AI System Detects Subtle Changes in Series of Medical Images Over Time
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 28 Feb 2025 |
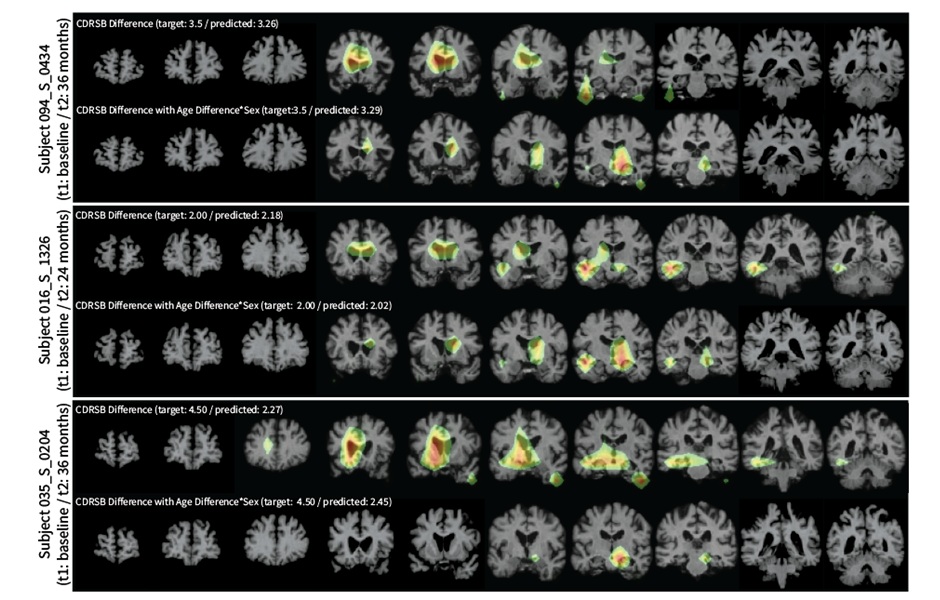
Traditional approaches for analyzing longitudinal image datasets typically require significant customization and extensive pre-processing. For instance, in studies of the brain, researchers often begin with raw brain MRI data, focusing on a specific brain area, correcting for variations in view angles, adjusting for size discrepancies, and eliminating artifacts—before proceeding with the main analysis. Now, a new AI-driven system that can effectively detect changes in medical images over time and predict outcomes offers enhanced sensitivity and adaptability, making it applicable to a wide variety of medical and scientific contexts.
This innovative system, called LILAC (Learning-based Inference of Longitudinal imAge Changes), leverages machine learning techniques and was developed by researchers at Weill Cornell Medicine (New York City, NY, USA). In a study published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, the team demonstrated how LILAC could analyze diverse time-series images, or longitudinal data, which included developing IVF embryos, healing tissues after injuries, and aging brains. The researchers found that LILAC can detect even minute differences between images taken over time and predict related outcomes, such as cognitive scores from brain scans. The system is designed to work with much greater flexibility by automatically handling corrections and identifying key changes.
In a proof-of-concept experiment, the researchers trained LILAC on hundreds of image sequences from in-vitro fertilized embryos as they developed. The system was then tested on new sequences to determine which image in each pair was taken first—a task that is difficult to perform without a clear time-related signal in the images. LILAC accurately completed this task with around 99% accuracy, with only a few errors in image pairs with short time intervals. Additionally, LILAC proved highly effective in ordering images of healing tissue from the same sequences and detecting group-level differences in healing rates between untreated tissue and tissue that had undergone an experimental treatment.
Similarly, LILAC was able to predict time intervals between MRI scans of healthy older adults' brains, as well as estimate individual cognitive scores from MRIs of patients with mild cognitive impairment, performing with much less error compared to conventional methods. In all these cases, the researchers showed that LILAC could be easily adapted to emphasize the most relevant image features for detecting changes in individual subjects or distinguishing between groups, potentially offering new clinical and scientific insights. The next phase of research will involve testing LILAC in real-world settings, such as predicting treatment responses from MRI scans of prostate cancer patients.
“This new tool will allow us to detect and quantify clinically relevant changes over time in ways that weren't possible before, and its flexibility means that it can be applied off-the-shelf to virtually any longitudinal imaging dataset,” said study senior author Dr. Mert Sabuncu. “We expect this tool to be useful especially in cases where we lack knowledge about the process being studied, and where there is a lot of variability across individuals.”
