AI Stroke Brain Scan Readings Twice as Accurate as Current Method
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 11 Dec 2024 |
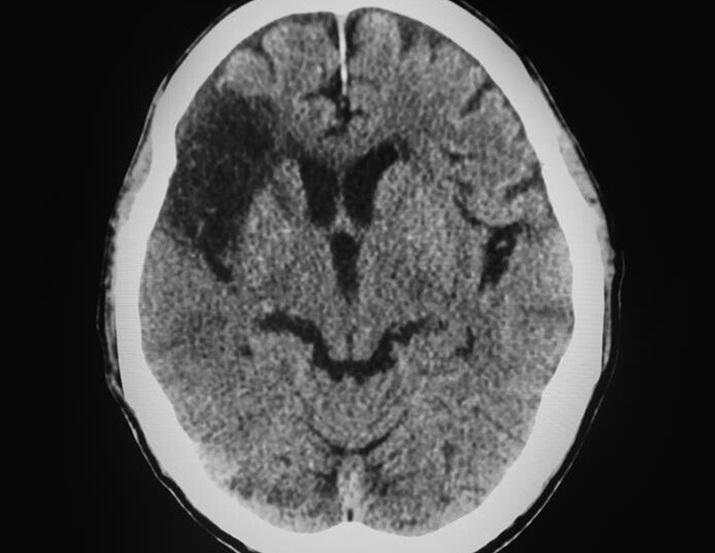
A stroke occurs when the blood flow to a part of the brain is interrupted or reduced, depriving brain tissue of oxygen and nutrients. This causes brain cells to die rapidly. As time passes, some treatments may become less effective or even worsen the situation. Knowing the exact time a stroke occurred is critical because standard treatments are most effective in the initial stages after a stroke and may cause further damage if applied later. However, determining the time of onset can be challenging. Some strokes may begin while a patient is asleep, and stroke symptoms can make communication difficult. When a patient arrives at the hospital with a suspected stroke, they typically undergo a CT scan, which doctors review to assess the extent of brain damage. Darker areas on the scan indicate that the stroke has progressed, helping doctors estimate the time of onset and whether treatment is still viable. However, predicting the stroke’s start time accurately is difficult because every brain is different. Even if an approximate onset time is known, factors like blood flow or vessel structure can cause the stroke to progress at different rates.
Researchers from Imperial College London (London, UK) have now developed artificial intelligence (AI) software that analyzes brain scans of stroke patients to more accurately determine when the stroke occurred and assist doctors in assessing its treatability. This technology aims to enhance the speed and precision of emergency treatments in hospitals. The AI software tackles two major challenges in stroke care: determining the stroke’s onset time and evaluating whether the damage can be reversed. The software has been shown to be twice as accurate as the current method, which relies on a medical professional’s visual assessment of CT scans by looking at the darkness of affected areas in the brain.
The AI algorithm was trained using a dataset of 800 brain scans where the stroke onset time was known. It not only extracts the relevant area from the scan but also analyzes the lesions to provide an estimated time of occurrence. When tested on nearly 2000 different patients, the software was found to be twice as accurate as the standard visual method. Researchers attribute this to the AI’s ability to consider additional features from the scans, such as texture, and to account for variations within the lesion and surrounding tissue. The study, published in NPJ Digital Medicine, found the AI system to be not only proficient at estimating the stroke’s onset but also at determining the biological age of the lesions, which indicates whether the damage may be reversible.
“Having this information at their fingertips will help doctors to make emergency decisions about what treatments should be undertaken in stroke patients,” said Dr. Paul Bentley at Imperial’s Department of Brain Sciences, who led the research study. “Not only is our software twice as accurate at time-reading as current best practice, but it can be fully automated once a stroke becomes visible on a scan.”
