New Treatment Combines MRI and Ultrasound to Control Prostate Cancer without Serious Side Effects
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 29 Mar 2024 |
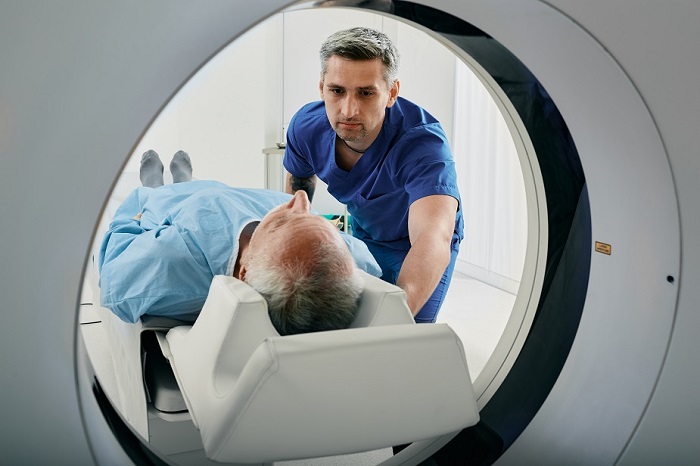
Prostate cancer is the most prevalent cancer among men, affecting one in eight during their lifetime. Traditional treatments like radiation or surgery carry potential side effects, including urinary incontinence and erectile dysfunction, which significantly impact the quality of life. Now, new research has revealed the efficacy of a minimally invasive approach using MRI and transurethral ultrasound for prostate cancer treatment.
Researchers at the David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA (Los Angeles, CA, USA) have found that a technique known as MRI-guided transurethral ultrasound ablation (TULSA) offers a durable alternative for whole-gland treatment and does not preclude future treatment with surgery or radiation. The TULSA procedure involves inserting a device through the urethra to the prostate, where MRI guides the precise placement of ultrasound elements for therapeutic purposes. MR thermometry helps in monitoring and controlling the temperature within the prostate, ensuring it exceeds 55 degrees Celsius for effective treatment while preserving surrounding nerve tissues. This outpatient procedure, requiring two to three hours under general or spinal anesthesia, has shown promising outcomes.
The study involved 115 men across 13 sites in five countries, with 25 undergoing subsequent traditional treatments due to residual or recurring tumors. The findings indicated notable improvements in cancer reduction, prostate shrinkage, and lower prostate-specific antigen (PSA) levels, a cancer marker. One year post-TULSA, 76% of patients had no detectable cancer in follow-up biopsies, with a median prostate volume reduction of 92% within a year and a significant drop in PSA levels from 6.3 ng/ml to 0.63 ng/ml over five years. TULSA's side-effect profile was markedly favorable when compared to conventional treatments, showcasing a high rate of continence recovery (92%) and erectile function preservation (87%) after five years.
The overall insights gained from the study included the identification of early TULSA failure predictors, such as urethral calcifications and procedural issues related to prostate swelling and alignment, leading to improved detection and management of these preventable errors during the procedure. This research underscores the significant role of interventional radiologists in prostate cancer treatment, similar to their contribution to treating other cancers like those of the lung, kidney, and liver. Their expertise in imaging and image-guided interventions, combined with ablation experience, make them a vital part of prostate cancer treatment.
“The success of TULSA represents a revolution in whole-gland treatment for prostate cancer,” said Steven S. Raman, M.D., FASR, FSIR, professor of radiology, urology and surgery at the David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA. “We have more research to do, but if validated, TULSA has the potential to change the standard of care for thousands of men.”
