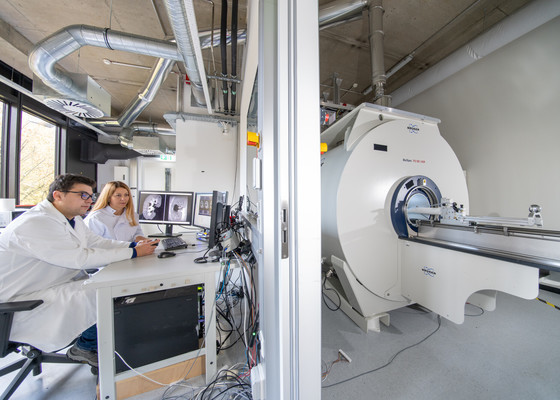
Researchers to Perform First-Ever Mixed-Reality Robotic Heart Surgery Inside MRI Machine
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 20 Oct 2022 |
Atrial fibrillation (AFib), the most common form of heart arrhythmia, or irregular heartbeat, is a problem with the rate or rhythm of the heartbeat - including beating too quickly or too slow. Many cases of AFib are controlled with medication, but those who cannot tolerate or do not respond to drugs often undergo an ablation procedure known as a Left Atrial Appendage Occlusion (LAAO) for managing stroke risk. In the LAAO procedure, doctors insert a catheter, or flexible tube, through a vein or artery in the groin and thread it up to the heart to deliver an implant that reduces blood clots in the heart that leads to strokes in Afib patients. However, using current technology, the doctor views the heart tissue and manually positions the implant with the help of an X-ray of the heart, which provides only a very hazy picture of the organ.
Now, a team of scientists has received a four-year, USD 3.7 million National Institutes of Health grant to attempt what they say would be a medical first: performing robotic heart catheterization while the patient is inside a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) machine. A physician controlling a micro-robotic device would perform the procedure wearing a mixed-reality headset and the goal would be to achieve unparalleled surgical precision. By demonstrating the benefits of using AR-guided robotic surgery for the LAAO procedure, the scientists at Case Western Reserve University (Cleveland, OH, USA) hope to increase its availability to AFib patients - especially those whose life expectancy is greater than 20 years. Both of the two big pieces of the work - the robotic catheter operating inside an MRI, and the high-speed MRI imaging itself - provide significant challenges, bringing together several experts from different disciplines.
“Using our technology, the physician would see clinical-quality, soft-tissue images in real time,” said lead researcher M. Cenk Cavusoglu, professor of electrical, computer, and systems engineering and director of the Medical Robotics and Computer Integrated Surgery (MeRCIS) Lab at the Case School of Engineering. “He or she would be able to pinpoint the exact location, and the micro-robot would perform the procedure. This would make this procedure safer, easier, far more effective, and even less expensive as a treatment for atrial fibrillation (AFib).”
Related Links:
Case Western Reserve University
Latest Surgical Techniques News
Channels
Radiography
view channel
Novel Breast Imaging System Proves As Effective As Mammography
Breast cancer remains the most frequently diagnosed cancer among women. It is projected that one in eight women will be diagnosed with breast cancer during her lifetime, and one in 42 women who turn 50... Read more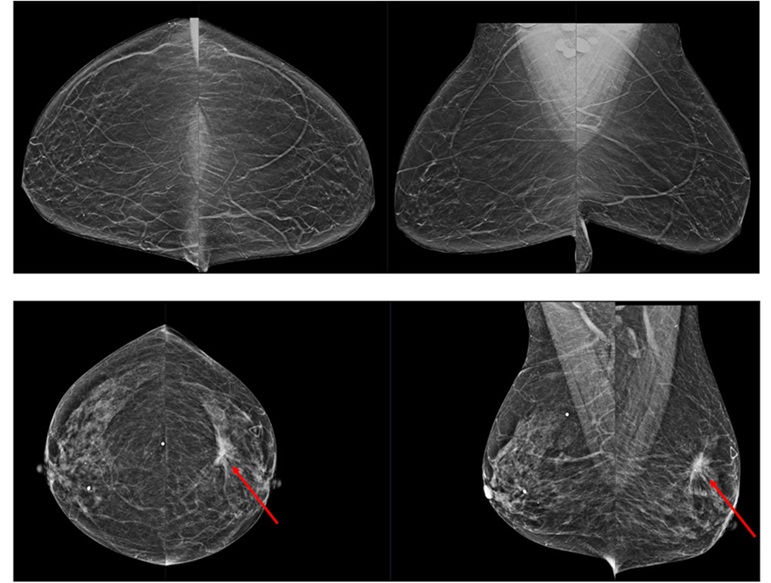
AI Assistance Improves Breast-Cancer Screening by Reducing False Positives
Radiologists typically detect one case of cancer for every 200 mammograms reviewed. However, these evaluations often result in false positives, leading to unnecessary patient recalls for additional testing,... Read moreMRI
view channel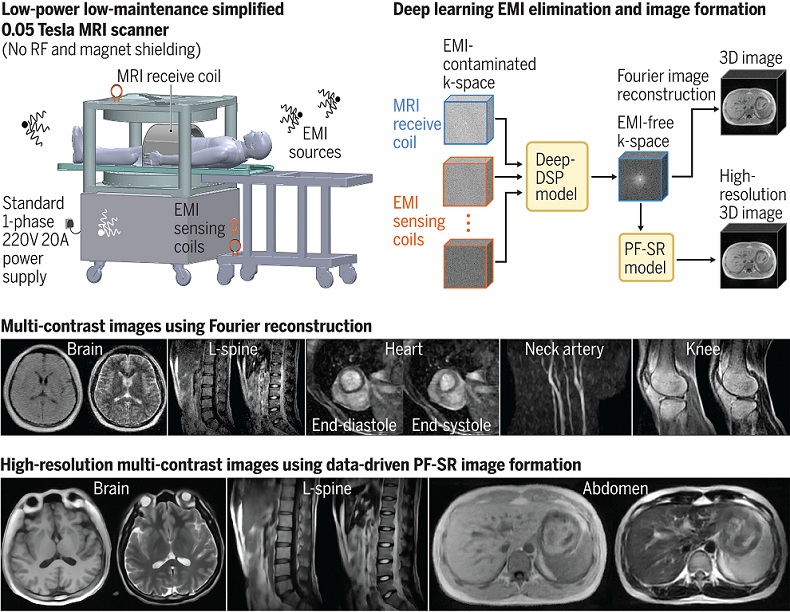
Low-Cost Whole-Body MRI Device Combined with AI Generates High-Quality Results
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) has significantly transformed healthcare, providing a noninvasive, radiation-free method for detailed imaging. It is especially promising for the future of medical diagnosis... Read more
World's First Whole-Body Ultra-High Field MRI Officially Comes To Market
