New CT Scanning Technology Is Faster, Uses Less Radiation, and Easier on the Kidneys
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 26 Aug 2014 |
Patients who must undergo computed tomography (CT) scanning now have a new option for screening that is extremely fast, uses less radiation, and is safer for the kidneys.
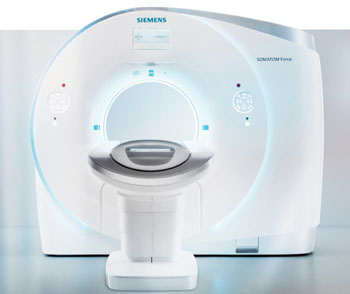
With US Food and Administration (FDA) approval granted in April 2014, the Siemens Healthcare (Erlangen, Germany) Somatom Force CT scanner is currently available for patient use in only two sites in the United States, the Medical University of South Carolina (MUSC; Charleston, USA) and the Mayo Clinic (Rochester, MN, USA).
Pioneering the new technology and evaluation its use in recent months, MUSC radiologist and professor Joseph Schoepf, MD, is excited about the new technology. “This technology is a dramatic leap that not only produces better images, but it really allows for a better patient experience,” he said. “Knowing there is less radiation and increased accuracy through this innovation in technology is invaluable to both patients and physicians. Similarly, knowing that only minimal amounts of contrast dye are needed is reassuring to patients with decreased kidney function and their doctors. Knowing the imaging study will be over in mere seconds can be a simple, yet dramatic comfort during a difficult time, especially in patients who have a difficult time staying still or holding their breath.”
With two sets of Siemens’ X-ray tubes and detectors, the Somatom Force CT extends sophisticated imaging to all patients, including some of the most challenging: young children, patients with kidney problems, and patients who are unable to hold their breath. By overcoming some of these imaging limitations, MUSC is making CT scanning available for a wider range of patients.
Former US Ambassador to the United Kingdom, Philip Lader, recently underwent his scan with the new technology at MUSC. “By increasing diagnostic accuracy and decreasing the amount of radiation, as a patient, it just gives me more confidence in the tools they are using to help monitor my heart and make sure that we are doing what we need to do, when we need to do it.”
Related Links:
Medical University of South Carolina
Siemens Healthcare
With US Food and Administration (FDA) approval granted in April 2014, the Siemens Healthcare (Erlangen, Germany) Somatom Force CT scanner is currently available for patient use in only two sites in the United States, the Medical University of South Carolina (MUSC; Charleston, USA) and the Mayo Clinic (Rochester, MN, USA).
Pioneering the new technology and evaluation its use in recent months, MUSC radiologist and professor Joseph Schoepf, MD, is excited about the new technology. “This technology is a dramatic leap that not only produces better images, but it really allows for a better patient experience,” he said. “Knowing there is less radiation and increased accuracy through this innovation in technology is invaluable to both patients and physicians. Similarly, knowing that only minimal amounts of contrast dye are needed is reassuring to patients with decreased kidney function and their doctors. Knowing the imaging study will be over in mere seconds can be a simple, yet dramatic comfort during a difficult time, especially in patients who have a difficult time staying still or holding their breath.”
With two sets of Siemens’ X-ray tubes and detectors, the Somatom Force CT extends sophisticated imaging to all patients, including some of the most challenging: young children, patients with kidney problems, and patients who are unable to hold their breath. By overcoming some of these imaging limitations, MUSC is making CT scanning available for a wider range of patients.
Former US Ambassador to the United Kingdom, Philip Lader, recently underwent his scan with the new technology at MUSC. “By increasing diagnostic accuracy and decreasing the amount of radiation, as a patient, it just gives me more confidence in the tools they are using to help monitor my heart and make sure that we are doing what we need to do, when we need to do it.”
Related Links:
Medical University of South Carolina
Siemens Healthcare
Read the full article by registering today, it's FREE! 

Register now for FREE to MedImaging.net and get complete access to news and events that shape the world of Radiology. 
