Artificial Intelligence Boosts ADHD Detection Using MRI
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 27 Dec 2019 |
Illustration
Researchers from the University of Cincinnati College of Medicine (Cincinnati, OH, USA) and Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center (Cincinnati, OH, USA) have proved that deep learning, a type of artificial intelligence, can boost the power of MRI in predicting attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). The researchers believe that the approach could also have applications for other neurological conditions.
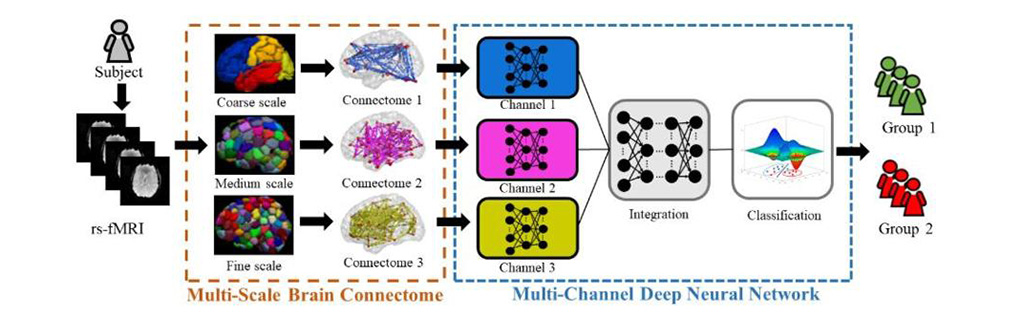
Brain MRI has a potential role in diagnosis, as research suggests that ADHD results from some type of breakdown or disruption in the connectome. The connectome is constructed from spatial regions across the MR image known as parcellations. Brain parcellations can be defined based on anatomical criteria, functional criteria, or both. The brain can be studied at different scales based on different brain parcellations. Prior studies have focused on the so-called single-scale approach, where the connectome is constructed based on only one parcellation. For the new study, researchers from the University of Cincinnati College of Medicine and Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center took a more comprehensive view. They developed a multi-scale method, which used multiple connectome maps based on multiple parcellations.
To build the deep learning model, the researchers used data from the NeuroBureau ADHD-200 dataset. The model used the multi-scale brain connectome data from the project's 973 participants along with relevant personal characteristics, such as gender and IQ. The multi-scale approach improved ADHD detection performance significantly over the use of a single-scale method. By improving diagnostic accuracy, deep-learning-aided MRI-based diagnosis could be critical in implementing early interventions for ADHD patients. In the future, the researchers expect to see the deep learning model improve as it is exposed to larger neuroimaging datasets. They also hope to better understand the specific breakdowns or disruptions in the connectome identified by the model that are associated with ADHD.
"Our results emphasize the predictive power of the brain connectome," said study senior author Lili He, Ph.D., from the Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center. "The constructed brain functional connectome that spans multiple scales provides supplementary information for the depicting of networks across the entire brain."
Related Links:
University of Cincinnati College of Medicine
Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center
Brain MRI has a potential role in diagnosis, as research suggests that ADHD results from some type of breakdown or disruption in the connectome. The connectome is constructed from spatial regions across the MR image known as parcellations. Brain parcellations can be defined based on anatomical criteria, functional criteria, or both. The brain can be studied at different scales based on different brain parcellations. Prior studies have focused on the so-called single-scale approach, where the connectome is constructed based on only one parcellation. For the new study, researchers from the University of Cincinnati College of Medicine and Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center took a more comprehensive view. They developed a multi-scale method, which used multiple connectome maps based on multiple parcellations.
To build the deep learning model, the researchers used data from the NeuroBureau ADHD-200 dataset. The model used the multi-scale brain connectome data from the project's 973 participants along with relevant personal characteristics, such as gender and IQ. The multi-scale approach improved ADHD detection performance significantly over the use of a single-scale method. By improving diagnostic accuracy, deep-learning-aided MRI-based diagnosis could be critical in implementing early interventions for ADHD patients. In the future, the researchers expect to see the deep learning model improve as it is exposed to larger neuroimaging datasets. They also hope to better understand the specific breakdowns or disruptions in the connectome identified by the model that are associated with ADHD.
