CT Dose Standardized Using Feedback Mechanism
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 24 Apr 2017 |
Researchers have shown how radiation doses can be effectively reduced, and patient safety improved, by using a feedback mechanism to share dose levels for common CT scans between hospitals.
There has been a steady increase in the use of Computed Tomography (CT) exams in the U.S. in the last 10 years, and radiation dose levels for these exams vary considerably between hospitals.
Researchers at the University of California, San Francisco used the feedback mechanism between radiologists at five academic medical centers in UCSF in order to assess and compare the radiation dose for CT exams. Best practices were then shared between the participating hospitals resulting in significantly lower radiation doses for abdominal and chest CT scans, and more consistent doses for head scans. The study was published in the April 10, 2017, issue of JAMA Internal Medicine.
Senior author of the study Professor Rebecca Smith-Bindman, MD, said, “We estimate that if the improvements we saw were applied to all abdominal CT scans performed in the U.S., this would result in the reduction of approximately 12,000 cancers annually. Reducing unnecessary and inconsistent radiation doses is an extremely important process for improving patient safety. We found that providing detailed and comparative feedback, and sharing best practices on how each institution was able to optimize their dose, leads to lower and more consistent CT doses. In short, it makes no sense for each institution to have to re-invent the wheel regarding how to optimize doses – this project focuses on helping the leaders at each institution learn from each other.”
There has been a steady increase in the use of Computed Tomography (CT) exams in the U.S. in the last 10 years, and radiation dose levels for these exams vary considerably between hospitals.
Researchers at the University of California, San Francisco used the feedback mechanism between radiologists at five academic medical centers in UCSF in order to assess and compare the radiation dose for CT exams. Best practices were then shared between the participating hospitals resulting in significantly lower radiation doses for abdominal and chest CT scans, and more consistent doses for head scans. The study was published in the April 10, 2017, issue of JAMA Internal Medicine.
Senior author of the study Professor Rebecca Smith-Bindman, MD, said, “We estimate that if the improvements we saw were applied to all abdominal CT scans performed in the U.S., this would result in the reduction of approximately 12,000 cancers annually. Reducing unnecessary and inconsistent radiation doses is an extremely important process for improving patient safety. We found that providing detailed and comparative feedback, and sharing best practices on how each institution was able to optimize their dose, leads to lower and more consistent CT doses. In short, it makes no sense for each institution to have to re-invent the wheel regarding how to optimize doses – this project focuses on helping the leaders at each institution learn from each other.”
