New Model Improves Comparison of MRIs Taken at Different Institutions
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 03 Mar 2025 |

Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) plays a crucial role in medicine by offering detailed views of the internal structures of the body and providing valuable insights into various pathologies. However, inconsistencies in image acquisition protocols across different institutions create significant challenges in ensuring reliable and consistent interpretation, especially in multi-center research. To address this issue, a new study has introduced a method for modifying MRI scans from different hospitals, making them more comparable and enabling more accurate and dependable comparisons.
Harmonizing MRI results is a fundamental issue in both research and healthcare quality. Each medical facility, clinic, or research institution uses its own set of imaging protocols, equipment, and parameters, leading to variations in contrast, brightness, and other characteristics of the images. This variability presents a major challenge in clinical research, particularly when data from multiple research centers are combined. In a collaborative study led by researchers from Université de Montreal (Montreal, Canada), a new harmonization technique was developed, which involves three main steps. The first step is to create a model that learns how MRI images in the source domain.
Once the distribution of the source domain is understood, the next goal is to "re-format" MRI scans from other institutions to remove variations caused by differences in machine settings or parameter choices, while still maintaining patient-specific differences. Finally, when the model is applied to new images (for example, from an unfamiliar machine), it must adapt to ensure that the newly processed images continue to follow the learned distribution. To validate their approach, the researchers tested the harmonization method on MRI brain scans from databases in the United States, as well as from a neonatal imaging consortium developed with Australian researchers. These data were used for two key tasks: first, to segment brain images in both adults and newborns to verify if brain structures remained consistent after harmonization, and second, to estimate the brain age of newborns.
The study, published in Medical Image Analysis, demonstrated that this new technique outperforms existing harmonization methods, showcasing its versatility across various tasks and population groups. Notably, the method was successfully validated on MRI scans of a newborn’s brain with lesions—something that all other available models fail to handle since they are typically trained on images of healthy brains. Looking ahead, the researchers plan to apply this approach on a larger scale in future collaborations and studies, which will help improve the comparison and analysis of research data and further enhance the accuracy and reliability of medical diagnoses.