The world's first whole-body ultra-high field (UHF) MRI has officially come to market, marking a remarkable advancement in diagnostic radiology. United Imaging (Shanghai, China) has secured clearance from the U.... Read moreUltrasound
view channel.jpg)
Diagnostic System Automatically Analyzes TTE Images to Identify Congenital Heart Disease
Congenital heart disease (CHD) is one of the most prevalent congenital anomalies worldwide, presenting substantial health and financial challenges for affected patients. Early detection and treatment of... Read more
Super-Resolution Imaging Technique Could Improve Evaluation of Cardiac Conditions
The heart depends on efficient blood circulation to pump blood throughout the body, delivering oxygen to tissues and removing carbon dioxide and waste. Yet, when heart vessels are damaged, it can disrupt... Read more
First AI-Powered POC Ultrasound Diagnostic Solution Helps Prioritize Cases Based On Severity
Ultrasound scans are essential for identifying and diagnosing various medical conditions, but often, patients must wait weeks or months for results due to a shortage of qualified medical professionals... Read moreNuclear Medicine
view channelNew PET Agent Rapidly and Accurately Visualizes Lesions in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma Patients
Clear cell renal cell cancer (ccRCC) represents 70-80% of renal cell carcinoma cases. While localized disease can be effectively treated with surgery and ablative therapies, one-third of patients either... Read more
New Imaging Technique Monitors Inflammation Disorders without Radiation Exposure
Imaging inflammation using traditional radiological techniques presents significant challenges, including radiation exposure, poor image quality, high costs, and invasive procedures. Now, new contrast... Read more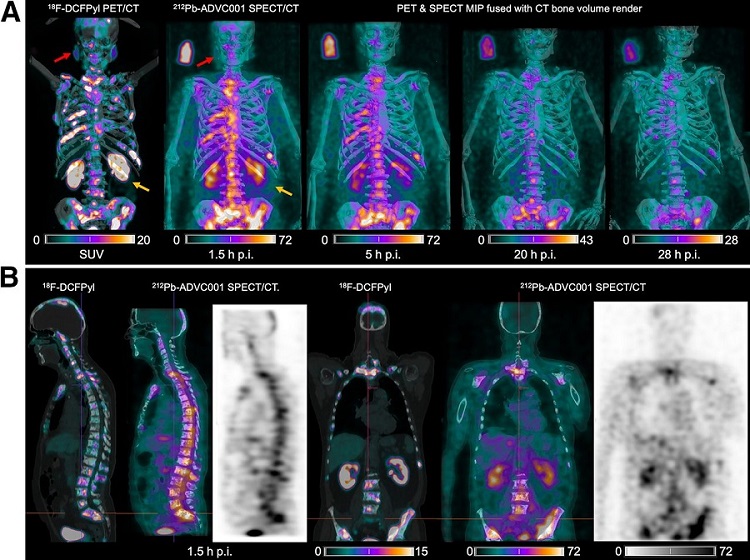
New SPECT/CT Technique Could Change Imaging Practices and Increase Patient Access
The development of lead-212 (212Pb)-PSMA–based targeted alpha therapy (TAT) is garnering significant interest in treating patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. The imaging of 212Pb,... Read moreGeneral/Advanced Imaging
view channelBone Density Test Uses Existing CT Images to Predict Fractures
Osteoporotic fractures are not only devastating and deadly, especially hip fractures, but also impose significant costs. They rank among the top chronic diseases in terms of disability-adjusted life years... Read more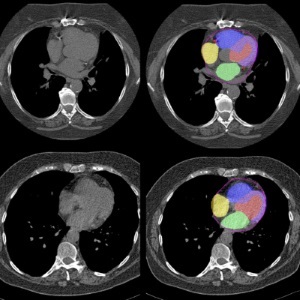
AI Predicts Cardiac Risk and Mortality from Routine Chest CT Scans
Heart disease remains the leading cause of death and is largely preventable, yet many individuals are unaware of their risk until it becomes severe. Early detection through screening can reveal heart issues,... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more
Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in medical diagnostics market is expanding with early disease detection being one of its key applications and image recognition becoming a compelling consumer proposition... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
Hologic Acquires UK-Based Breast Surgical Guidance Company Endomagnetics Ltd.
Hologic, Inc. (Marlborough, MA, USA) has entered into a definitive agreement to acquire Endomagnetics Ltd. (Cambridge, UK), a privately held developer of breast cancer surgery technologies, for approximately... Read more
Bayer and Google Partner on New AI Product for Radiologists
Medical imaging data comprises around 90% of all healthcare data, and it is a highly complex and rich clinical data modality and serves as a vital tool for diagnosing patients. Each year, billions of medical... Read more