Latest General/Advanced Imaging News
- AI Reduces CT Lung Cancer Screening Workload by Almost 80%
- Cutting-Edge Technology Combines Light and Sound for Real-Time Stroke Monitoring
- AI System Detects Subtle Changes in Series of Medical Images Over Time
- New CT Scan Technique to Improve Prognosis and Treatments for Head and Neck Cancers
- World’s First Mobile Whole-Body CT Scanner to Provide Diagnostics at POC
- Comprehensive CT Scans Could Identify Atherosclerosis Among Lung Cancer Patients
- AI Improves Detection of Colorectal Cancer on Routine Abdominopelvic CT Scans
- Super-Resolution Technology Enhances Clinical Bone Imaging to Predict Osteoporotic Fracture Risk
- AI-Powered Abdomen Map Enables Early Cancer Detection
- Deep Learning Model Detects Lung Tumors on CT
- AI Predicts Cardiovascular Risk from CT Scans
- Deep Learning Based Algorithms Improve Tumor Detection in PET/CT Scans
- New Technology Provides Coronary Artery Calcification Scoring on Ungated Chest CT Scans
- Deep Learning Model Accurately Diagnoses COPD Using Single Inhalation Lung CT Scan
- AI Model Reconstructs Sparse-View 3D CT Scan With Much Lower X-Ray Dose
- New Medical Scanner Identifies Brain Damage in Stroke Patients at Lower Magnetic Fields
Channels
Radiography
view channel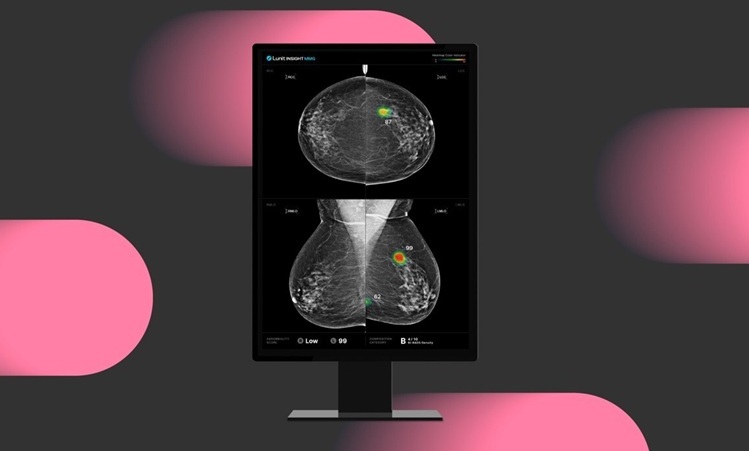
AI-Powered Mammography Screening Boosts Cancer Detection in Single-Reader Settings
A new study has revealed that an artificial intelligence (AI)-powered solution significantly improves cancer detection in single-reader mammography settings without increasing recall rates, offering a... Read more
Photon Counting Detectors Promise Fast Color X-Ray Images
