4D MRI Could Improve Clinical Assessment of Heart Blood Flow Abnormalities
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 19 Mar 2024 |
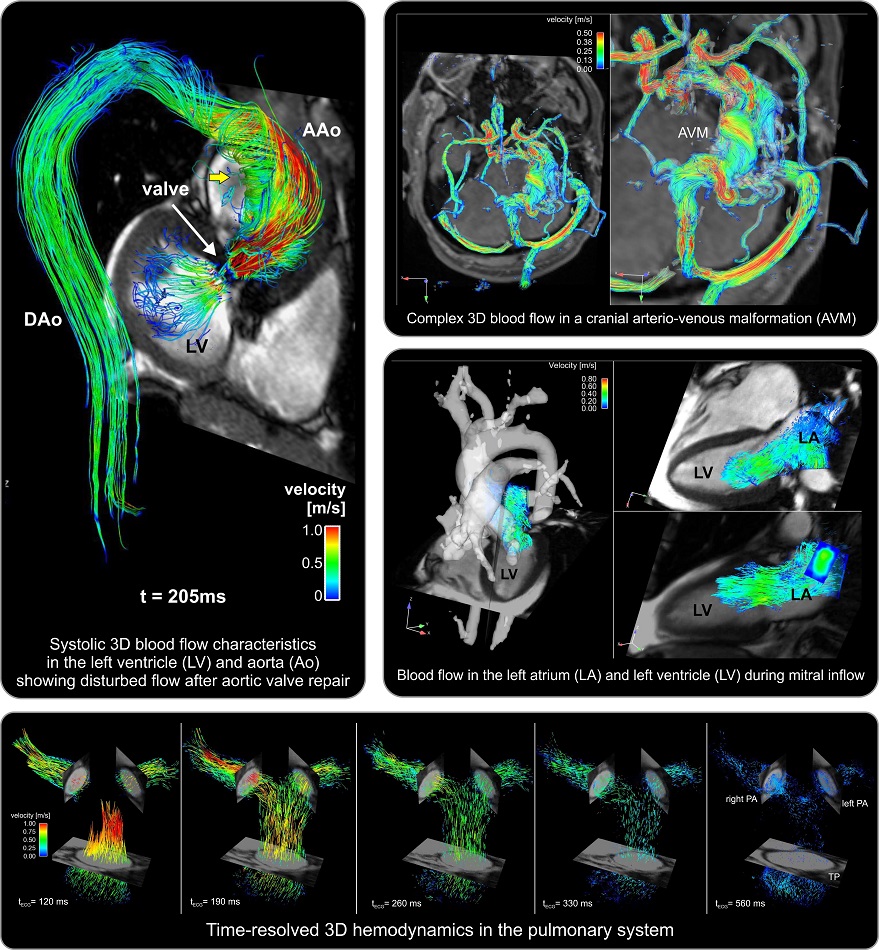
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) utilizes magnets and pulsed radio frequency to generate computer images for screening and diagnosing medical conditions. 4D flow MRI, an advanced imaging technique, provides a more detailed view of the heart and the aorta by adding movement as a fourth dimension. This allows healthcare professionals to see how blood moves through the cardiovascular system in detail and identify any potential issues that may require further examination. Previous studies have indicated that evaluating blood stasis and peak velocity in the left atrium and its appendage using 4D flow could aid in identifying impaired blood flow, which increases the risk of forming blood clots. However, the relationship between conventional volumetric and functional left atrium parameters with flow characteristics in the left atrium and left atrium appendage had not been fully investigated until now.
Now, a study by researchers from Northwestern University (Evanston, IL, USA) has discovered that combining whole-heart 4D flow with short-axis cine MRI can identify characteristics linked to poor blood flow in the heart’s left atrial chamber. These insights could enable doctors to more accurately diagnose abnormalities in heart blood flow. The study aimed to explore whether the relation between 4D flow parameters and conventional volumetric-based left atrial assessment could help better identify participants with impaired flow characteristics and improve the understanding of mechanistic relationships between left atrial flow and volumetric parameters. The study involved data from 158 patients all of whom underwent prospective cardiac MRI exams consisting of whole-heart 4D flow and short-axis cine imaging. The analysis of the 4D flow MRI involved manual 3D segmentation of the left atrium and its appendage to measure peak velocity and blood stasis.