“Thanks to this model, we can now interpret data from several thousands of families and children who are monitored at various hospitals – data that come from different scanners," said Dr. Gregory Lodygensky, a clinical professor at Université de Montreal. "The analysis of these large cohorts in children and adults was hampered by the major harmonization problem, which has now been resolved.”
Latest MRI News
- New MRI Technique Reveals Hidden Heart Issues
- Shorter MRI Exam Effectively Detects Cancer in Dense Breasts
- MRI to Replace Painful Spinal Tap for Faster MS Diagnosis
- MRI Scans Can Identify Cardiovascular Disease Ten Years in Advance
- Simple Brain Scan Diagnoses Parkinson's Disease Years Before It Becomes Untreatable
- Cutting-Edge MRI Technology to Revolutionize Diagnosis of Common Heart Problem
- New MRI Technique Reveals True Heart Age to Prevent Attacks and Strokes
- AI Tool Predicts Relapse of Pediatric Brain Cancer from Brain MRI Scans
- AI Tool Tracks Effectiveness of Multiple Sclerosis Treatments Using Brain MRI Scans
- Ultra-Powerful MRI Scans Enable Life-Changing Surgery in Treatment-Resistant Epileptic Patients
- AI-Powered MRI Technology Improves Parkinson’s Diagnoses
- Biparametric MRI Combined with AI Enhances Detection of Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer
- First-Of-Its-Kind AI-Driven Brain Imaging Platform to Better Guide Stroke Treatment Options
- Groundbreaking New Scanner Sees 'Previously Undetectable' Cancer Spread
- First-Of-Its-Kind Tool Analyzes MRI Scans to Measure Brain Aging
- AI-Enhanced MRI Images Make Cancerous Breast Tissue Glow
Channels
Radiography
view channel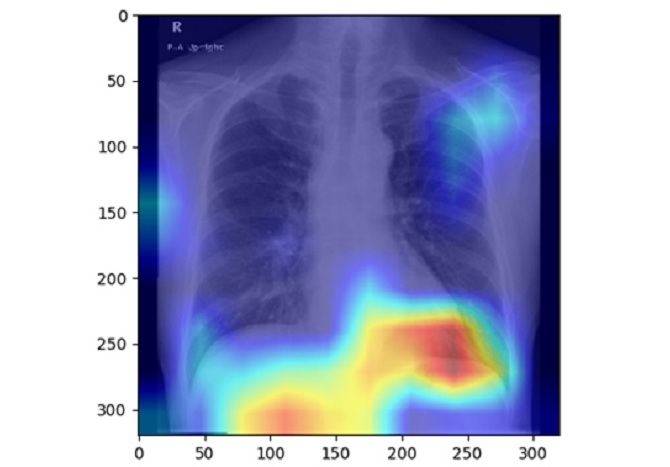
AI Detects Fatty Liver Disease from Chest X-Rays
Fatty liver disease, which results from excess fat accumulation in the liver, is believed to impact approximately one in four individuals globally. If not addressed in time, it can progress to severe conditions... Read more
AI Detects Hidden Heart Disease in Existing CT Chest Scans
Coronary artery calcium (CAC) is a major indicator of cardiovascular risk, but its assessment typically requires a specialized “gated” CT scan that synchronizes with the heartbeat. In contrast, most chest... Read moreUltrasound
view channel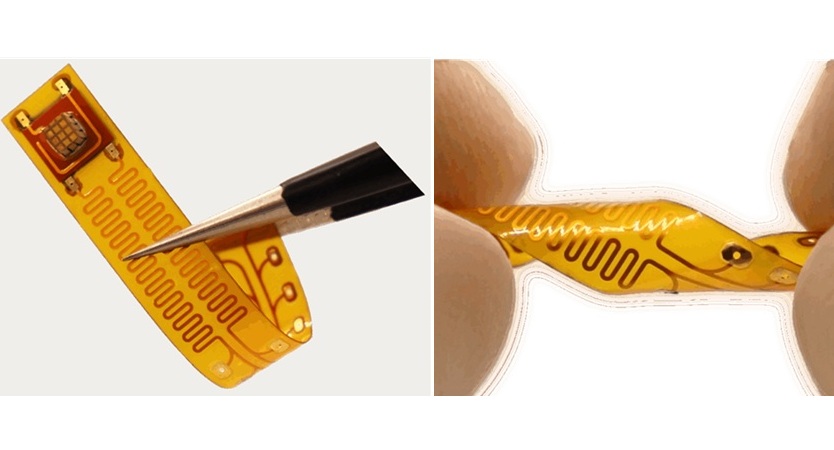
Wireless Chronic Pain Management Device to Reduce Need for Painkillers and Surgery
Chronic pain affects millions of people globally, often leading to long-term disability and dependence on opioid medications, which carry significant risks of side effects and addiction.... Read more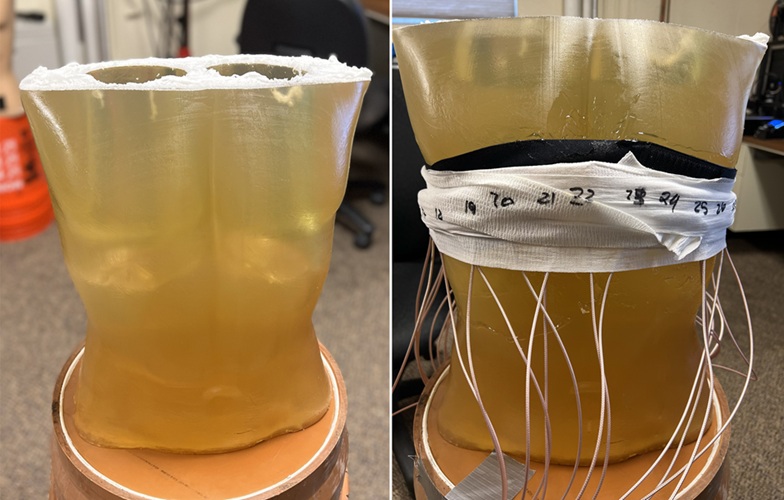
New Medical Ultrasound Imaging Technique Enables ICU Bedside Monitoring
Ultrasound computed tomography (USCT) presents a safer alternative to imaging techniques like X-ray computed tomography (commonly known as CT or “CAT” scans) because it does not produce ionizing radiation.... Read moreNuclear Medicine
