AI-Guided Handheld Surgical Robot Can Stem Fatal Blood Loss
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 21 Mar 2022 |
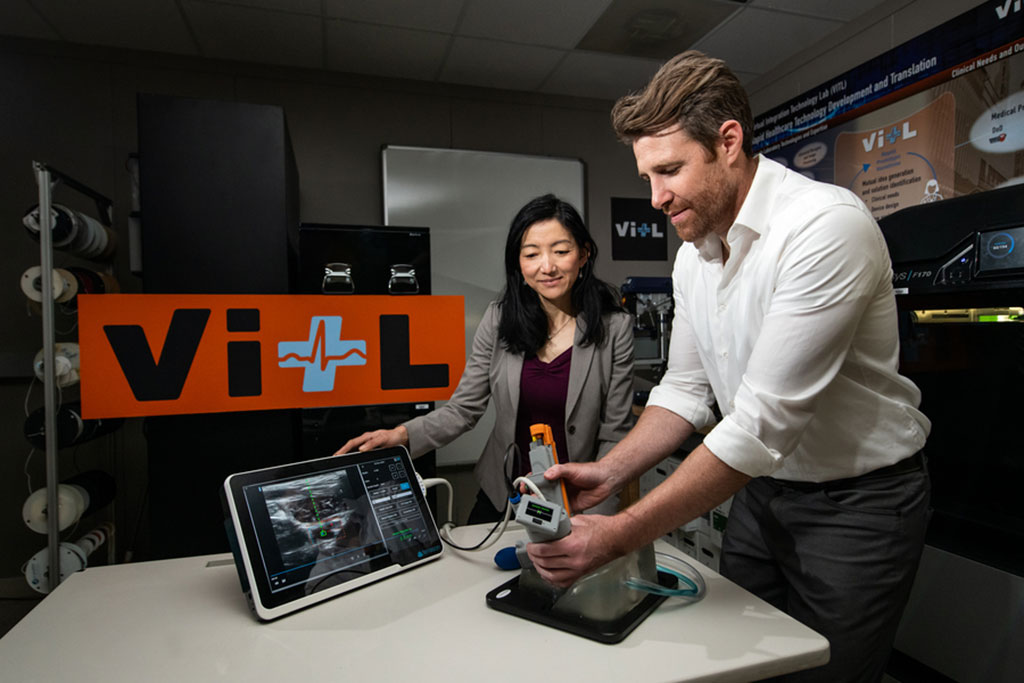

After a traumatic accident, there is a small window of time when medical professionals can apply lifesaving treatment to victims with severe internal bleeding. Delivering this type of care is complex, and key interventions require inserting a needle and catheter into a central blood vessel, through which fluids, medications, or other aids can be given. Researchers have developed a lifesaving technology that helps a range of users deliver complex medical interventions at the point of injury.
A team of researchers at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT, Cambridge, MA, USA) and physicians at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH, Boston, MA, USA) have developed a solution to this problem. The Artificial Intelligence–Guided Ultrasound Intervention Device (AI-GUIDE) is a handheld platform technology that has the potential to help personnel with simple training to quickly install a catheter into a common femoral vessel, enabling rapid treatment at the point of injury.
AI-GUIDE is a platform device made of custom-built algorithms and integrated robotics that could pair with most commercial portable ultrasound devices. To operate AI-GUIDE, a user first places it on the patient’s body, near where the thigh meets the abdomen. A simple targeting display guides the user to the correct location and then instructs them to pull a trigger, which precisely inserts the needle into the vessel. The device verifies that the needle has penetrated the blood vessel, and then prompts the user to advance an integrated guidewire, a thin wire inserted into the body to guide a larger instrument, such as a catheter, into a vessel. The user then manually advances a catheter. Once the catheter is securely in the blood vessel, the device withdraws the needle and the user can remove the device. With the catheter safely inside the vessel, responders can then deliver fluid, medicine, or other interventions.
