AI-Driven Algorithm Uses fMRI Scans to Detect Autism and Predict Severity
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 07 Apr 2022 |
Autism is one of the most common neurodevelopmental disorders but lacks objective biomarkers - telltale measurements that reveal a medical condition’s presence and sometimes severity -meaning there is no simple test for the disorder. Instead, diagnosis is based on observing patients’ behaviors, which are naturally highly variable and thus make diagnosis a challenge. Researchers have now developed an algorithm that may help discern if someone has autism by looking at brain scans.
The novel algorithm, developed by researchers at Stanford University (Stanford, CA, USA) and driven by recent advances in artificial intelligence (AI), also successfully predicts the severity of autism symptoms in individual patients. With further honing, the algorithm could lead to earlier diagnoses, more targeted therapies, and broadened understanding of autism’s origins in the brain.
The algorithm pores over data gathered through functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) scans. These scans capture patterns of neural activity throughout the brain. Scientists have long searched for biomarkers via fMRI scans. Yet studies to date with small populations have reported conflicting results, stemming from natural variability in patients’ brains and confounded further by differences in fMRI machines and testing methods. In deriving their image-recognition algorithms, the researchers sought to make the artificial intelligence explainable (or XAI), or understandable to human researchers.
By mapping this activity over time in the brain’s many regions, the algorithm generates neural activity “fingerprints.” Although unique for each individual just like real fingerprints, the brain fingerprints nevertheless share similar features, allowing them to be sorted and classified. In a new study, the algorithm assessed brain scans from a sample of approximately 1,100 patients. With 82% accuracy, the algorithm selected out a group of patients whom human clinicians had diagnosed with autism. The XAI algorithm alit upon three brain regions exhibiting significant differences in interconnectivity in a groupable portion of the dataset. Lending credibility to the XAI algorithm’s findings, those three brain regions have been previously implicated in autism pathology.
While the XAI algorithm performed admirably at this early stage of development, the researchers will need to improve its accuracy further still to raise brain fingerprinting to the level of a definitive biomarker. The researchers intend to explore the algorithm's efficacy in sibling studies, where one sibling has autism and the other does not, to hone the ability to detect fine-tuned, yet critical differences between potentially very similar brains. The researchers envision brain fingerprinting being used to assess the brains of very young children, perhaps as early as six months or a year old, who are at high risk of developing autism. Earlier diagnosis is critical in achieving better outcomes, with therapies proving more effective when introduced while patients are still toddler-aged versus later in childhood
“Although autism is one of the most common neurodevelopmental disorders, there is so much about it that we still don’t understand,” said lead author Kaustubh Supekar, a Stanford clinical assistant professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences and Stanford HAI affiliate faculty. “In this study, we’ve shown that our AI-driven brain ‘fingerprinting’ model could potentially be a powerful new tool in advancing diagnosis and treatment.”
“We need to create objective biomarkers for autism,” added Supekar, “and brain fingerprints get us one step closer. We hope that the approach demonstrated in our study could diagnose autism during the window of opportunity when interventions are maximally most effective.”
