Wearable Ultrasound Patch Enables Continuous Blood Pressure Monitoring
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 21 Nov 2024 |
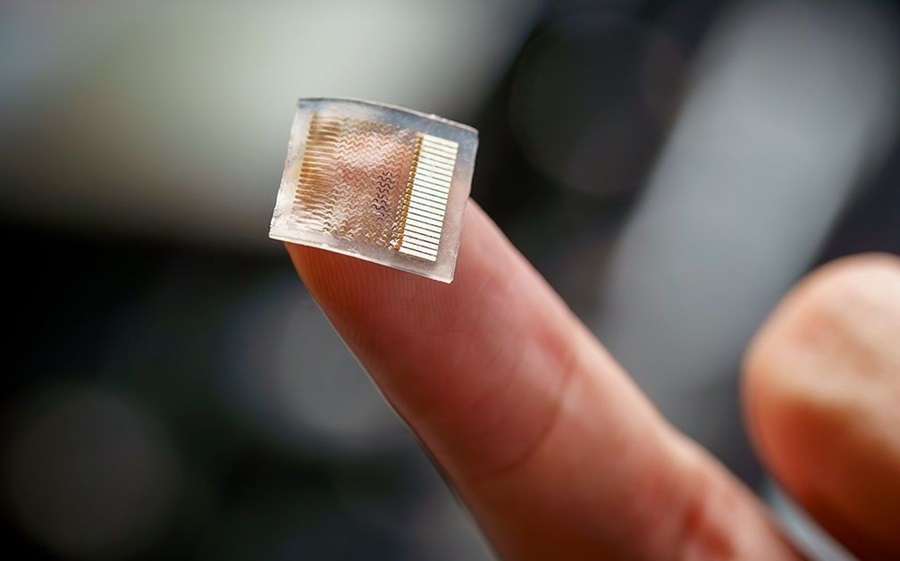

