Portable MRI Machine with Automatic Motion Correction Enables Brain Scans Inside Ambulance
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 06 Jan 2022 |
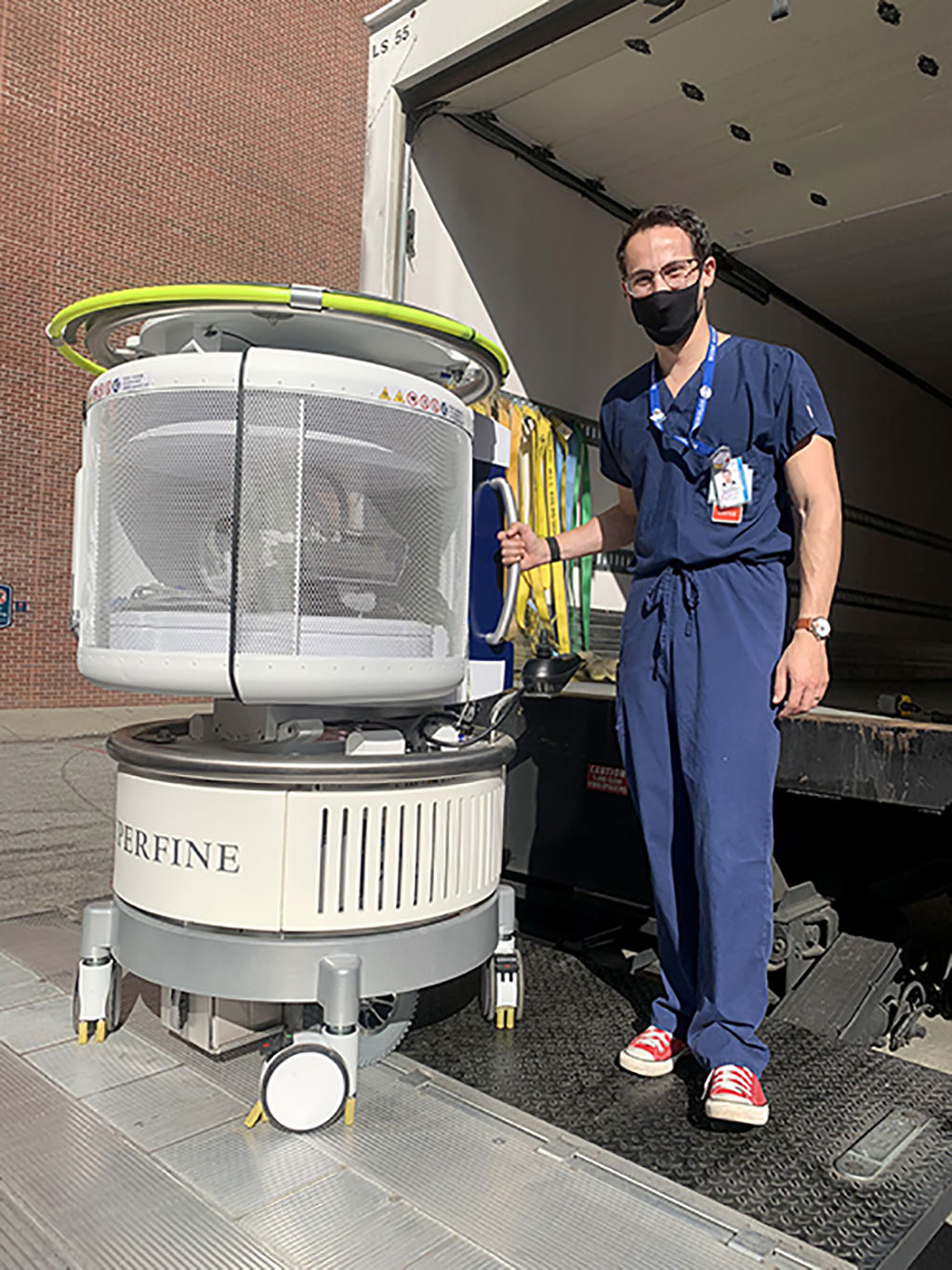

A new portable MRI system that is likely to be used in space could also be used to take brain scans inside stroke patients inside their home or the back of the ambulance.