Related Links:
Stanford University
Latest MRI News
- AI Tool Tracks Effectiveness of Multiple Sclerosis Treatments Using Brain MRI Scans
- Ultra-Powerful MRI Scans Enable Life-Changing Surgery in Treatment-Resistant Epileptic Patients
- AI-Powered MRI Technology Improves Parkinson’s Diagnoses
- Biparametric MRI Combined with AI Enhances Detection of Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer
- First-Of-Its-Kind AI-Driven Brain Imaging Platform to Better Guide Stroke Treatment Options
- New Model Improves Comparison of MRIs Taken at Different Institutions
- Groundbreaking New Scanner Sees 'Previously Undetectable' Cancer Spread
- First-Of-Its-Kind Tool Analyzes MRI Scans to Measure Brain Aging
- AI-Enhanced MRI Images Make Cancerous Breast Tissue Glow
- AI Model Automatically Segments MRI Images
- New Research Supports Routine Brain MRI Screening in Asymptomatic Late-Stage Breast Cancer Patients
- Revolutionary Portable Device Performs Rapid MRI-Based Stroke Imaging at Patient's Bedside
- AI Predicts After-Effects of Brain Tumor Surgery from MRI Scans
- MRI-First Strategy for Prostate Cancer Detection Proven Safe
- First-Of-Its-Kind 10' x 48' Mobile MRI Scanner Transforms User and Patient Experience
- New Model Makes MRI More Accurate and Reliable
Channels
Radiography
view channel
World's Largest Class Single Crystal Diamond Radiation Detector Opens New Possibilities for Diagnostic Imaging
Diamonds possess ideal physical properties for radiation detection, such as exceptional thermal and chemical stability along with a quick response time. Made of carbon with an atomic number of six, diamonds... Read more
AI-Powered Imaging Technique Shows Promise in Evaluating Patients for PCI
Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), also known as coronary angioplasty, is a minimally invasive procedure where small metal tubes called stents are inserted into partially blocked coronary arteries... Read moreUltrasound
view channel
Ultrasound-Based Microscopy Technique to Help Diagnose Small Vessel Diseases
Clinical ultrasound, commonly used in pregnancy scans, provides real-time images of body structures. It is one of the most widely used imaging techniques in medicine, but until recently, it had little... Read more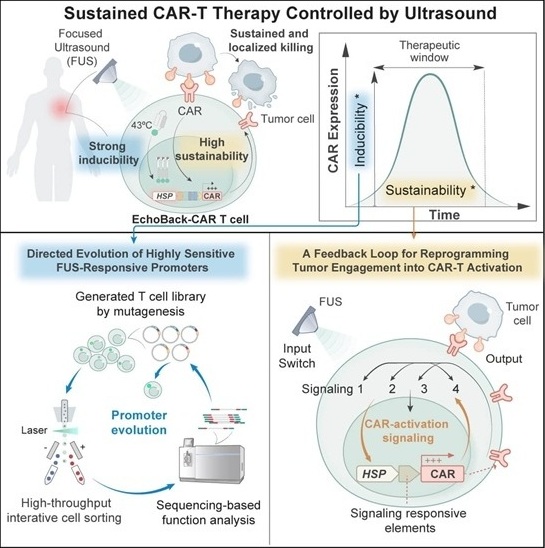
Smart Ultrasound-Activated Immune Cells Destroy Cancer Cells for Extended Periods
Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy has emerged as a highly promising cancer treatment, especially for bloodborne cancers like leukemia. This highly personalized therapy involves extracting... Read moreNuclear Medicine
view channel
Novel PET Imaging Approach Offers Never-Before-Seen View of Neuroinflammation
COX-2, an enzyme that plays a key role in brain inflammation, can be significantly upregulated by inflammatory stimuli and neuroexcitation. Researchers suggest that COX-2 density in the brain could serve... Read more
Novel Radiotracer Identifies Biomarker for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC), which represents 15-20% of all breast cancer cases, is one of the most aggressive subtypes, with a five-year survival rate of about 40%. Due to its significant heterogeneity... Read moreGeneral/Advanced Imaging
view channel
AI-Powered Imaging System Improves Lung Cancer Diagnosis
Given the need to detect lung cancer at earlier stages, there is an increasing need for a definitive diagnostic pathway for patients with suspicious pulmonary nodules. However, obtaining tissue samples... Read more
AI Model Significantly Enhances Low-Dose CT Capabilities
Lung cancer remains one of the most challenging diseases, making early diagnosis vital for effective treatment. Fortunately, advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) are revolutionizing lung cancer... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more
Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in medical diagnostics market is expanding with early disease detection being one of its key applications and image recognition becoming a compelling consumer proposition... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
GE HealthCare and NVIDIA Collaboration to Reimagine Diagnostic Imaging
GE HealthCare (Chicago, IL, USA) has entered into a collaboration with NVIDIA (Santa Clara, CA, USA), expanding the existing relationship between the two companies to focus on pioneering innovation in... Read more
Patient-Specific 3D-Printed Phantoms Transform CT Imaging
New research has highlighted how anatomically precise, patient-specific 3D-printed phantoms are proving to be scalable, cost-effective, and efficient tools in the development of new CT scan algorithms... Read more
Siemens and Sectra Collaborate on Enhancing Radiology Workflows
Siemens Healthineers (Forchheim, Germany) and Sectra (Linköping, Sweden) have entered into a collaboration aimed at enhancing radiologists' diagnostic capabilities and, in turn, improving patient care... Read more