"Our results emphasize the predictive power of the brain connectome," said study senior author Lili He, Ph.D., from the Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center. "The constructed brain functional connectome that spans multiple scales provides supplementary information for the depicting of networks across the entire brain."
Related Links:
University of Cincinnati College of Medicine
Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center
Latest Industry News News
- Hologic Acquires UK-Based Breast Surgical Guidance Company Endomagnetics Ltd.
- Bayer and Google Partner on New AI Product for Radiologists
- Samsung and Bracco Enter Into New Diagnostic Ultrasound Technology Agreement
- IBA Acquires Radcal to Expand Medical Imaging Quality Assurance Offering
- International Societies Suggest Key Considerations for AI Radiology Tools
- Samsung's X-Ray Devices to Be Powered by Lunit AI Solutions for Advanced Chest Screening
- Canon Medical and Olympus Collaborate on Endoscopic Ultrasound Systems
- GE HealthCare Acquires AI Imaging Analysis Company MIM Software
- First Ever International Criteria Lays Foundation for Improved Diagnostic Imaging of Brain Tumors
- RSNA Unveils 10 Most Cited Radiology Studies of 2023
- RSNA 2023 Technical Exhibits to Offer Innovations in AI, 3D Printing and More
- AI Medical Imaging Products to Increase Five-Fold by 2035, Finds Study
- RSNA 2023 Technical Exhibits to Highlight Latest Medical Imaging Innovations
- AI-Powered Technologies to Aid Interpretation of X-Ray and MRI Images for Improved Disease Diagnosis
- Hologic and Bayer Partner to Improve Mammography Imaging
- Global Fixed and Mobile C-Arms Market Driven by Increasing Surgical Procedures
Channels
Radiography
view channel
Novel Breast Imaging System Proves As Effective As Mammography
Breast cancer remains the most frequently diagnosed cancer among women. It is projected that one in eight women will be diagnosed with breast cancer during her lifetime, and one in 42 women who turn 50... Read more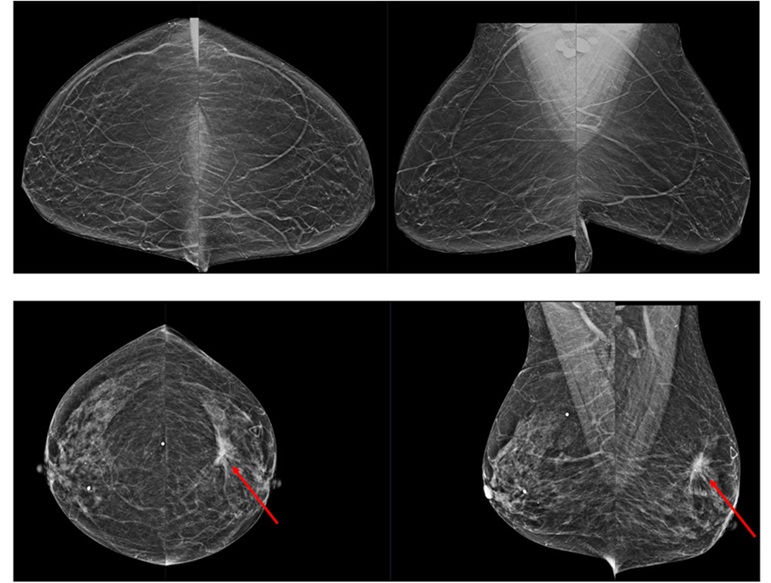