- Free digital version edition of Medical Imaging International sent by email on regular basis
- Free print version of Medical Imaging International magazine (available only outside USA and Canada).
- Free and unlimited access to back issues of Medical Imaging International in digital format
- Free Medical Imaging International Newsletter sent every week containing the latest news
- Free breaking news sent via email
- Free access to Events Calendar
- Free access to LinkXpress new product services
- REGISTRATION IS FREE AND EASY!
Sign in: Registered website members
Sign in: Registered magazine subscribers
Latest Radiography News
- Novel Breast Imaging System Proves As Effective As Mammography
- AI Assistance Improves Breast-Cancer Screening by Reducing False Positives
- AI Could Boost Clinical Adoption of Chest DDR
- 3D Mammography Almost Halves Breast Cancer Incidence between Two Screening Tests
- AI Model Predicts 5-Year Breast Cancer Risk from Mammograms
- Deep Learning Framework Detects Fractures in X-Ray Images With 99% Accuracy
- Direct AI-Based Medical X-Ray Imaging System a Paradigm-Shift from Conventional DR and CT
- Chest X-Ray AI Solution Automatically Identifies, Categorizes and Highlights Suspicious Areas
- AI Diagnoses Wrist Fractures As Well As Radiologists
- Annual Mammography Beginning At 40 Cuts Breast Cancer Mortality By 42%
- 3D Human GPS Powered By Light Paves Way for Radiation-Free Minimally-Invasive Surgery
- Novel AI Technology to Revolutionize Cancer Detection in Dense Breasts
- AI Solution Provides Radiologists with 'Second Pair' Of Eyes to Detect Breast Cancers
- AI Helps General Radiologists Achieve Specialist-Level Performance in Interpreting Mammograms
- Novel Imaging Technique Could Transform Breast Cancer Detection
- Computer Program Combines AI and Heat-Imaging Technology for Early Breast Cancer Detection
Channels
MRI
view channel
Diamond Dust Could Offer New Contrast Agent Option for Future MRI Scans
Gadolinium, a heavy metal used for over three decades as a contrast agent in medical imaging, enhances the clarity of MRI scans by highlighting affected areas. Despite its utility, gadolinium not only... Read more.jpg)
Combining MRI with PSA Testing Improves Clinical Outcomes for Prostate Cancer Patients
