AI System Detects Subtle Changes in Series of Medical Images Over Time
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 28 Feb 2025 |
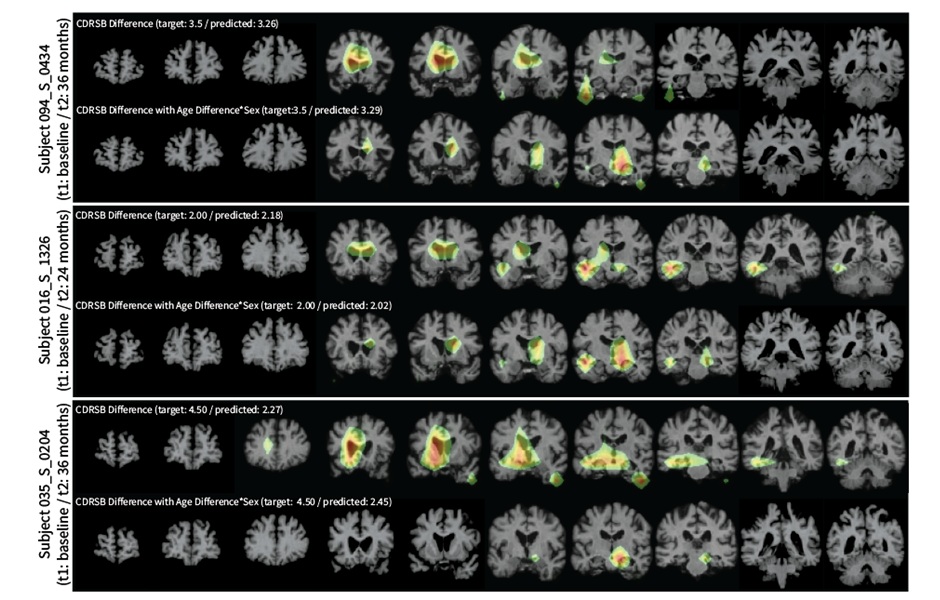
Traditional approaches for analyzing longitudinal image datasets typically require significant customization and extensive pre-processing. For instance, in studies of the brain, researchers often begin with raw brain MRI data, focusing on a specific brain area, correcting for variations in view angles, adjusting for size discrepancies, and eliminating artifacts—before proceeding with the main analysis. Now, a new AI-driven system that can effectively detect changes in medical images over time and predict outcomes offers enhanced sensitivity and adaptability, making it applicable to a wide variety of medical and scientific contexts.
This innovative system, called LILAC (Learning-based Inference of Longitudinal imAge Changes), leverages machine learning techniques and was developed by researchers at Weill Cornell Medicine (New York City, NY, USA). In a study published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, the team demonstrated how LILAC could analyze diverse time-series images, or longitudinal data, which included developing IVF embryos, healing tissues after injuries, and aging brains. The researchers found that LILAC can detect even minute differences between images taken over time and predict related outcomes, such as cognitive scores from brain scans. The system is designed to work with much greater flexibility by automatically handling corrections and identifying key changes.
In a proof-of-concept experiment, the researchers trained LILAC on hundreds of image sequences from in-vitro fertilized embryos as they developed. The system was then tested on new sequences to determine which image in each pair was taken first—a task that is difficult to perform without a clear time-related signal in the images. LILAC accurately completed this task with around 99% accuracy, with only a few errors in image pairs with short time intervals. Additionally, LILAC proved highly effective in ordering images of healing tissue from the same sequences and detecting group-level differences in healing rates between untreated tissue and tissue that had undergone an experimental treatment.
Similarly, LILAC was able to predict time intervals between MRI scans of healthy older adults' brains, as well as estimate individual cognitive scores from MRIs of patients with mild cognitive impairment, performing with much less error compared to conventional methods. In all these cases, the researchers showed that LILAC could be easily adapted to emphasize the most relevant image features for detecting changes in individual subjects or distinguishing between groups, potentially offering new clinical and scientific insights. The next phase of research will involve testing LILAC in real-world settings, such as predicting treatment responses from MRI scans of prostate cancer patients.
“This new tool will allow us to detect and quantify clinically relevant changes over time in ways that weren't possible before, and its flexibility means that it can be applied off-the-shelf to virtually any longitudinal imaging dataset,” said study senior author Dr. Mert Sabuncu. “We expect this tool to be useful especially in cases where we lack knowledge about the process being studied, and where there is a lot of variability across individuals.”