AI Assistance Improves Breast-Cancer Screening by Reducing False Positives
Radiologists typically detect one case of cancer for every 200 mammograms reviewed. However, these evaluations often result in false positives, leading to unnecessary patient recalls for additional testing,... Read moreMRI
view channel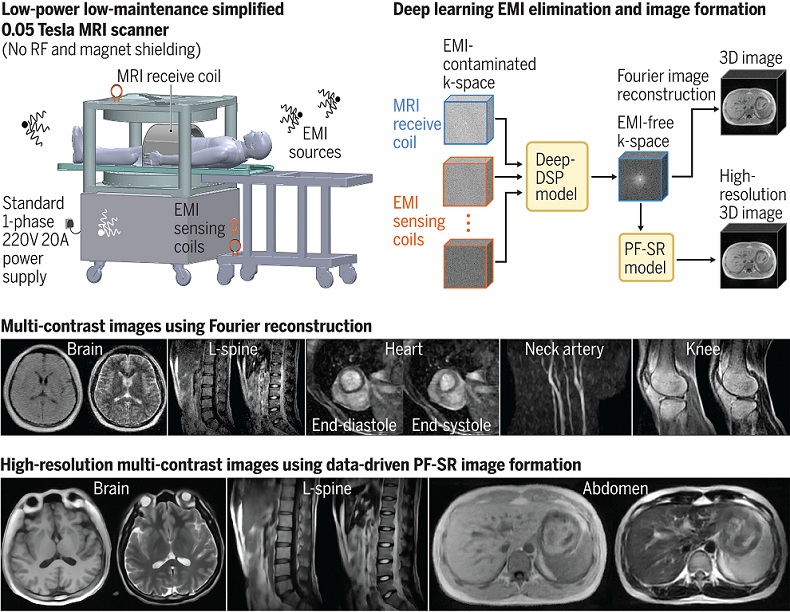
Low-Cost Whole-Body MRI Device Combined with AI Generates High-Quality Results
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) has significantly transformed healthcare, providing a noninvasive, radiation-free method for detailed imaging. It is especially promising for the future of medical diagnosis... Read more
World's First Whole-Body Ultra-High Field MRI Officially Comes To Market
The world's first whole-body ultra-high field (UHF) MRI has officially come to market, marking a remarkable advancement in diagnostic radiology. United Imaging (Shanghai, China) has secured clearance from the U.... Read moreUltrasound
view channel.jpg)
Diagnostic System Automatically Analyzes TTE Images to Identify Congenital Heart Disease
Congenital heart disease (CHD) is one of the most prevalent congenital anomalies worldwide, presenting substantial health and financial challenges for affected patients. Early detection and treatment of... Read more
Super-Resolution Imaging Technique Could Improve Evaluation of Cardiac Conditions
The heart depends on efficient blood circulation to pump blood throughout the body, delivering oxygen to tissues and removing carbon dioxide and waste. Yet, when heart vessels are damaged, it can disrupt... Read more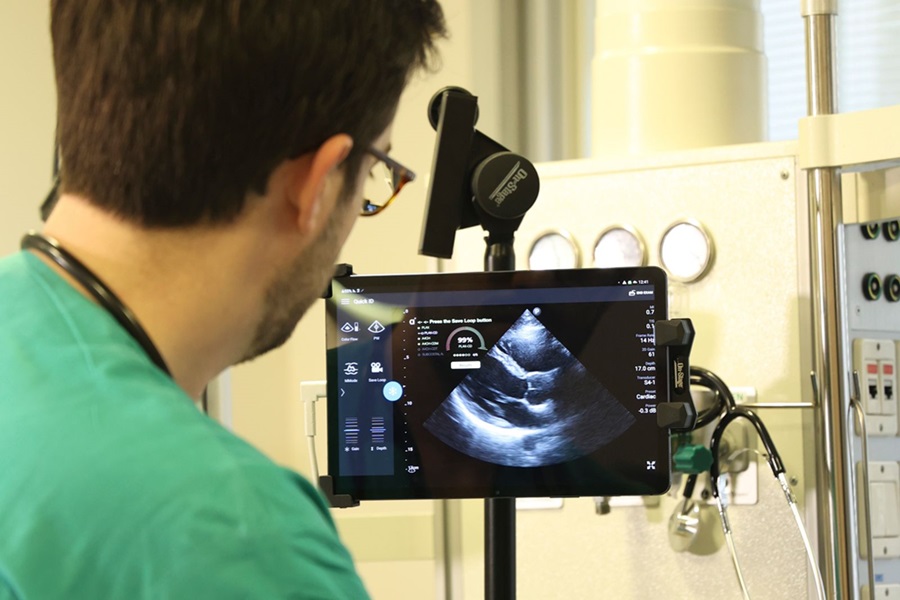
First AI-Powered POC Ultrasound Diagnostic Solution Helps Prioritize Cases Based On Severity
Ultrasound scans are essential for identifying and diagnosing various medical conditions, but often, patients must wait weeks or months for results due to a shortage of qualified medical professionals... Read moreNuclear Medicine