Prostate cancer is a leading health concern globally, consistently being one of the most common types of cancer among men and a major cause of cancer-related deaths. In the United States, it is the most... Read more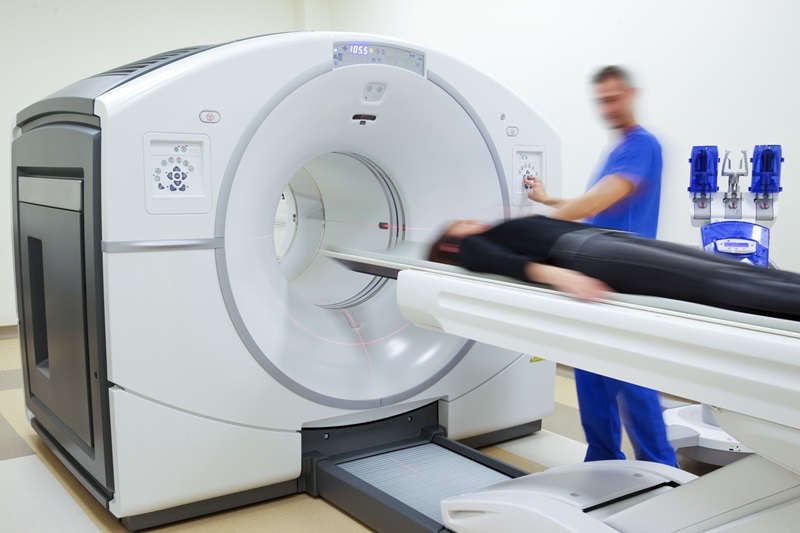
PET/MRI Improves Diagnostic Accuracy for Prostate Cancer Patients
The Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System (PI-RADS) is a five-point scale to assess potential prostate cancer in MR images. PI-RADS category 3 which offers an unclear suggestion of clinically significant... Read more
Next Generation MR-Guided Focused Ultrasound Ushers In Future of Incisionless Neurosurgery
Essential tremor, often called familial, idiopathic, or benign tremor, leads to uncontrollable shaking that significantly affects a person’s life. When traditional medications do not alleviate symptoms,... Read moreUltrasound
view channel.jpg)
Groundbreaking Technology Enables Precise, Automatic Measurement of Peripheral Blood Vessels
The current standard of care of using angiographic information is often inadequate for accurately assessing vessel size in the estimated 20 million people in the U.S. who suffer from peripheral vascular disease.... Read more
Deep Learning Advances Super-Resolution Ultrasound Imaging
Ultrasound localization microscopy (ULM) is an advanced imaging technique that offers high-resolution visualization of microvascular structures. It employs microbubbles, FDA-approved contrast agents, injected... Read more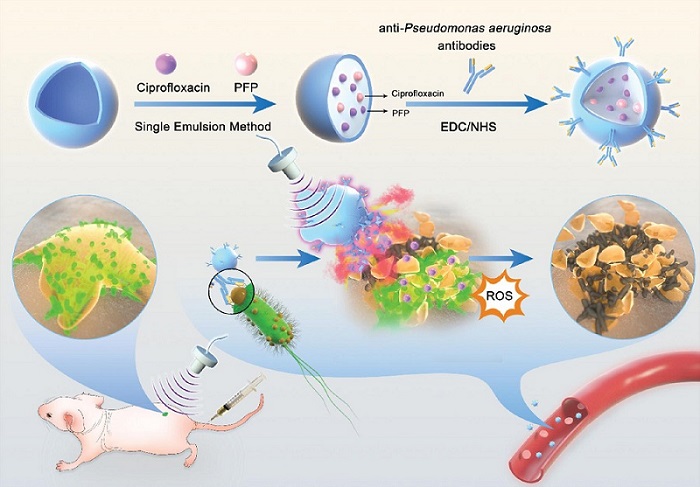
Novel Ultrasound-Launched Targeted Nanoparticle Eliminates Biofilm and Bacterial Infection
Biofilms, formed by bacteria aggregating into dense communities for protection against harsh environmental conditions, are a significant contributor to various infectious diseases. Biofilms frequently... Read moreNuclear Medicine
view channel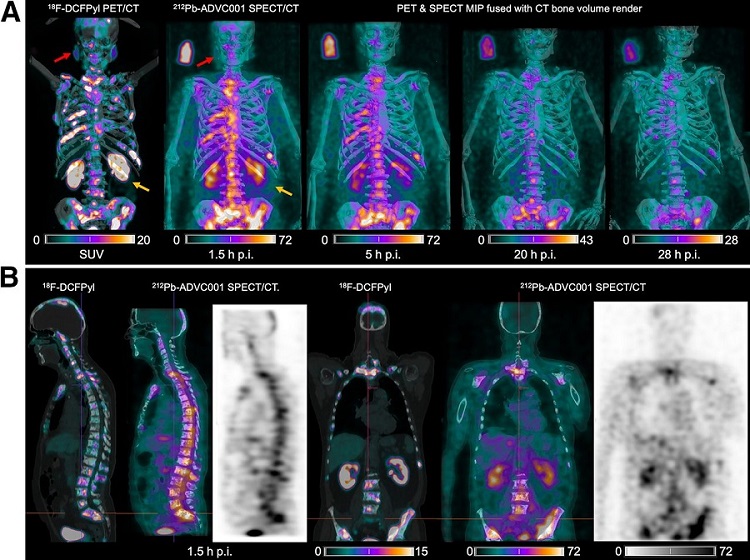
New SPECT/CT Technique Could Change Imaging Practices and Increase Patient Access
The development of lead-212 (212Pb)-PSMA–based targeted alpha therapy (TAT) is garnering significant interest in treating patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. The imaging of 212Pb,... Read moreNew Radiotheranostic System Detects and Treats Ovarian Cancer Noninvasively