Traditional blood pressure measurements using a cuff provide a single, snapshot reading, which can miss important patterns in blood pressure fluctuations. Researchers have now developed an advanced wearable ultrasound patch that allows for continuous, noninvasive blood pressure monitoring. This wearable device offers a constant flow of blood pressure waveform data, enabling detailed tracking of blood pressure trends. The device, which has undergone extensive clinical validation on more than 100 patients, marks a major achievement in continuous cardiovascular health monitoring. Published in Nature Biomedical Engineering, this technology has the potential to transform blood pressure monitoring both in clinical settings and at home.
Developed by researchers at the University of California San Diego (La Jolla, CA, USA), the patch, about the size of a postage stamp, is small, flexible, and adheres to the skin. When placed on the forearm, it provides real-time, precise readings of blood pressure from deep within the body. The patch is composed of silicone elastomer and includes a series of small piezoelectric transducers sandwiched between stretchable copper electrodes. These transducers emit and receive ultrasound waves that track changes in the diameter of blood vessels, translating these signals into blood pressure readings. The new wearable patch builds on an earlier prototype, improving upon it with two key innovations aimed at enhancing its performance for continuous monitoring.
First, the piezoelectric transducers were packed closer together, expanding the patch’s coverage to better target smaller, clinically relevant arteries, such as the brachial and radial arteries. Second, a backing layer was added to dampen excess vibrations from the transducers, improving the clarity of the signals and the accuracy of the tracking. In validation tests, the patch’s results were comparable to those from a traditional blood pressure cuff and the arterial line, a clinical device used for continuous blood pressure monitoring, though the arterial line is highly invasive, limits patient mobility, and can cause discomfort. The patch, however, offers a more simple, reliable, and comfortable alternative.
The researchers performed extensive safety and accuracy tests, involving 117 participants. One set of tests had seven individuals wearing the patch during daily activities like cycling, raising arms and legs, performing mental tasks, meditating, eating, and drinking energy drinks. In a larger group of 85 participants, the patch was evaluated during postural changes, such as moving from sitting to standing. In all tests, the patch’s readings closely matched those of a blood pressure cuff. The device was also tested in a clinical setting with 21 patients in a cardiac catheterization lab and four patients in the intensive care unit after surgery, where the patch’s measurements closely aligned with those from the arterial line. This shows the patch's potential as a noninvasive alternative for blood pressure monitoring. Looking forward, the team is preparing for large-scale clinical trials and plans to incorporate machine learning to enhance the device’s capabilities. They are also working on a wireless, battery-powered version for long-term use, which will integrate seamlessly with hospital systems.
“A big advance of this work is how thoroughly we validated this technology, thanks to the work of our medical collaborators,” said Sheng Xu, a professor in the Aiiso Yufeng Li Family Department of Chemical and Nano Engineering at UC San Diego, in whose lab the device was pioneered. “Blood pressure can be all over the place depending on factors like white coat syndrome, masked hypertension, daily activities or use of medication, which makes it tricky to get an accurate diagnosis or manage treatment. That’s why it was so important for us to test this device in a wide variety of real-world and clinical settings. Many studies on wearable devices skip these steps during development, but we made sure to cover it all.”
Latest Ultrasound News
- Artificial Intelligence Detects Undiagnosed Liver Disease from Echocardiograms
- Ultrasound Imaging Non-Invasively Tracks Tumor Response to Radiation and Immunotherapy
- AI Improves Detection of Congenital Heart Defects on Routine Prenatal Ultrasounds
- AI Diagnoses Lung Diseases from Ultrasound Videos with 96.57% Accuracy
- New Contrast Agent for Ultrasound Imaging Ensures Affordable and Safer Medical Diagnostics
- Ultrasound-Directed Microbubbles Boost Immune Response Against Tumors
- POC Ultrasound Enhances Early Pregnancy Care and Cuts Emergency Visits
- AI-Based Models Outperform Human Experts at Identifying Ovarian Cancer in Ultrasound Images
- Automated Breast Ultrasound Provides Alternative to Mammography in Low-Resource Settings
- Transparent Ultrasound Transducer for Photoacoustic and Ultrasound Endoscopy to Improve Diagnostic Accuracy
- AI Image-Recognition Program Reads Echocardiograms Faster, Cuts Results Wait Time
- Ultrasound Device Non-Invasively Improves Blood Circulation in Lower Limbs
- Wearable Ultrasound Device Provides Long-Term, Wireless Muscle Monitoring

- Ultrasound Can Identify Sources of Brain-Related Issues and Disorders Before Treatment