Doctors at the Medical University of South Carolina’s Comprehensive Stroke Center (Charleston, SC, USA) used a portable MRI developed by Hyperfine (Guilford, CT, USA) to test whether an MRI scan could be successfully completed in the back of a moving ambulance.
Minutes matter for stroke patients when the brain is being deprived of oxygen. Reducing the time before treatment begins isn’t simply a matter of reducing the number of stroke deaths but also about reducing the severity of disabilities for those who survive. For every 15-minute reduction in ‘door-to-needle time’ there is a significant improvement in patient outcomes, including reduction in disabilities and reduction in mortality. Doctors at MUSC Health constantly work with their community hospital colleagues on initiatives to cut down the steps that need to happen between the time a stroke patient is wheeled through the ambulance bay until treatment can begin – for example, by developing a TeleEMS program so emergency medical technicians can consult with stroke specialists while inside a patient’s home or the back of the ambulance.
However, some things still need to happen at the hospital before treatment can begin, though, like scans of the brain to confirm a stroke and determine what type it is. If it were possible to do an MRI scan in the ambulance, then not only would doctors be better prepared when the ambulance arrived, but the stroke specialists could determine whether the patient could be treated at a community hospital or would need to go directly to a specialized stroke center.
Hyperfine’s portable MRI is designed to be wheeled around a hospital to conduct brain scans at the bedside for patients who cannot be moved. It weighs 1,400 pounds and is roughly the size of an office printer turned on its side, making it smaller than the average MRI machine. The portable MRI features automatic motion correction and as the MUSC team drove along in the ambulance, it could see that as the ambulance bounced over the roads the scanner actually moved. The team wanted to demonstrate whether the portable MRI would still be able to function and acquire diagnostic images in a moving vehicle and was amazed to see that the scanner itself was able to sense the motion and correct that in real time, enabling crystal clear images.
Some areas have started deploying mobile stroke units, which are ambulances with CT scanners, a critical care nurse and a CT technician in addition to a paramedic. While these units have been shown to improve patients’ outcomes by decreasing the time to treatment, they are expensive at USD 600,000 to USD 1 million per unit. A portable MRI machine would be a fraction of that cost and would bring the advantages of MRI scanning. MRI, unlike CT, does not use radiation, thus eliminating radiation exposure to the patient or the first responders.
Additionally, an MRI is also a more accurate diagnostic tool for stroke. It can show smaller blockages, and, in the case of strokes caused by blood clots, it would allow doctors to determine whether a patient needed the clot-busting drug tPA, which can be administered at community hospitals, or a thrombectomy, a surgical procedure to remove the clot. The current triage system calls for patients to first go to a tPA-capable center and receive tPA. Although tPA works well for small blood clots, it is much less likely to work on large clots.
“So, if you can imagine, if a patient has a large clot in the brain, they go to the tPA center and get tPA and then transfer here. By the time they get here, there is a very good chance that those patients will no longer be eligible for thrombectomy because there's already so much damage,” said Sami Al Kasab, M.D., associate medical director of the MUSC Health Teleneuroscience Program.