Latest MRI News
- New MRI Technique Reveals True Heart Age to Prevent Attacks and Strokes
- AI Tool Predicts Relapse of Pediatric Brain Cancer from Brain MRI Scans
- AI Tool Tracks Effectiveness of Multiple Sclerosis Treatments Using Brain MRI Scans
- Ultra-Powerful MRI Scans Enable Life-Changing Surgery in Treatment-Resistant Epileptic Patients
- AI-Powered MRI Technology Improves Parkinson’s Diagnoses
- Biparametric MRI Combined with AI Enhances Detection of Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer
- First-Of-Its-Kind AI-Driven Brain Imaging Platform to Better Guide Stroke Treatment Options
- New Model Improves Comparison of MRIs Taken at Different Institutions
- Groundbreaking New Scanner Sees 'Previously Undetectable' Cancer Spread
- First-Of-Its-Kind Tool Analyzes MRI Scans to Measure Brain Aging
- AI-Enhanced MRI Images Make Cancerous Breast Tissue Glow
- AI Model Automatically Segments MRI Images
- New Research Supports Routine Brain MRI Screening in Asymptomatic Late-Stage Breast Cancer Patients
- Revolutionary Portable Device Performs Rapid MRI-Based Stroke Imaging at Patient's Bedside
- AI Predicts After-Effects of Brain Tumor Surgery from MRI Scans
- MRI-First Strategy for Prostate Cancer Detection Proven Safe
Channels
Radiography
view channel
AI Improves Early Detection of Interval Breast Cancers
Interval breast cancers, which occur between routine screenings, are easier to treat when detected earlier. Early detection can reduce the need for aggressive treatments and improve the chances of better outcomes.... Read more
World's Largest Class Single Crystal Diamond Radiation Detector Opens New Possibilities for Diagnostic Imaging
Diamonds possess ideal physical properties for radiation detection, such as exceptional thermal and chemical stability along with a quick response time. Made of carbon with an atomic number of six, diamonds... Read moreMRI
view channel
New MRI Technique Reveals True Heart Age to Prevent Attacks and Strokes
Heart disease remains one of the leading causes of death worldwide. Individuals with conditions such as diabetes or obesity often experience accelerated aging of their hearts, sometimes by decades.... Read more
AI Tool Predicts Relapse of Pediatric Brain Cancer from Brain MRI Scans
Many pediatric gliomas are treatable with surgery alone, but relapses can be catastrophic. Predicting which patients are at risk for recurrence remains challenging, leading to frequent follow-ups with... Read more
AI Tool Tracks Effectiveness of Multiple Sclerosis Treatments Using Brain MRI Scans
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a condition in which the immune system attacks the brain and spinal cord, leading to impairments in movement, sensation, and cognition. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) markers... Read more
Ultra-Powerful MRI Scans Enable Life-Changing Surgery in Treatment-Resistant Epileptic Patients
Approximately 360,000 individuals in the UK suffer from focal epilepsy, a condition in which seizures spread from one part of the brain. Around a third of these patients experience persistent seizures... Read moreUltrasound
view channel.jpeg)
AI-Powered Lung Ultrasound Outperforms Human Experts in Tuberculosis Diagnosis
Despite global declines in tuberculosis (TB) rates in previous years, the incidence of TB rose by 4.6% from 2020 to 2023. Early screening and rapid diagnosis are essential elements of the World Health... Read more
AI Identifies Heart Valve Disease from Common Imaging Test
Tricuspid regurgitation is a condition where the heart's tricuspid valve does not close completely during contraction, leading to backward blood flow, which can result in heart failure. A new artificial... Read moreNuclear Medicine
view channel
Novel Radiolabeled Antibody Improves Diagnosis and Treatment of Solid Tumors
Interleukin-13 receptor α-2 (IL13Rα2) is a cell surface receptor commonly found in solid tumors such as glioblastoma, melanoma, and breast cancer. It is minimally expressed in normal tissues, making it... Read more
Novel PET Imaging Approach Offers Never-Before-Seen View of Neuroinflammation
COX-2, an enzyme that plays a key role in brain inflammation, can be significantly upregulated by inflammatory stimuli and neuroexcitation. Researchers suggest that COX-2 density in the brain could serve... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more
Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in medical diagnostics market is expanding with early disease detection being one of its key applications and image recognition becoming a compelling consumer proposition... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
GE HealthCare and NVIDIA Collaboration to Reimagine Diagnostic Imaging
GE HealthCare (Chicago, IL, USA) has entered into a collaboration with NVIDIA (Santa Clara, CA, USA), expanding the existing relationship between the two companies to focus on pioneering innovation in... Read more
Patient-Specific 3D-Printed Phantoms Transform CT Imaging
New research has highlighted how anatomically precise, patient-specific 3D-printed phantoms are proving to be scalable, cost-effective, and efficient tools in the development of new CT scan algorithms... Read more
Siemens and Sectra Collaborate on Enhancing Radiology Workflows
Siemens Healthineers (Forchheim, Germany) and Sectra (Linköping, Sweden) have entered into a collaboration aimed at enhancing radiologists' diagnostic capabilities and, in turn, improving patient care... Read more



