- New Guideline on Handling Endobronchial Ultrasound Transbronchial Needle Samples
- Groundbreaking Ultrasound-Guided Needle Insertion System Improves Medical Procedures
Channels
Radiography
view channel
AI-Powered Mammography Screening Boosts Cancer Detection in Single-Reader Settings
A new study has revealed that an artificial intelligence (AI)-powered solution significantly improves cancer detection in single-reader mammography settings without increasing recall rates, offering a... Read more
Photon Counting Detectors Promise Fast Color X-Ray Images
For many years, healthcare professionals have depended on traditional 2D X-rays to diagnose common bone fractures, though small fractures or soft tissue damage, such as cancers, can often be missed.... Read moreMRI
view channel
Biparametric MRI Combined with AI Enhances Detection of Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer
Artificial intelligence (AI) technologies are transforming the way medical images are analyzed, offering unprecedented capabilities in quantitatively extracting features that go beyond traditional visual... Read more
First-Of-Its-Kind AI-Driven Brain Imaging Platform to Better Guide Stroke Treatment Options
Each year, approximately 800,000 people in the U.S. experience strokes, with marginalized and minoritized groups being disproportionately affected. Strokes vary in terms of size and location within the... Read moreNuclear Medicine
view channel
Novel Radiotracer Identifies Biomarker for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC), which represents 15-20% of all breast cancer cases, is one of the most aggressive subtypes, with a five-year survival rate of about 40%. Due to its significant heterogeneity... Read more
Innovative PET Imaging Technique to Help Diagnose Neurodegeneration
Neurodegenerative diseases, such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and Alzheimer’s disease, are often diagnosed only after physical symptoms appear, by which time treatment may no longer be effective.... Read moreGeneral/Advanced Imaging
view channel
AI Reduces CT Lung Cancer Screening Workload by Almost 80%
Lung cancer impacts over 48,000 individuals in the UK annually, and early detection is key to improving survival rates. The UK Lung Cancer Screening (UKLS) trial has already shown that low-dose CT (LDCT)... Read more
Cutting-Edge Technology Combines Light and Sound for Real-Time Stroke Monitoring
Stroke is the second leading cause of death globally, claiming millions of lives each year. Ischemic stroke, in particular, occurs when a blood vessel that supplies blood to the brain becomes blocked.... Read more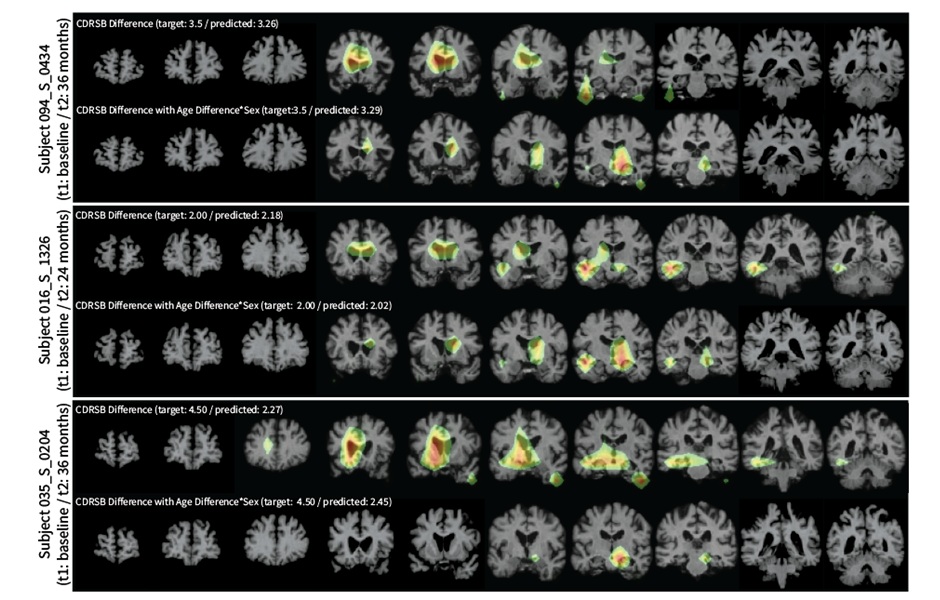
AI System Detects Subtle Changes in Series of Medical Images Over Time
Traditional approaches for analyzing longitudinal image datasets typically require significant customization and extensive pre-processing. For instance, in studies of the brain, researchers often begin... Read more
New CT Scan Technique to Improve Prognosis and Treatments for Head and Neck Cancers
Cancers of the mouth, nose, and throat are becoming increasingly common in the U.S., particularly among younger individuals. Approximately 60,000 new cases are diagnosed annually, with 20% of these cases... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more
Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in medical diagnostics market is expanding with early disease detection being one of its key applications and image recognition becoming a compelling consumer proposition... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
Siemens and Sectra Collaborate on Enhancing Radiology Workflows
Siemens Healthineers (Forchheim, Germany) and Sectra (Linköping, Sweden) have entered into a collaboration aimed at enhancing radiologists' diagnostic capabilities and, in turn, improving patient care... Read more













![Image: [18F]3F4AP in a human subject after mild incomplete spinal cord injury (Photo courtesy of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine, DOI:10.2967/jnumed.124.268242) Image: [18F]3F4AP in a human subject after mild incomplete spinal cord injury (Photo courtesy of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine, DOI:10.2967/jnumed.124.268242)](https://globetechcdn.com/mobile_medicalimaging/images/stories/articles/article_images/2025-02-24/Brugarolas_F8.large.jpg)


.jpg)
.jpeg)