Latest MRI News
- New MRI Technique Reveals Hidden Heart Issues
- Shorter MRI Exam Effectively Detects Cancer in Dense Breasts
- MRI to Replace Painful Spinal Tap for Faster MS Diagnosis
- MRI Scans Can Identify Cardiovascular Disease Ten Years in Advance
- Simple Brain Scan Diagnoses Parkinson's Disease Years Before It Becomes Untreatable
- Cutting-Edge MRI Technology to Revolutionize Diagnosis of Common Heart Problem
- New MRI Technique Reveals True Heart Age to Prevent Attacks and Strokes
- AI Tool Predicts Relapse of Pediatric Brain Cancer from Brain MRI Scans
- AI Tool Tracks Effectiveness of Multiple Sclerosis Treatments Using Brain MRI Scans
- Ultra-Powerful MRI Scans Enable Life-Changing Surgery in Treatment-Resistant Epileptic Patients
- AI-Powered MRI Technology Improves Parkinson’s Diagnoses
- Biparametric MRI Combined with AI Enhances Detection of Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer
- First-Of-Its-Kind AI-Driven Brain Imaging Platform to Better Guide Stroke Treatment Options
- New Model Improves Comparison of MRIs Taken at Different Institutions
- Groundbreaking New Scanner Sees 'Previously Undetectable' Cancer Spread
- First-Of-Its-Kind Tool Analyzes MRI Scans to Measure Brain Aging
Channels
Radiography
view channel
AI Detects Fatty Liver Disease from Chest X-Rays
Fatty liver disease, which results from excess fat accumulation in the liver, is believed to impact approximately one in four individuals globally. If not addressed in time, it can progress to severe conditions... Read more
AI Detects Hidden Heart Disease in Existing CT Chest Scans
Coronary artery calcium (CAC) is a major indicator of cardiovascular risk, but its assessment typically requires a specialized “gated” CT scan that synchronizes with the heartbeat. In contrast, most chest... Read moreMRI
view channel
New MRI Technique Reveals Hidden Heart Issues
Traditional exercise stress tests conducted within an MRI machine require patients to lie flat, a position that artificially improves heart function by increasing stroke volume due to gravity-driven blood... Read more
Shorter MRI Exam Effectively Detects Cancer in Dense Breasts
Women with extremely dense breasts face a higher risk of missed breast cancer diagnoses, as dense glandular and fibrous tissue can obscure tumors on mammograms. While breast MRI is recommended for supplemental... Read moreUltrasound
view channel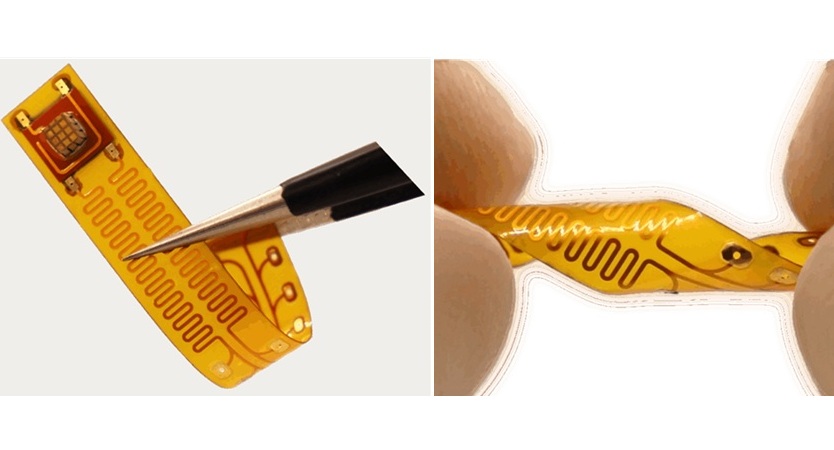
Wireless Chronic Pain Management Device to Reduce Need for Painkillers and Surgery
Chronic pain affects millions of people globally, often leading to long-term disability and dependence on opioid medications, which carry significant risks of side effects and addiction.... Read more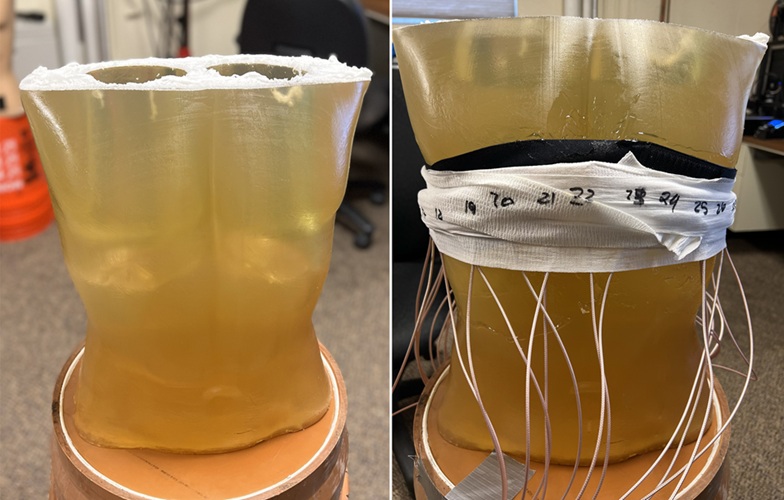
New Medical Ultrasound Imaging Technique Enables ICU Bedside Monitoring
Ultrasound computed tomography (USCT) presents a safer alternative to imaging techniques like X-ray computed tomography (commonly known as CT or “CAT” scans) because it does not produce ionizing radiation.... Read moreNuclear Medicine
view channel
Novel Bacteria-Specific PET Imaging Approach Detects Hard-To-Diagnose Lung Infections
Mycobacteroides abscessus is a rapidly growing mycobacteria that primarily affects immunocompromised patients and those with underlying lung diseases, such as cystic fibrosis or chronic obstructive pulmonary... Read more
New Imaging Approach Could Reduce Need for Biopsies to Monitor Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer is the second leading cause of cancer-related death among men in the United States. However, the majority of older men diagnosed with prostate cancer have slow-growing, low-risk forms of... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more
Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in medical diagnostics market is expanding with early disease detection being one of its key applications and image recognition becoming a compelling consumer proposition... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
GE HealthCare and NVIDIA Collaboration to Reimagine Diagnostic Imaging
GE HealthCare (Chicago, IL, USA) has entered into a collaboration with NVIDIA (Santa Clara, CA, USA), expanding the existing relationship between the two companies to focus on pioneering innovation in... Read more
Patient-Specific 3D-Printed Phantoms Transform CT Imaging
New research has highlighted how anatomically precise, patient-specific 3D-printed phantoms are proving to be scalable, cost-effective, and efficient tools in the development of new CT scan algorithms... Read more
Siemens and Sectra Collaborate on Enhancing Radiology Workflows
Siemens Healthineers (Forchheim, Germany) and Sectra (Linköping, Sweden) have entered into a collaboration aimed at enhancing radiologists' diagnostic capabilities and, in turn, improving patient care... Read more













.jpeg)



