MRI Technology to Visualize Metabolic Processes in Real Time Could Improve Heart Disease Diagnosis
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 21 Nov 2022 |
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) has become an indispensable part of medicine. It allows unique insights into the body and diagnosis of various diseases. However, current MRI technology has its limitations: although it can be used to map the structure and function of organs and tissues, it cannot be used to map changes in metabolism, which play a key role in many diseases. However, researchers are now aiming to make that possible by advancing MRI technology so that it can be used to visualize metabolism in real time. The researchers are focusing on the heart, the metabolism of which is particularly complex because it can choose from multiple energy sources. Their new MRI new method to visualize metabolic processes in the body could improve the future diagnosis and treatment of heart disease.
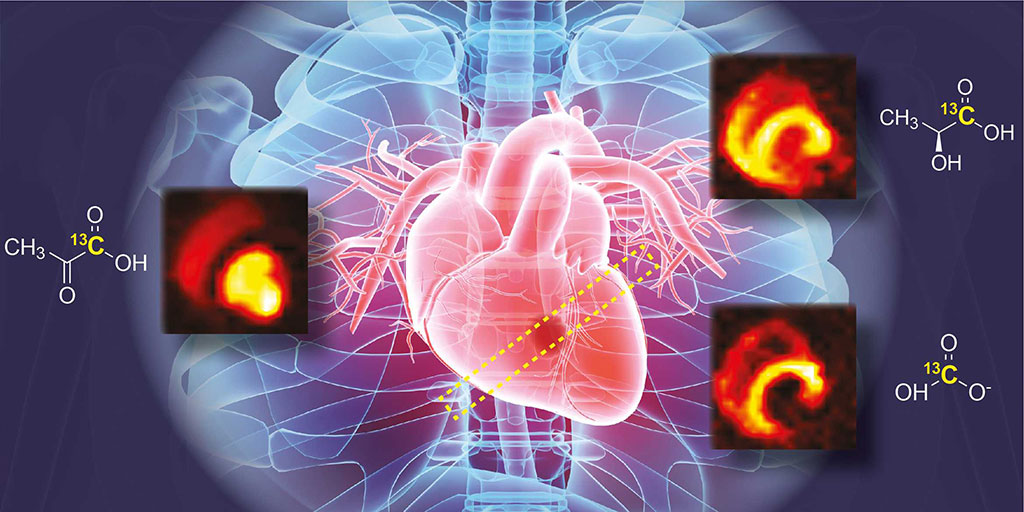
The heart is constantly in motion, which makes imaging a big challenge. Another challenge is that the metabolic molecules are present only in small concentrations – too small to capture with conventional magnetic resonance imaging. Researchers at ETH Zurich (Zurich, Switzerland) and the University of Zurich (Zurich, Switzerland) have succeeded in overcoming these obstacles with the help of hyperpolarized MRI: with it, the researchers can amplify the signal of metabolic molecules by a factor of more than 25,000. The research team adapted hyperpolarized MRI to the specific needs of cardiac and metabolic imaging. The result is a device of the size of a refrigerator operating alongside a clinical MRI machine. The “fridge” certainly lives up to its name: to increase the signal strength, a sugar intermediate (pyruvate) is deep-frozen at −272 degrees Celsius and then magnetized in a magnetic field with the help of microwaves. Once it has been warmed back to body temperature, pyruvate can be used for imaging in a way similar to conventional contrast agents.
This novel method is able to show, non-invasively and in real time, how the heart metabolizes nutrients – in other words, how it converts them into usable energy. While conventional MRI can show whether the heart is pumping and how, the method now also reveals where the heart gets its energy from. To be able to capture and understand this in detail is a major development, especially with regard to heart disease. A problem with metabolism can be an early sign of a heart condition. For example: Under normal circumstances, the heart primarily uses fat as an energy source. If there is a lack of oxygen, however, the heart switches over to sugar as an energy source, as this requires less oxygen to metabolize. If physicians were able to detect such processes by imaging, they could identify a possible oxygen deficiency at an early stage. This would pave the way towards treating the causes of cardiovascular diseases, and not just their effects.
The researchers were able to show that the method they developed does indeed do a good job of visualizing the heart’s metabolism. Pigs were used as a model, as their hearts are most similar to the human heart. This made it possible to map the metabolic changes following a heart attack in detail. Among other things, the study revealed the parts of the heart muscle which recovered after the infarction. The new MRI method could become an important step towards personalized medicine. The researchers hope that the innovative procedure will also help physicians understand why certain people have much greater impairment after a heart attack than others. However, the method has to prove itself in larger clinical studies in the coming years. To this end, the researchers will further refine the technology of the prototype “fridge”. The researchers have also launched their first clinical trial in which patients with heart failure or risk factors for heart failure will be examined.