view channel
New PET Biomarker Predicts Success of Immune Checkpoint Blockade Therapy
Immunotherapies, such as immune checkpoint blockade (ICB), have shown promising clinical results in treating melanoma, non-small cell lung cancer, and other tumor types. However, the effectiveness of these... Read moreNew PET Agent Rapidly and Accurately Visualizes Lesions in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma Patients
Clear cell renal cell cancer (ccRCC) represents 70-80% of renal cell carcinoma cases. While localized disease can be effectively treated with surgery and ablative therapies, one-third of patients either... Read more
New Imaging Technique Monitors Inflammation Disorders without Radiation Exposure
Imaging inflammation using traditional radiological techniques presents significant challenges, including radiation exposure, poor image quality, high costs, and invasive procedures. Now, new contrast... Read more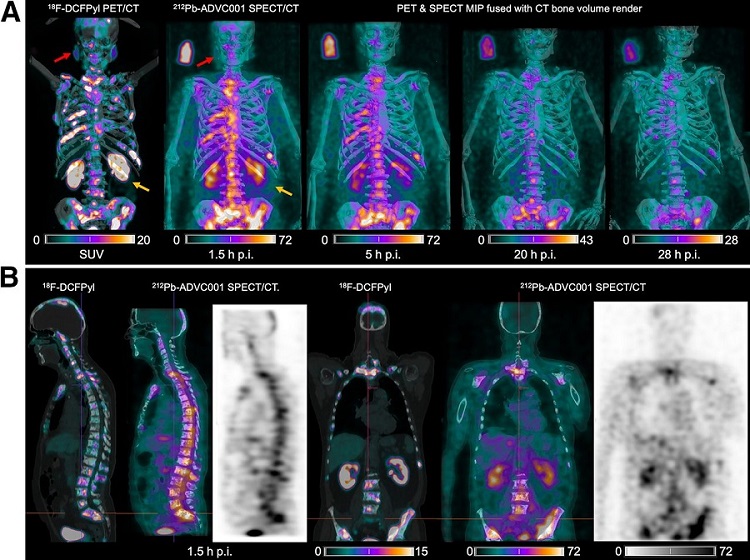
New SPECT/CT Technique Could Change Imaging Practices and Increase Patient Access
The development of lead-212 (212Pb)-PSMA–based targeted alpha therapy (TAT) is garnering significant interest in treating patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. The imaging of 212Pb,... Read moreGeneral/Advanced Imaging
view channelBone Density Test Uses Existing CT Images to Predict Fractures
Osteoporotic fractures are not only devastating and deadly, especially hip fractures, but also impose significant costs. They rank among the top chronic diseases in terms of disability-adjusted life years... Read more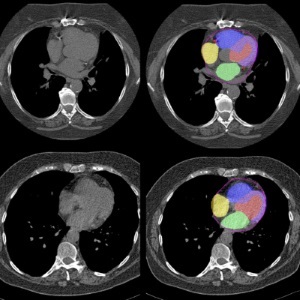
AI Predicts Cardiac Risk and Mortality from Routine Chest CT Scans
Heart disease remains the leading cause of death and is largely preventable, yet many individuals are unaware of their risk until it becomes severe. Early detection through screening can reveal heart issues,... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more