Latest Radiography News
- Novel Breast Imaging System Proves As Effective As Mammography
- AI Assistance Improves Breast-Cancer Screening by Reducing False Positives
- AI Could Boost Clinical Adoption of Chest DDR
- 3D Mammography Almost Halves Breast Cancer Incidence between Two Screening Tests
- AI Model Predicts 5-Year Breast Cancer Risk from Mammograms
- Deep Learning Framework Detects Fractures in X-Ray Images With 99% Accuracy
- Direct AI-Based Medical X-Ray Imaging System a Paradigm-Shift from Conventional DR and CT
- Chest X-Ray AI Solution Automatically Identifies, Categorizes and Highlights Suspicious Areas
- AI Diagnoses Wrist Fractures As Well As Radiologists
- Annual Mammography Beginning At 40 Cuts Breast Cancer Mortality By 42%
- 3D Human GPS Powered By Light Paves Way for Radiation-Free Minimally-Invasive Surgery
- Novel AI Technology to Revolutionize Cancer Detection in Dense Breasts
- AI Solution Provides Radiologists with 'Second Pair' Of Eyes to Detect Breast Cancers
- AI Helps General Radiologists Achieve Specialist-Level Performance in Interpreting Mammograms
- Novel Imaging Technique Could Transform Breast Cancer Detection
- Computer Program Combines AI and Heat-Imaging Technology for Early Breast Cancer Detection
Channels
MRI
view channel
Diamond Dust Could Offer New Contrast Agent Option for Future MRI Scans
Gadolinium, a heavy metal used for over three decades as a contrast agent in medical imaging, enhances the clarity of MRI scans by highlighting affected areas. Despite its utility, gadolinium not only... Read more.jpg)
Combining MRI with PSA Testing Improves Clinical Outcomes for Prostate Cancer Patients
Prostate cancer is a leading health concern globally, consistently being one of the most common types of cancer among men and a major cause of cancer-related deaths. In the United States, it is the most... Read more
PET/MRI Improves Diagnostic Accuracy for Prostate Cancer Patients
The Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System (PI-RADS) is a five-point scale to assess potential prostate cancer in MR images. PI-RADS category 3 which offers an unclear suggestion of clinically significant... Read more
Next Generation MR-Guided Focused Ultrasound Ushers In Future of Incisionless Neurosurgery
Essential tremor, often called familial, idiopathic, or benign tremor, leads to uncontrollable shaking that significantly affects a person’s life. When traditional medications do not alleviate symptoms,... Read moreUltrasound
view channel.jpg)
Groundbreaking Technology Enables Precise, Automatic Measurement of Peripheral Blood Vessels
The current standard of care of using angiographic information is often inadequate for accurately assessing vessel size in the estimated 20 million people in the U.S. who suffer from peripheral vascular disease.... Read more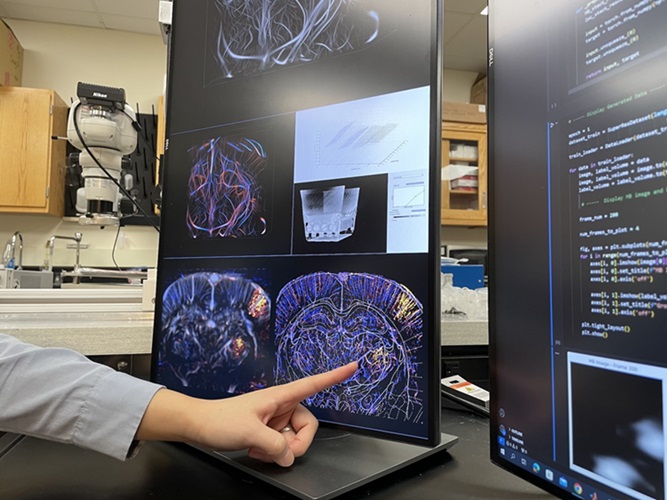
Deep Learning Advances Super-Resolution Ultrasound Imaging
Ultrasound localization microscopy (ULM) is an advanced imaging technique that offers high-resolution visualization of microvascular structures. It employs microbubbles, FDA-approved contrast agents, injected... Read more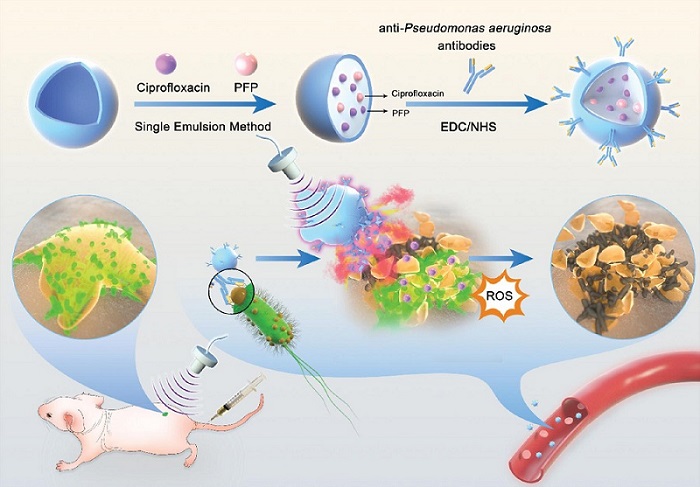