The team utilized short-axis cine data to define left atrial contours, extracting 3D–based left atrial volume measures to calculate left atrial emptying fractions [total LA emptying fractions (LAEFtotal), active LA emptying fraction (LAEFactive), and passive LA emptying fraction (LAEFpassive)]. They also measured left atrial stasis, left atrial peak velocity, left atrium appendage stasis, and left atrium appendage peak velocity flow parameters to detect any connection with left atrial volume and left atrial emptying fraction. The researchers found that a one-unit increase in LAEFtotal was related to reduced left atrial stasis (p < 0.001) and higher LAEFactive was related to increased left atrial peak velocity (p < 0.001). They also found that increased minimum left atrial volume was most likely related to impaired left atrial appendage flow and lower left atrial appendage peak velocity.
"Increased absolute and indexed minimum left atrial volume was most closely associated with impaired left atrial flow, which is a known risk factor for left atrial thrombus formation and potentially ischemic stroke," the researchers concluded. "Thus, 3D-based left atrial volume quantification may be a useful surrogate measure for left atrial and left atrial appendage flow abnormalities in future studies."
Related Links:
Northwestern University
Latest MRI News
- New MRI Technique Reveals Hidden Heart Issues
- Shorter MRI Exam Effectively Detects Cancer in Dense Breasts
- MRI to Replace Painful Spinal Tap for Faster MS Diagnosis
- MRI Scans Can Identify Cardiovascular Disease Ten Years in Advance
- Simple Brain Scan Diagnoses Parkinson's Disease Years Before It Becomes Untreatable
- Cutting-Edge MRI Technology to Revolutionize Diagnosis of Common Heart Problem
- New MRI Technique Reveals True Heart Age to Prevent Attacks and Strokes
- AI Tool Predicts Relapse of Pediatric Brain Cancer from Brain MRI Scans
- AI Tool Tracks Effectiveness of Multiple Sclerosis Treatments Using Brain MRI Scans
- Ultra-Powerful MRI Scans Enable Life-Changing Surgery in Treatment-Resistant Epileptic Patients
- AI-Powered MRI Technology Improves Parkinson’s Diagnoses
- Biparametric MRI Combined with AI Enhances Detection of Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer
- First-Of-Its-Kind AI-Driven Brain Imaging Platform to Better Guide Stroke Treatment Options
- New Model Improves Comparison of MRIs Taken at Different Institutions
- Groundbreaking New Scanner Sees 'Previously Undetectable' Cancer Spread
- First-Of-Its-Kind Tool Analyzes MRI Scans to Measure Brain Aging
Channels
Radiography
view channel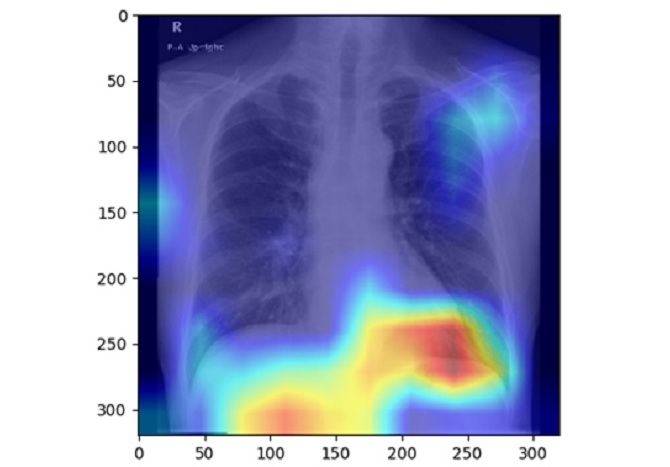
AI Detects Fatty Liver Disease from Chest X-Rays
Fatty liver disease, which results from excess fat accumulation in the liver, is believed to impact approximately one in four individuals globally. If not addressed in time, it can progress to severe conditions... Read more
AI Detects Hidden Heart Disease in Existing CT Chest Scans
Coronary artery calcium (CAC) is a major indicator of cardiovascular risk, but its assessment typically requires a specialized “gated” CT scan that synchronizes with the heartbeat. In contrast, most chest... Read moreUltrasound
view channel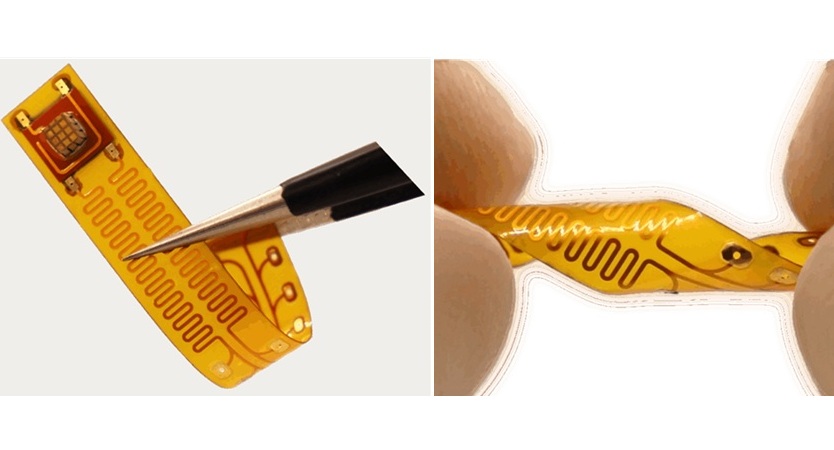
Wireless Chronic Pain Management Device to Reduce Need for Painkillers and Surgery
Chronic pain affects millions of people globally, often leading to long-term disability and dependence on opioid medications, which carry significant risks of side effects and addiction.... Read more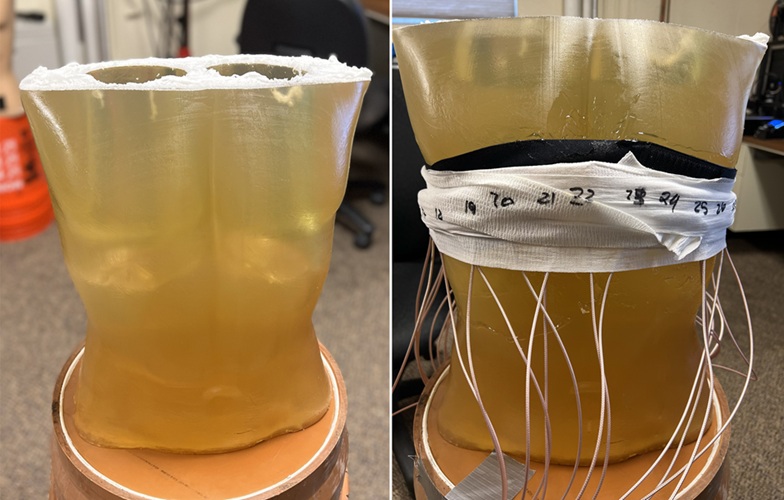
New Medical Ultrasound Imaging Technique Enables ICU Bedside Monitoring
Ultrasound computed tomography (USCT) presents a safer alternative to imaging techniques like X-ray computed tomography (commonly known as CT or “CAT” scans) because it does not produce ionizing radiation.... Read moreNuclear Medicine
view channel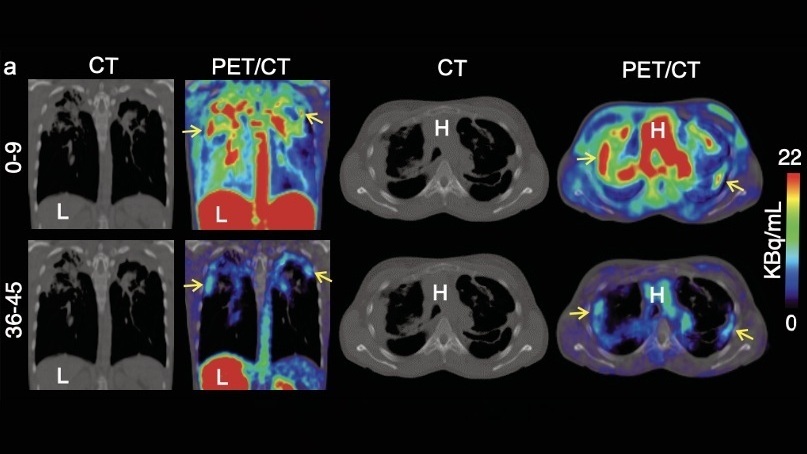
Novel Bacteria-Specific PET Imaging Approach Detects Hard-To-Diagnose Lung Infections
Mycobacteroides abscessus is a rapidly growing mycobacteria that primarily affects immunocompromised patients and those with underlying lung diseases, such as cystic fibrosis or chronic obstructive pulmonary... Read more
New Imaging Approach Could Reduce Need for Biopsies to Monitor Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer is the second leading cause of cancer-related death among men in the United States. However, the majority of older men diagnosed with prostate cancer have slow-growing, low-risk forms of... Read moreGeneral/Advanced Imaging