Ovarian cancer is the most lethal gynecological cancer, with less than a 30% five-year survival rate for those diagnosed in late stages. Despite surgery and platinum-based chemotherapy being the standard... Read more
AI System Automatically and Reliably Detects Cardiac Amyloidosis Using Scintigraphy Imaging
Cardiac amyloidosis, a condition characterized by the buildup of abnormal protein deposits (amyloids) in the heart muscle, severely affects heart function and can lead to heart failure or death without... Read moreGeneral/Advanced Imaging
view channel
PET Scans Reveal Hidden Inflammation in Multiple Sclerosis Patients
A key challenge for clinicians treating patients with multiple sclerosis (MS) is that after a certain amount of time, they continue to worsen even though their MRIs show no change. A new study has now... Read more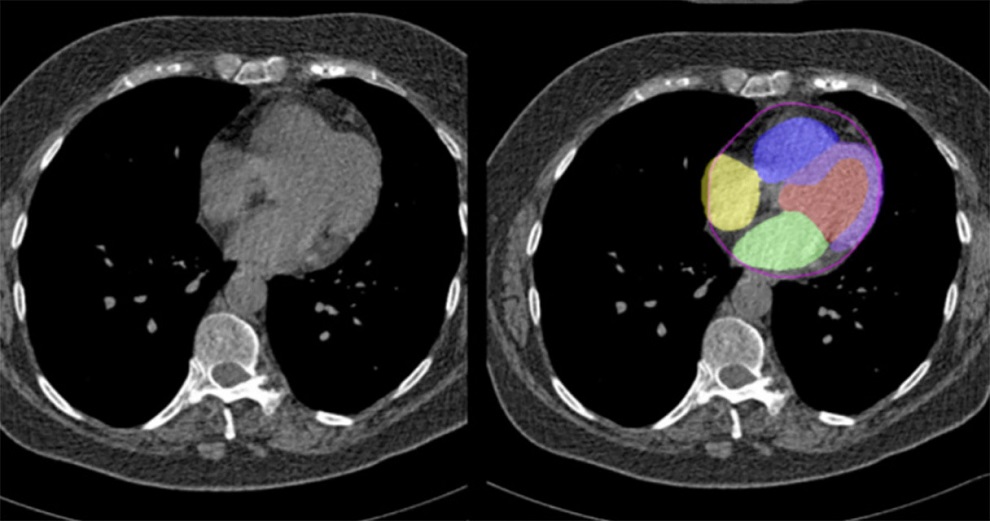
Artificial Intelligence Evaluates Cardiovascular Risk from CT Scans
Chest computed tomography (CT) is a common diagnostic tool, with approximately 15 million scans conducted each year in the United States, though many are underutilized or not fully explored.... Read more
New AI Method Captures Uncertainty in Medical Images
In the field of biomedicine, segmentation is the process of annotating pixels from an important structure in medical images, such as organs or cells. Artificial Intelligence (AI) models are utilized to... Read more.jpg)
CT Coronary Angiography Reduces Need for Invasive Tests to Diagnose Coronary Artery Disease
Coronary artery disease (CAD), one of the leading causes of death worldwide, involves the narrowing of coronary arteries due to atherosclerosis, resulting in insufficient blood flow to the heart muscle.... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more
Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in medical diagnostics market is expanding with early disease detection being one of its key applications and image recognition becoming a compelling consumer proposition... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
Bayer and Google Partner on New AI Product for Radiologists
Medical imaging data comprises around 90% of all healthcare data, and it is a highly complex and rich clinical data modality and serves as a vital tool for diagnosing patients. Each year, billions of medical... Read more