For many years, healthcare professionals have depended on traditional 2D X-rays to diagnose common bone fractures, though small fractures or soft tissue damage, such as cancers, can often be missed.... Read moreMRI
view channel
Biparametric MRI Combined with AI Enhances Detection of Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer
Artificial intelligence (AI) technologies are transforming the way medical images are analyzed, offering unprecedented capabilities in quantitatively extracting features that go beyond traditional visual... Read more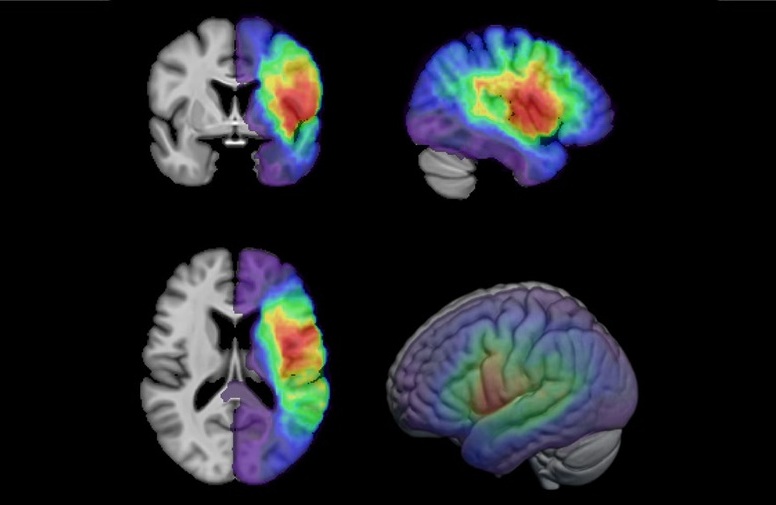
First-Of-Its-Kind AI-Driven Brain Imaging Platform to Better Guide Stroke Treatment Options
Each year, approximately 800,000 people in the U.S. experience strokes, with marginalized and minoritized groups being disproportionately affected. Strokes vary in terms of size and location within the... Read moreUltrasound
view channel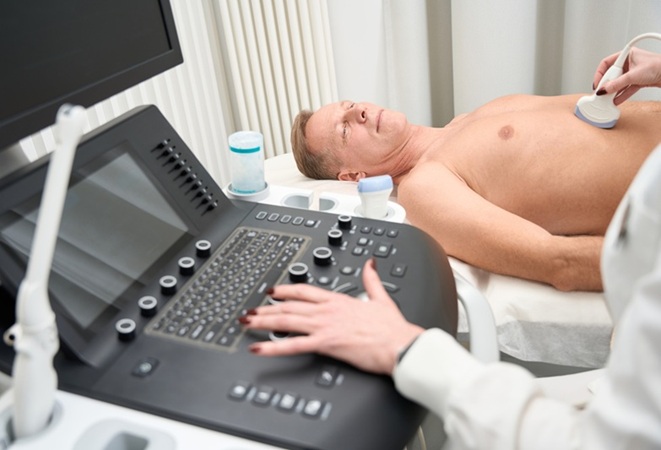
Artificial Intelligence Detects Undiagnosed Liver Disease from Echocardiograms
Echocardiography is a diagnostic procedure that uses ultrasound to visualize the heart and its associated structures. This imaging test is commonly used as an early screening method when doctors suspect... Read more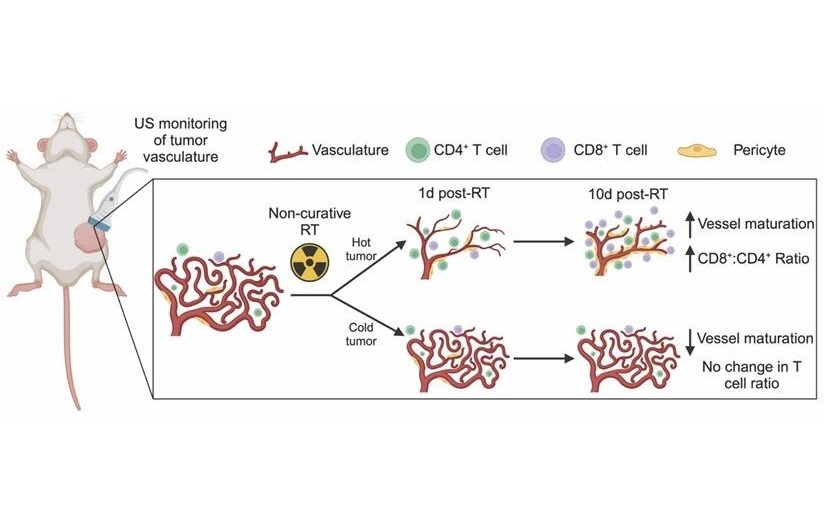
Ultrasound Imaging Non-Invasively Tracks Tumor Response to Radiation and Immunotherapy
While immunotherapy holds promise in the fight against triple-negative breast cancer, many patients fail to respond to current treatments. A major challenge has been predicting and monitoring how individual... Read moreGeneral/Advanced Imaging
view channel
AI Reduces CT Lung Cancer Screening Workload by Almost 80%