view channel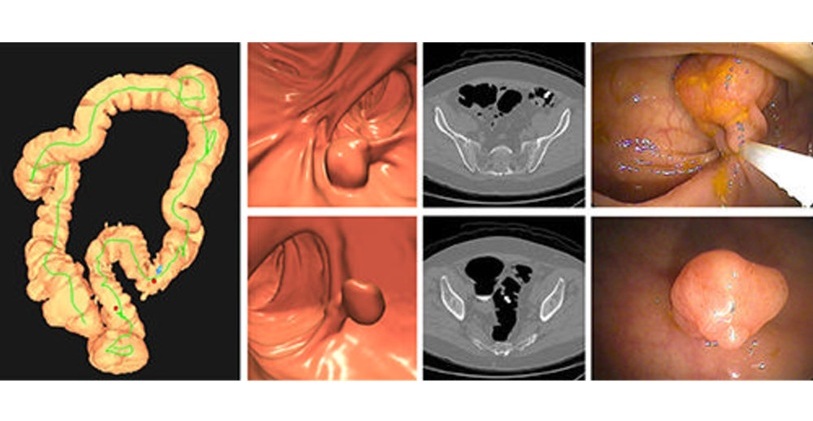
CT Colonography Beats Stool DNA Testing for Colon Cancer Screening
As colorectal cancer remains the second leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide, early detection through screening is vital to reduce advanced-stage treatments and associated costs.... Read more
First-Of-Its-Kind Wearable Device Offers Revolutionary Alternative to CT Scans
Currently, patients with conditions such as heart failure, pneumonia, or respiratory distress often require multiple imaging procedures that are intermittent, disruptive, and involve high levels of radiation.... Read more
AI-Based CT Scan Analysis Predicts Early-Stage Kidney Damage Due to Cancer Treatments
Radioligand therapy, a form of targeted nuclear medicine, has recently gained attention for its potential in treating specific types of tumors. However, one of the potential side effects of this therapy... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more
Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in medical diagnostics market is expanding with early disease detection being one of its key applications and image recognition becoming a compelling consumer proposition... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
GE HealthCare and NVIDIA Collaboration to Reimagine Diagnostic Imaging
GE HealthCare (Chicago, IL, USA) has entered into a collaboration with NVIDIA (Santa Clara, CA, USA), expanding the existing relationship between the two companies to focus on pioneering innovation in... Read more
Patient-Specific 3D-Printed Phantoms Transform CT Imaging
New research has highlighted how anatomically precise, patient-specific 3D-printed phantoms are proving to be scalable, cost-effective, and efficient tools in the development of new CT scan algorithms... Read more
Siemens and Sectra Collaborate on Enhancing Radiology Workflows
Siemens Healthineers (Forchheim, Germany) and Sectra (Linköping, Sweden) have entered into a collaboration aimed at enhancing radiologists' diagnostic capabilities and, in turn, improving patient care... Read more













.jpeg)