The MIT researchers developed the AI in the device by leveraging technology used for real-time object detection in images. These algorithms trained on a large dataset of ultrasound scans interpret the visual data coming in from the ultrasound that is paired with AI-GUIDE and then indicate the correct blood vessel location to the user on the display. For the user, the device may seem as easy to use as pressing a button to advance a needle, but to ensure rapid and reliable success, a lot is happening behind the scenes. For example, when a patient has lost a large volume of blood and becomes hypotensive, veins that would typically be round and full of blood become flat. When the needle tip reaches the center of the vein, the wall of the vein is likely to “tent” inward, rather than being punctured by the needle. As a result, though the needle was injected to the proper location, it fails to enter the vessel. To ensure that the needle reliably punctures the vessel, the team engineered the device to be able to check its own work.
AI-GUIDE has shown very high injection success rates, even in hypotensive scenarios where veins are likely to tent. Users with medical experience ranging from zero to greater than 15 years tested AI-GUIDE on an artificial model of human tissue and blood vessels and one expert user tested it on a series of live, sedated pigs. The team reported that after only two minutes of verbal training, all users of the device on the artificial human tissue were successful in placing a needle, with all but one completing the task in less than one minute. The expert user was also successful in quickly placing both the needle and the integrated guidewire and catheter in about a minute. The needle insertion speed and accuracy were comparable to that of experienced clinicians operating in hospital environments on human patients. AI-GUIDE’s design makes it stable and easy to use, directly translates to low training requirements and effective performance. Right now, the team is continuing to test the device and work on fully automating every step of its operation. In particular, they want to automate the guidewire and catheter insertion steps to further reduce risk of user error or potential for infection.
“AI-GUIDE has the potential to be faster, more precise, safer, and require less training than current manual image-guided needle placement procedures,” said Theodore Pierce, a radiologist and collaborator from MGH. “The modular design also permits easy adaptation to a variety of clinical scenarios beyond vascular access, including minimally invasive surgery, image-guided biopsy, and imaging-directed cancer therapy.”
“We see the AI-GUIDE platform technology becoming ubiquitous throughout the health-care system, enabling faster and more accurate treatment by users with a broad range of expertise, for both pre-hospital emergency interventions and routine image-guided procedures,” said Matt Johnson, a research team member from the MIT laboratory’s Human Health and Performance Systems Group.
Latest Ultrasound News
- Wearable Ultrasound Imaging System to Enable Real-Time Disease Monitoring
- Ultrasound Technique Visualizes Deep Blood Vessels in 3D Without Contrast Agents
- Ultrasound Probe Images Entire Organ in 4D

- Disposable Ultrasound Patch Performs Better Than Existing Devices
- Non-Invasive Ultrasound-Based Tool Accurately Detects Infant Meningitis
- Breakthrough Deep Learning Model Enhances Handheld 3D Medical Imaging
- Pain-Free Breast Imaging System Performs One Minute Cancer Scan
- Wireless Chronic Pain Management Device to Reduce Need for Painkillers and Surgery
- New Medical Ultrasound Imaging Technique Enables ICU Bedside Monitoring
- New Incision-Free Technique Halts Growth of Debilitating Brain Lesions
- AI-Powered Lung Ultrasound Outperforms Human Experts in Tuberculosis Diagnosis
- AI Identifies Heart Valve Disease from Common Imaging Test
- Novel Imaging Method Enables Early Diagnosis and Treatment Monitoring of Type 2 Diabetes
- Ultrasound-Based Microscopy Technique to Help Diagnose Small Vessel Diseases
- Smart Ultrasound-Activated Immune Cells Destroy Cancer Cells for Extended Periods
- Tiny Magnetic Robot Takes 3D Scans from Deep Within Body
Channels
Radiography
view channel
Routine Mammograms Could Predict Future Cardiovascular Disease in Women
Mammograms are widely used to screen for breast cancer, but they may also contain overlooked clues about cardiovascular health. Calcium deposits in the arteries of the breast signal stiffening blood vessels,... Read more
AI Detects Early Signs of Aging from Chest X-Rays
Chronological age does not always reflect how fast the body is truly aging, and current biological age tests often rely on DNA-based markers that may miss early organ-level decline. Detecting subtle, age-related... Read moreMRI