“For us physicians, it’s very valuable to map the metabolism of the heart. In the future, this could enable us to improve diagnoses and prognoses of heart disease – and thus to tailor treatment more closely to the individual,” said Professor Robert Manka, Director of Cardiac MRI at the Heart Center of University Hospital Zurich. “Metabolism probably plays a role in this, but we don’t know it yet. In the future, we’ll be able to see what’s really going on in the heart muscle and its cells.”
Related Links:
ETH Zurich
University of Zurich
Latest MRI News
- AI Tool Tracks Effectiveness of Multiple Sclerosis Treatments Using Brain MRI Scans
- Ultra-Powerful MRI Scans Enable Life-Changing Surgery in Treatment-Resistant Epileptic Patients
- AI-Powered MRI Technology Improves Parkinson’s Diagnoses
- Biparametric MRI Combined with AI Enhances Detection of Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer
- First-Of-Its-Kind AI-Driven Brain Imaging Platform to Better Guide Stroke Treatment Options
- New Model Improves Comparison of MRIs Taken at Different Institutions
- Groundbreaking New Scanner Sees 'Previously Undetectable' Cancer Spread
- First-Of-Its-Kind Tool Analyzes MRI Scans to Measure Brain Aging
- AI-Enhanced MRI Images Make Cancerous Breast Tissue Glow
- AI Model Automatically Segments MRI Images
- New Research Supports Routine Brain MRI Screening in Asymptomatic Late-Stage Breast Cancer Patients
- Revolutionary Portable Device Performs Rapid MRI-Based Stroke Imaging at Patient's Bedside
- AI Predicts After-Effects of Brain Tumor Surgery from MRI Scans
- MRI-First Strategy for Prostate Cancer Detection Proven Safe
- First-Of-Its-Kind 10' x 48' Mobile MRI Scanner Transforms User and Patient Experience
- New Model Makes MRI More Accurate and Reliable
Channels
Radiography
view channel
World's Largest Class Single Crystal Diamond Radiation Detector Opens New Possibilities for Diagnostic Imaging
Diamonds possess ideal physical properties for radiation detection, such as exceptional thermal and chemical stability along with a quick response time. Made of carbon with an atomic number of six, diamonds... Read more
AI-Powered Imaging Technique Shows Promise in Evaluating Patients for PCI
Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), also known as coronary angioplasty, is a minimally invasive procedure where small metal tubes called stents are inserted into partially blocked coronary arteries... Read moreUltrasound
view channel
AI Identifies Heart Valve Disease from Common Imaging Test
Tricuspid regurgitation is a condition where the heart's tricuspid valve does not close completely during contraction, leading to backward blood flow, which can result in heart failure. A new artificial... Read more
Novel Imaging Method Enables Early Diagnosis and Treatment Monitoring of Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is recognized as an autoimmune inflammatory disease, where chronic inflammation leads to alterations in pancreatic islet microvasculature, a key factor in β-cell dysfunction.... Read moreNuclear Medicine
view channel
Novel PET Imaging Approach Offers Never-Before-Seen View of Neuroinflammation
COX-2, an enzyme that plays a key role in brain inflammation, can be significantly upregulated by inflammatory stimuli and neuroexcitation. Researchers suggest that COX-2 density in the brain could serve... Read more
Novel Radiotracer Identifies Biomarker for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC), which represents 15-20% of all breast cancer cases, is one of the most aggressive subtypes, with a five-year survival rate of about 40%. Due to its significant heterogeneity... Read moreGeneral/Advanced Imaging
view channel
AI-Powered Imaging System Improves Lung Cancer Diagnosis
Given the need to detect lung cancer at earlier stages, there is an increasing need for a definitive diagnostic pathway for patients with suspicious pulmonary nodules. However, obtaining tissue samples... Read more
AI Model Significantly Enhances Low-Dose CT Capabilities
Lung cancer remains one of the most challenging diseases, making early diagnosis vital for effective treatment. Fortunately, advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) are revolutionizing lung cancer... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more
Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in medical diagnostics market is expanding with early disease detection being one of its key applications and image recognition becoming a compelling consumer proposition... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
GE HealthCare and NVIDIA Collaboration to Reimagine Diagnostic Imaging
GE HealthCare (Chicago, IL, USA) has entered into a collaboration with NVIDIA (Santa Clara, CA, USA), expanding the existing relationship between the two companies to focus on pioneering innovation in... Read more
Patient-Specific 3D-Printed Phantoms Transform CT Imaging
New research has highlighted how anatomically precise, patient-specific 3D-printed phantoms are proving to be scalable, cost-effective, and efficient tools in the development of new CT scan algorithms... Read more
Siemens and Sectra Collaborate on Enhancing Radiology Workflows
Siemens Healthineers (Forchheim, Germany) and Sectra (Linköping, Sweden) have entered into a collaboration aimed at enhancing radiologists' diagnostic capabilities and, in turn, improving patient care... Read more