Novel Ultrasound-Launched Targeted Nanoparticle Eliminates Biofilm and Bacterial Infection
Biofilms, formed by bacteria aggregating into dense communities for protection against harsh environmental conditions, are a significant contributor to various infectious diseases. Biofilms frequently... Read moreNuclear Medicine
view channel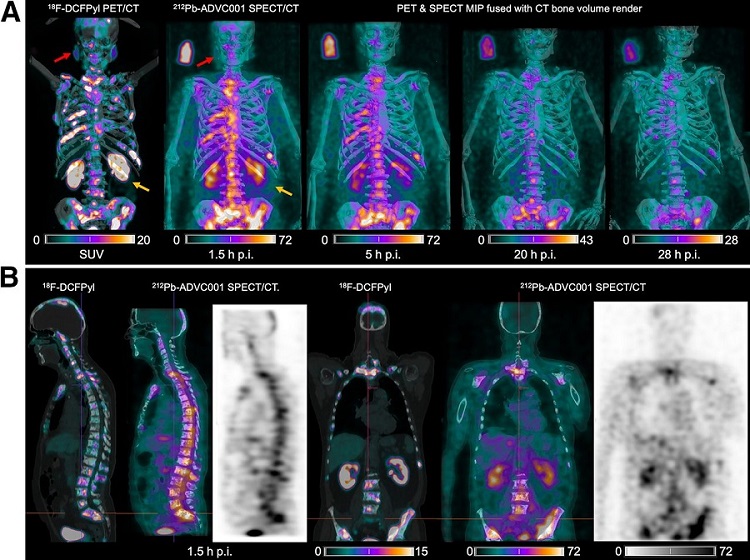
New SPECT/CT Technique Could Change Imaging Practices and Increase Patient Access
The development of lead-212 (212Pb)-PSMA–based targeted alpha therapy (TAT) is garnering significant interest in treating patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. The imaging of 212Pb,... Read moreNew Radiotheranostic System Detects and Treats Ovarian Cancer Noninvasively
Ovarian cancer is the most lethal gynecological cancer, with less than a 30% five-year survival rate for those diagnosed in late stages. Despite surgery and platinum-based chemotherapy being the standard... Read more
AI System Automatically and Reliably Detects Cardiac Amyloidosis Using Scintigraphy Imaging
Cardiac amyloidosis, a condition characterized by the buildup of abnormal protein deposits (amyloids) in the heart muscle, severely affects heart function and can lead to heart failure or death without... Read moreGeneral/Advanced Imaging
view channel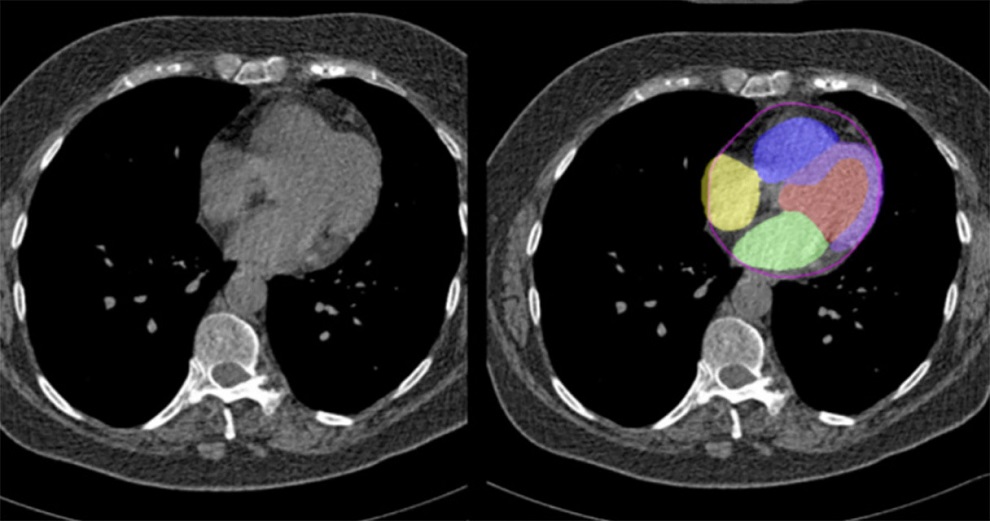
Artificial Intelligence Evaluates Cardiovascular Risk from CT Scans
Chest computed tomography (CT) is a common diagnostic tool, with approximately 15 million scans conducted each year in the United States, though many are underutilized or not fully explored.... Read more
New AI Method Captures Uncertainty in Medical Images
In the field of biomedicine, segmentation is the process of annotating pixels from an important structure in medical images, such as organs or cells. Artificial Intelligence (AI) models are utilized to... Read more.jpg)
CT Coronary Angiography Reduces Need for Invasive Tests to Diagnose Coronary Artery Disease
Coronary artery disease (CAD), one of the leading causes of death worldwide, involves the narrowing of coronary arteries due to atherosclerosis, resulting in insufficient blood flow to the heart muscle.... Read more
Novel Blood Test Could Reduce Need for PET Imaging of Patients with Alzheimer’s
Alzheimer's disease (AD), a condition marked by cognitive decline and the presence of beta-amyloid (Aβ) plaques and neurofibrillary tangles in the brain, poses diagnostic challenges. Amyloid positron emission... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more
Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in medical diagnostics market is expanding with early disease detection being one of its key applications and image recognition becoming a compelling consumer proposition... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
Bayer and Google Partner on New AI Product for Radiologists
Medical imaging data comprises around 90% of all healthcare data, and it is a highly complex and rich clinical data modality and serves as a vital tool for diagnosing patients. Each year, billions of medical... Read more