view channel
MRI Scans Reveal Signature Patterns of Brain Activity to Predict Recovery from TBI
Recovery after traumatic brain injury (TBI) varies widely, with some patients regaining full function while others are left with lasting disabilities. Prognosis is especially difficult to assess in patients... Read more
Novel Imaging Approach to Improve Treatment for Spinal Cord Injuries
Vascular dysfunction in the spinal cord contributes to multiple neurological conditions, including traumatic injuries and degenerative cervical myelopathy, where reduced blood flow can lead to progressive... Read more
AI-Assisted Model Enhances MRI Heart Scans
A cardiac MRI can reveal critical information about the heart’s function and any abnormalities, but traditional scans take 30 to 90 minutes and often suffer from poor image quality due to patient movement.... Read more
AI Model Outperforms Doctors at Identifying Patients Most At-Risk of Cardiac Arrest
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is one of the most common inherited heart conditions and a leading cause of sudden cardiac death in young individuals and athletes. While many patients live normal lives, some... Read moreUltrasound
view channel
Wearable Ultrasound Imaging System to Enable Real-Time Disease Monitoring
Chronic conditions such as hypertension and heart failure require close monitoring, yet today’s ultrasound imaging is largely confined to hospitals and short, episodic scans. This reactive model limits... Read more
Ultrasound Technique Visualizes Deep Blood Vessels in 3D Without Contrast Agents
Producing clear 3D images of deep blood vessels has long been difficult without relying on contrast agents, CT scans, or MRI. Standard ultrasound typically provides only 2D cross-sections, limiting clinicians’... Read moreNuclear Medicine
view channel
Cancer “Flashlight” Shows Who Can Benefit from Targeted Treatments
Targeted cancer therapies can be highly effective, but only when a patient’s tumor expresses the specific protein the treatment is designed to attack. Determining this usually requires biopsies or advanced... Read more
PET Imaging of Inflammation Predicts Recovery and Guides Therapy After Heart Attack
Acute myocardial infarction can trigger lasting heart damage, yet clinicians still lack reliable tools to identify which patients will regain function and which may develop heart failure.... Read more
Radiotheranostic Approach Detects, Kills and Reprograms Aggressive Cancers
Aggressive cancers such as osteosarcoma and glioblastoma often resist standard therapies, thrive in hostile tumor environments, and recur despite surgery, radiation, or chemotherapy. These tumors also... Read more
New Imaging Solution Improves Survival for Patients with Recurring Prostate Cancer
Detecting recurrent prostate cancer remains one of the most difficult challenges in oncology, as standard imaging methods such as bone scans and CT scans often fail to accurately locate small or early-stage tumors.... Read moreGeneral/Advanced Imaging
view channel
AI-Based Tool Predicts Future Cardiovascular Events in Angina Patients
Stable coronary artery disease is a common cause of chest pain, yet accurately identifying patients at the highest risk of future heart attacks or death remains difficult. Standard coronary CT scans show... Read more
AI-Based Tool Accelerates Detection of Kidney Cancer
Diagnosing kidney cancer depends on computed tomography scans, often using contrast agents to reveal abnormalities in kidney structure. Tumors are not always searched for deliberately, as many scans are... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more
Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in medical diagnostics market is expanding with early disease detection being one of its key applications and image recognition becoming a compelling consumer proposition... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
GE HealthCare and NVIDIA Collaboration to Reimagine Diagnostic Imaging
GE HealthCare (Chicago, IL, USA) has entered into a collaboration with NVIDIA (Santa Clara, CA, USA), expanding the existing relationship between the two companies to focus on pioneering innovation in... Read more
Patient-Specific 3D-Printed Phantoms Transform CT Imaging
New research has highlighted how anatomically precise, patient-specific 3D-printed phantoms are proving to be scalable, cost-effective, and efficient tools in the development of new CT scan algorithms... Read more
Siemens and Sectra Collaborate on Enhancing Radiology Workflows
Siemens Healthineers (Forchheim, Germany) and Sectra (Linköping, Sweden) have entered into a collaboration aimed at enhancing radiologists' diagnostic capabilities and, in turn, improving patient care... Read more