Lung cancer impacts over 48,000 individuals in the UK annually, and early detection is key to improving survival rates. The UK Lung Cancer Screening (UKLS) trial has already shown that low-dose CT (LDCT)... Read more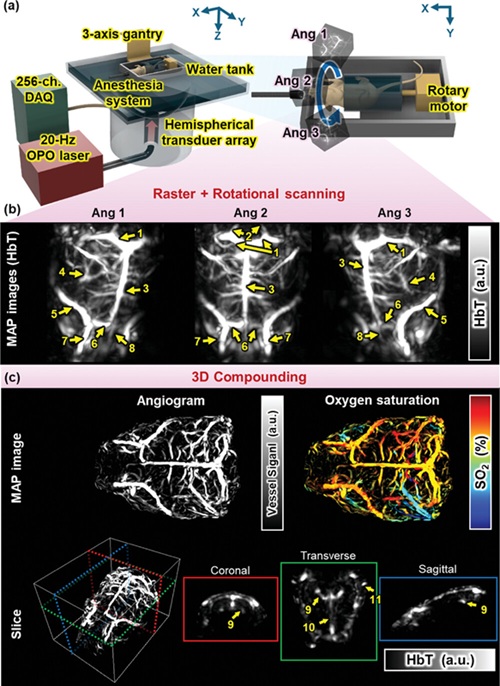
Cutting-Edge Technology Combines Light and Sound for Real-Time Stroke Monitoring
Stroke is the second leading cause of death globally, claiming millions of lives each year. Ischemic stroke, in particular, occurs when a blood vessel that supplies blood to the brain becomes blocked.... Read more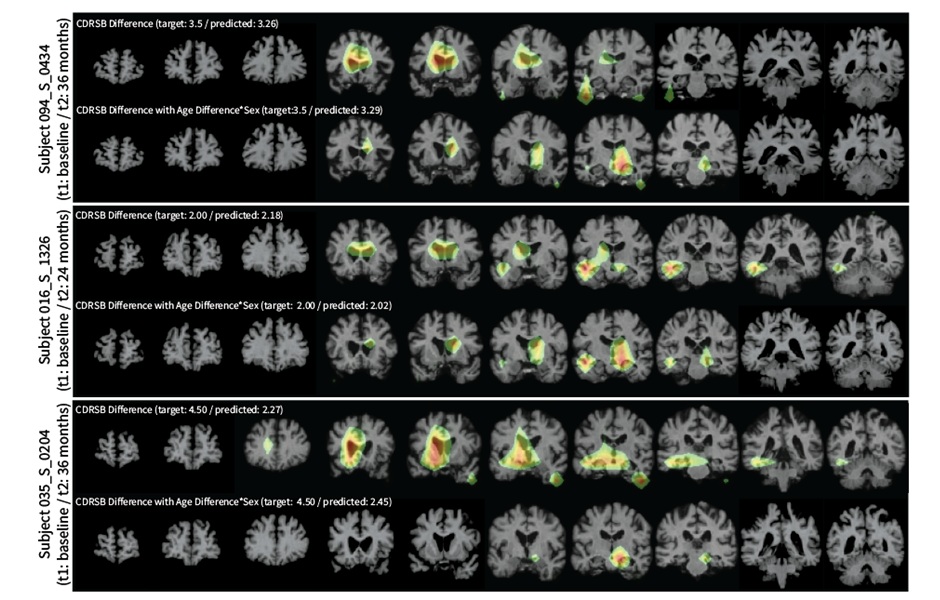
AI System Detects Subtle Changes in Series of Medical Images Over Time
Traditional approaches for analyzing longitudinal image datasets typically require significant customization and extensive pre-processing. For instance, in studies of the brain, researchers often begin... Read more
New CT Scan Technique to Improve Prognosis and Treatments for Head and Neck Cancers
Cancers of the mouth, nose, and throat are becoming increasingly common in the U.S., particularly among younger individuals. Approximately 60,000 new cases are diagnosed annually, with 20% of these cases... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more
Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in medical diagnostics market is expanding with early disease detection being one of its key applications and image recognition becoming a compelling consumer proposition... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
Siemens and Sectra Collaborate on Enhancing Radiology Workflows
Siemens Healthineers (Forchheim, Germany) and Sectra (Linköping, Sweden) have entered into a collaboration aimed at enhancing radiologists' diagnostic capabilities and, in turn, improving patient care... Read more
















.jpg)
.jpeg)