Related Links:
UCLA
Latest Ultrasound News
- Artificial Intelligence Detects Undiagnosed Liver Disease from Echocardiograms
- Ultrasound Imaging Non-Invasively Tracks Tumor Response to Radiation and Immunotherapy
- AI Improves Detection of Congenital Heart Defects on Routine Prenatal Ultrasounds
- AI Diagnoses Lung Diseases from Ultrasound Videos with 96.57% Accuracy
- New Contrast Agent for Ultrasound Imaging Ensures Affordable and Safer Medical Diagnostics
- Ultrasound-Directed Microbubbles Boost Immune Response Against Tumors
- POC Ultrasound Enhances Early Pregnancy Care and Cuts Emergency Visits
- AI-Based Models Outperform Human Experts at Identifying Ovarian Cancer in Ultrasound Images
- Automated Breast Ultrasound Provides Alternative to Mammography in Low-Resource Settings
- Transparent Ultrasound Transducer for Photoacoustic and Ultrasound Endoscopy to Improve Diagnostic Accuracy
- Wearable Ultrasound Patch Enables Continuous Blood Pressure Monitoring
- AI Image-Recognition Program Reads Echocardiograms Faster, Cuts Results Wait Time
- Ultrasound Device Non-Invasively Improves Blood Circulation in Lower Limbs
- Wearable Ultrasound Device Provides Long-Term, Wireless Muscle Monitoring

- Ultrasound Can Identify Sources of Brain-Related Issues and Disorders Before Treatment

- New Guideline on Handling Endobronchial Ultrasound Transbronchial Needle Samples
Channels
Radiography
view channel
AI-Powered Mammography Screening Boosts Cancer Detection in Single-Reader Settings
A new study has revealed that an artificial intelligence (AI)-powered solution significantly improves cancer detection in single-reader mammography settings without increasing recall rates, offering a... Read more
Photon Counting Detectors Promise Fast Color X-Ray Images
For many years, healthcare professionals have depended on traditional 2D X-rays to diagnose common bone fractures, though small fractures or soft tissue damage, such as cancers, can often be missed.... Read moreUltrasound
view channel
Artificial Intelligence Detects Undiagnosed Liver Disease from Echocardiograms
Echocardiography is a diagnostic procedure that uses ultrasound to visualize the heart and its associated structures. This imaging test is commonly used as an early screening method when doctors suspect... Read more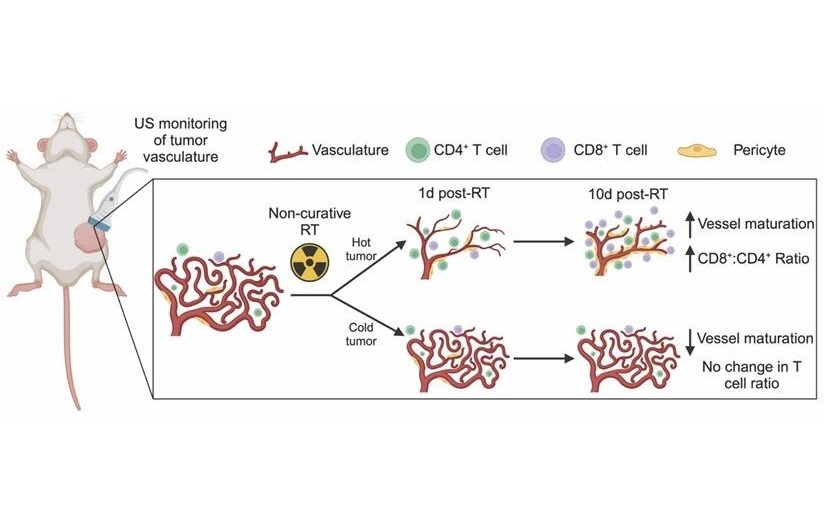
Ultrasound Imaging Non-Invasively Tracks Tumor Response to Radiation and Immunotherapy
While immunotherapy holds promise in the fight against triple-negative breast cancer, many patients fail to respond to current treatments. A major challenge has been predicting and monitoring how individual... Read moreNuclear Medicine
view channel
Novel Radiotracer Identifies Biomarker for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC), which represents 15-20% of all breast cancer cases, is one of the most aggressive subtypes, with a five-year survival rate of about 40%. Due to its significant heterogeneity... Read more
