Identifies Life-Threatening Conditions in Milliseconds
Radiology is emerging as one of healthcare’s most pressing bottlenecks. By 2033, the U.S. could face a shortage of up to 42,000 radiologists, even as imaging volumes grow by 5% annually.... Read more
Machine Learning Algorithm Identifies Cardiovascular Risk from Routine Bone Density Scans
A new study published in the Journal of Bone and Mineral Research reveals that an automated machine learning program can predict the risk of cardiovascular events and falls or fractures by analyzing bone... Read more
AI Improves Early Detection of Interval Breast Cancers
Interval breast cancers, which occur between routine screenings, are easier to treat when detected earlier. Early detection can reduce the need for aggressive treatments and improve the chances of better outcomes.... Read more
World's Largest Class Single Crystal Diamond Radiation Detector Opens New Possibilities for Diagnostic Imaging
Diamonds possess ideal physical properties for radiation detection, such as exceptional thermal and chemical stability along with a quick response time. Made of carbon with an atomic number of six, diamonds... Read moreMRI
view channel
New MRI Technique Reveals Hidden Heart Issues
Traditional exercise stress tests conducted within an MRI machine require patients to lie flat, a position that artificially improves heart function by increasing stroke volume due to gravity-driven blood... Read more
Shorter MRI Exam Effectively Detects Cancer in Dense Breasts
Women with extremely dense breasts face a higher risk of missed breast cancer diagnoses, as dense glandular and fibrous tissue can obscure tumors on mammograms. While breast MRI is recommended for supplemental... Read moreUltrasound
view channel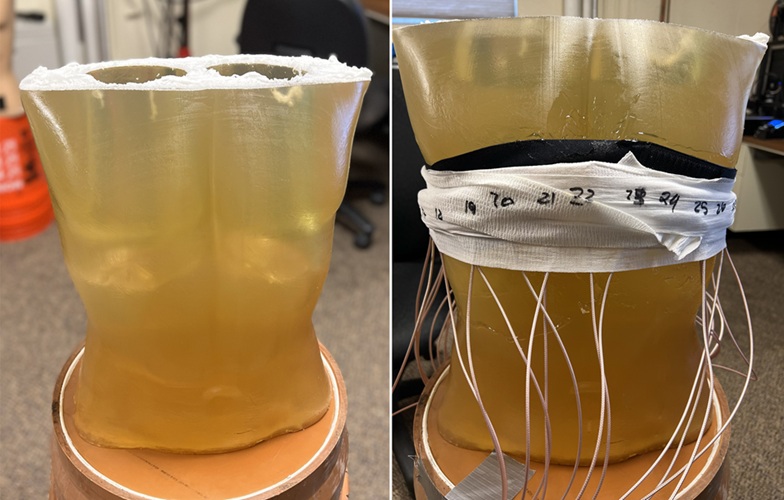
New Medical Ultrasound Imaging Technique Enables ICU Bedside Monitoring
Ultrasound computed tomography (USCT) presents a safer alternative to imaging techniques like X-ray computed tomography (commonly known as CT or “CAT” scans) because it does not produce ionizing radiation.... Read more
New Incision-Free Technique Halts Growth of Debilitating Brain Lesions
Cerebral cavernous malformations (CCMs), also known as cavernomas, are abnormal clusters of blood vessels that can grow in the brain, spinal cord, or other parts of the body. While most cases remain asymptomatic,... Read moreNuclear Medicine
view channel
New Imaging Approach Could Reduce Need for Biopsies to Monitor Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer is the second leading cause of cancer-related death among men in the United States. However, the majority of older men diagnosed with prostate cancer have slow-growing, low-risk forms of... Read more
Novel Radiolabeled Antibody Improves Diagnosis and Treatment of Solid Tumors
Interleukin-13 receptor α-2 (IL13Rα2) is a cell surface receptor commonly found in solid tumors such as glioblastoma, melanoma, and breast cancer. It is minimally expressed in normal tissues, making it... Read moreGeneral/Advanced Imaging
view channel
CT Colonography Beats Stool DNA Testing for Colon Cancer Screening
As colorectal cancer remains the second leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide, early detection through screening is vital to reduce advanced-stage treatments and associated costs.... Read more
First-Of-Its-Kind Wearable Device Offers Revolutionary Alternative to CT Scans
Currently, patients with conditions such as heart failure, pneumonia, or respiratory distress often require multiple imaging procedures that are intermittent, disruptive, and involve high levels of radiation.... Read more
AI-Based CT Scan Analysis Predicts Early-Stage Kidney Damage Due to Cancer Treatments
Radioligand therapy, a form of targeted nuclear medicine, has recently gained attention for its potential in treating specific types of tumors. However, one of the potential side effects of this therapy... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more












.jpeg)