Related Links:
Medical University of South Carolina
Hyperfine
Latest MRI News
- Novel Imaging Approach to Improve Treatment for Spinal Cord Injuries
- AI-Assisted Model Enhances MRI Heart Scans
- AI Model Outperforms Doctors at Identifying Patients Most At-Risk of Cardiac Arrest
- New MRI Technique Reveals Hidden Heart Issues
- Shorter MRI Exam Effectively Detects Cancer in Dense Breasts
- MRI to Replace Painful Spinal Tap for Faster MS Diagnosis
- MRI Scans Can Identify Cardiovascular Disease Ten Years in Advance
- Simple Brain Scan Diagnoses Parkinson's Disease Years Before It Becomes Untreatable
- Cutting-Edge MRI Technology to Revolutionize Diagnosis of Common Heart Problem
- New MRI Technique Reveals True Heart Age to Prevent Attacks and Strokes
- AI Tool Predicts Relapse of Pediatric Brain Cancer from Brain MRI Scans
- AI Tool Tracks Effectiveness of Multiple Sclerosis Treatments Using Brain MRI Scans
- Ultra-Powerful MRI Scans Enable Life-Changing Surgery in Treatment-Resistant Epileptic Patients
- AI-Powered MRI Technology Improves Parkinson’s Diagnoses
- Biparametric MRI Combined with AI Enhances Detection of Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer
- First-Of-Its-Kind AI-Driven Brain Imaging Platform to Better Guide Stroke Treatment Options
Channels
Radiography
view channel
X-Ray Breakthrough Captures Three Image-Contrast Types in Single Shot
Detecting early-stage cancer or subtle changes deep inside tissues has long challenged conventional X-ray systems, which rely only on how structures absorb radiation. This limitation keeps many microstructural... Read more
AI Generates Future Knee X-Rays to Predict Osteoarthritis Progression Risk
Osteoarthritis, a degenerative joint disease affecting over 500 million people worldwide, is the leading cause of disability among older adults. Current diagnostic tools allow doctors to assess damage... Read moreUltrasound
view channel
Wearable Ultrasound Imaging System to Enable Real-Time Disease Monitoring
Chronic conditions such as hypertension and heart failure require close monitoring, yet today’s ultrasound imaging is largely confined to hospitals and short, episodic scans. This reactive model limits... Read more
Ultrasound Technique Visualizes Deep Blood Vessels in 3D Without Contrast Agents
Producing clear 3D images of deep blood vessels has long been difficult without relying on contrast agents, CT scans, or MRI. Standard ultrasound typically provides only 2D cross-sections, limiting clinicians’... Read moreNuclear Medicine
view channel
PET Imaging of Inflammation Predicts Recovery and Guides Therapy After Heart Attack
Acute myocardial infarction can trigger lasting heart damage, yet clinicians still lack reliable tools to identify which patients will regain function and which may develop heart failure.... Read more
Radiotheranostic Approach Detects, Kills and Reprograms Aggressive Cancers
Aggressive cancers such as osteosarcoma and glioblastoma often resist standard therapies, thrive in hostile tumor environments, and recur despite surgery, radiation, or chemotherapy. These tumors also... Read more
New Imaging Solution Improves Survival for Patients with Recurring Prostate Cancer
Detecting recurrent prostate cancer remains one of the most difficult challenges in oncology, as standard imaging methods such as bone scans and CT scans often fail to accurately locate small or early-stage tumors.... Read moreGeneral/Advanced Imaging
view channel
3D Scanning Approach Enables Ultra-Precise Brain Surgery
Precise navigation is critical in neurosurgery, yet even small alignment errors can affect outcomes when operating deep within the brain. A new 3D surface-scanning approach now provides a radiation-free... Read more
AI Tool Improves Medical Imaging Process by 90%
Accurately labeling different regions within medical scans, a process known as medical image segmentation, is critical for diagnosis, surgery planning, and research. Traditionally, this has been a manual... Read more
New Ultrasmall, Light-Sensitive Nanoparticles Could Serve as Contrast Agents
Medical imaging technologies face ongoing challenges in capturing accurate, detailed views of internal processes, especially in conditions like cancer, where tracking disease development and treatment... Read more
AI Algorithm Accurately Predicts Pancreatic Cancer Metastasis Using Routine CT Images
In pancreatic cancer, detecting whether the disease has spread to other organs is critical for determining whether surgery is appropriate. If metastasis is present, surgery is not recommended, yet current... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more
Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in medical diagnostics market is expanding with early disease detection being one of its key applications and image recognition becoming a compelling consumer proposition... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
GE HealthCare and NVIDIA Collaboration to Reimagine Diagnostic Imaging
GE HealthCare (Chicago, IL, USA) has entered into a collaboration with NVIDIA (Santa Clara, CA, USA), expanding the existing relationship between the two companies to focus on pioneering innovation in... Read more
Patient-Specific 3D-Printed Phantoms Transform CT Imaging
New research has highlighted how anatomically precise, patient-specific 3D-printed phantoms are proving to be scalable, cost-effective, and efficient tools in the development of new CT scan algorithms... Read more
Siemens and Sectra Collaborate on Enhancing Radiology Workflows
Siemens Healthineers (Forchheim, Germany) and Sectra (Linköping, Sweden) have entered into a collaboration aimed at enhancing radiologists' diagnostic capabilities and, in turn, improving patient care... Read more