Innovative PET Imaging Technique to Help Diagnose Neurodegeneration
Neurodegenerative diseases, such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and Alzheimer’s disease, are often diagnosed only after physical symptoms appear, by which time treatment may no longer be effective.... Read moreGeneral/Advanced Imaging
view channel
AI Reduces CT Lung Cancer Screening Workload by Almost 80%
Lung cancer impacts over 48,000 individuals in the UK annually, and early detection is key to improving survival rates. The UK Lung Cancer Screening (UKLS) trial has already shown that low-dose CT (LDCT)... Read more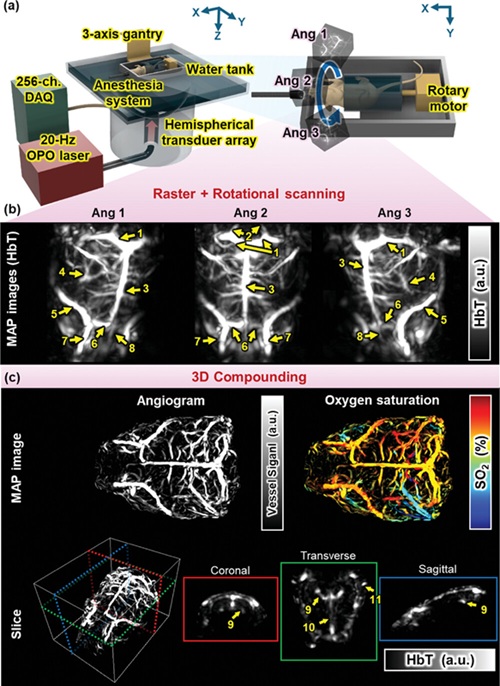
Cutting-Edge Technology Combines Light and Sound for Real-Time Stroke Monitoring
Stroke is the second leading cause of death globally, claiming millions of lives each year. Ischemic stroke, in particular, occurs when a blood vessel that supplies blood to the brain becomes blocked.... Read more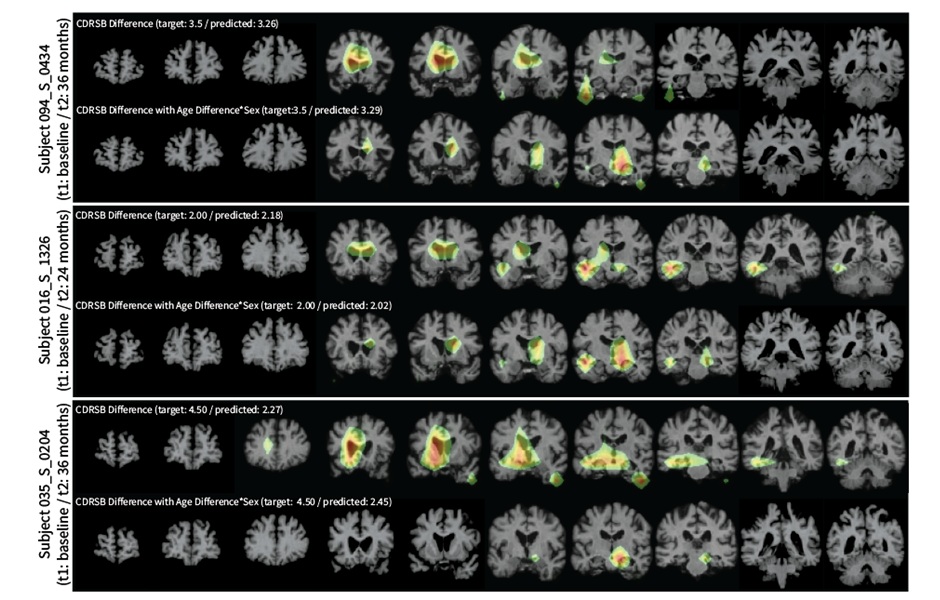
AI System Detects Subtle Changes in Series of Medical Images Over Time
Traditional approaches for analyzing longitudinal image datasets typically require significant customization and extensive pre-processing. For instance, in studies of the brain, researchers often begin... Read more
New CT Scan Technique to Improve Prognosis and Treatments for Head and Neck Cancers
Cancers of the mouth, nose, and throat are becoming increasingly common in the U.S., particularly among younger individuals. Approximately 60,000 new cases are diagnosed annually, with 20% of these cases... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more
Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in medical diagnostics market is expanding with early disease detection being one of its key applications and image recognition becoming a compelling consumer proposition... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
Siemens and Sectra Collaborate on Enhancing Radiology Workflows
Siemens Healthineers (Forchheim, Germany) and Sectra (Linköping, Sweden) have entered into a collaboration aimed at enhancing radiologists' diagnostic capabilities and, in turn, improving patient care... Read more













![Image: [18F]3F4AP in a human subject after mild incomplete spinal cord injury (Photo courtesy of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine, DOI:10.2967/jnumed.124.268242) Image: [18F]3F4AP in a human subject after mild incomplete spinal cord injury (Photo courtesy of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine, DOI:10.2967/jnumed.124.268242)](https://globetechcdn.com/mobile_medicalimaging/images/stories/articles/article_images/2025-02-24/Brugarolas_F8.large.jpg)


.jpg)
.jpeg)