view channel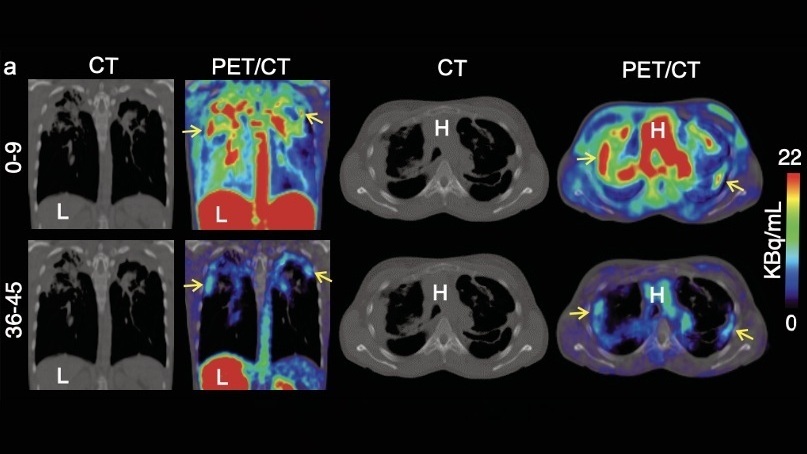
Novel Bacteria-Specific PET Imaging Approach Detects Hard-To-Diagnose Lung Infections
Mycobacteroides abscessus is a rapidly growing mycobacteria that primarily affects immunocompromised patients and those with underlying lung diseases, such as cystic fibrosis or chronic obstructive pulmonary... Read more
New Imaging Approach Could Reduce Need for Biopsies to Monitor Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer is the second leading cause of cancer-related death among men in the United States. However, the majority of older men diagnosed with prostate cancer have slow-growing, low-risk forms of... Read moreGeneral/Advanced Imaging
view channel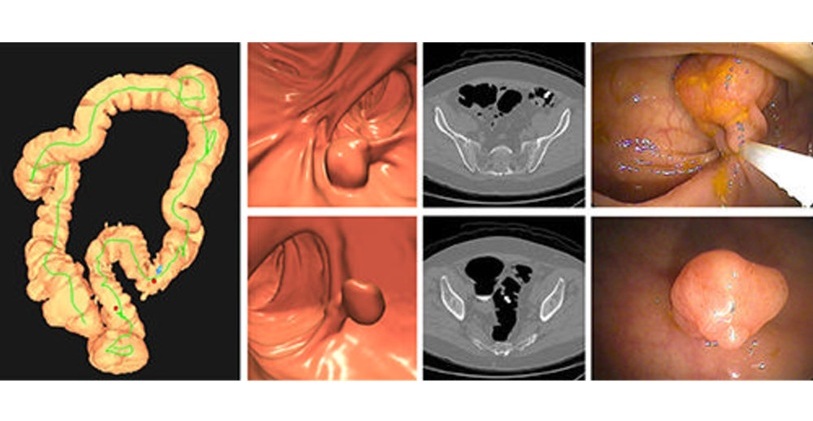
CT Colonography Beats Stool DNA Testing for Colon Cancer Screening
As colorectal cancer remains the second leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide, early detection through screening is vital to reduce advanced-stage treatments and associated costs.... Read more
First-Of-Its-Kind Wearable Device Offers Revolutionary Alternative to CT Scans
Currently, patients with conditions such as heart failure, pneumonia, or respiratory distress often require multiple imaging procedures that are intermittent, disruptive, and involve high levels of radiation.... Read more
AI-Based CT Scan Analysis Predicts Early-Stage Kidney Damage Due to Cancer Treatments
Radioligand therapy, a form of targeted nuclear medicine, has recently gained attention for its potential in treating specific types of tumors. However, one of the potential side effects of this therapy... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more
Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in medical diagnostics market is expanding with early disease detection being one of its key applications and image recognition becoming a compelling consumer proposition... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
GE HealthCare and NVIDIA Collaboration to Reimagine Diagnostic Imaging
GE HealthCare (Chicago, IL, USA) has entered into a collaboration with NVIDIA (Santa Clara, CA, USA), expanding the existing relationship between the two companies to focus on pioneering innovation in... Read more
Patient-Specific 3D-Printed Phantoms Transform CT Imaging
New research has highlighted how anatomically precise, patient-specific 3D-printed phantoms are proving to be scalable, cost-effective, and efficient tools in the development of new CT scan algorithms... Read more
Siemens and Sectra Collaborate on Enhancing Radiology Workflows
Siemens Healthineers (Forchheim, Germany) and Sectra (Linköping, Sweden) have entered into a collaboration aimed at enhancing radiologists' diagnostic capabilities and, in turn, improving patient care... Read more










 Guided Devices.jpg)


.jpeg)




