MRI-Based Technology Assesses Muscle Composition 
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 21 Dec 2021 |
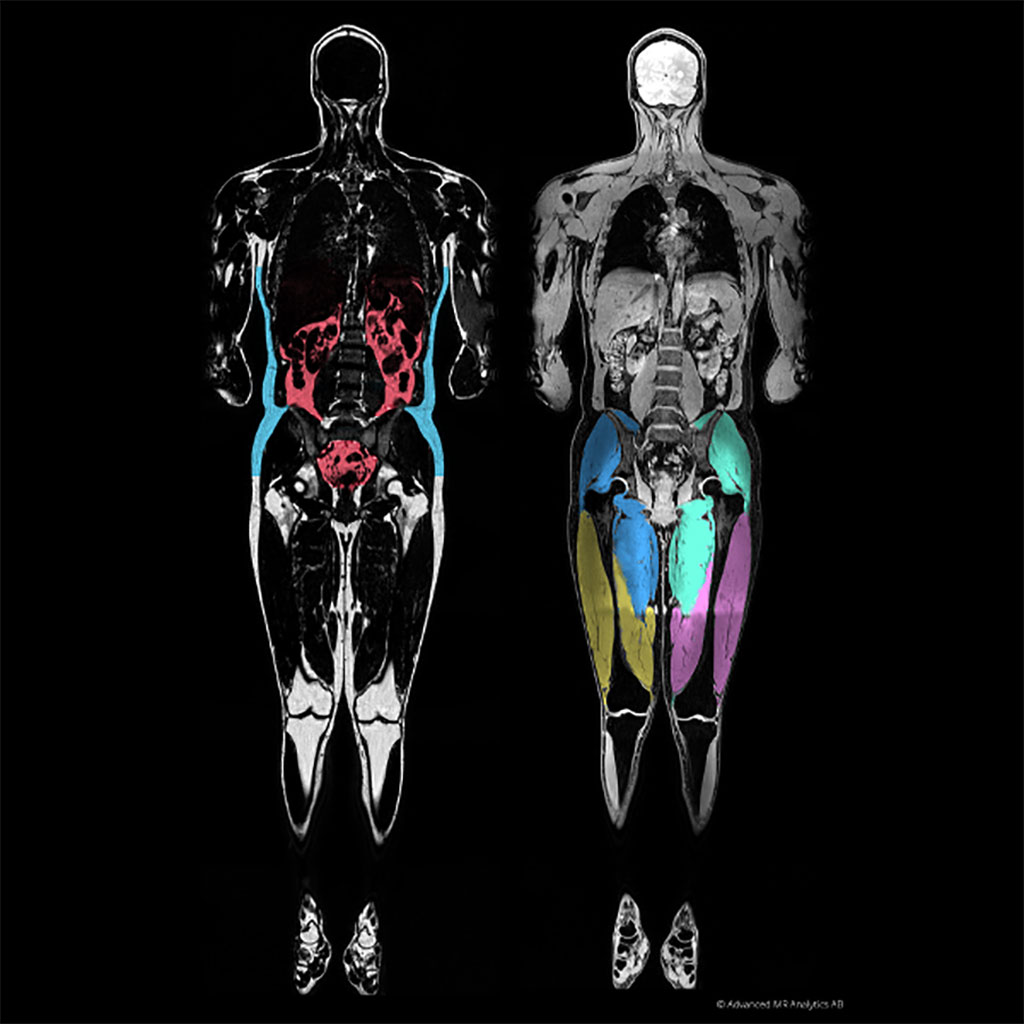
Image: A graphical MAsS score of visceral fat (L) and muscle (R) (Photo courtesy of AMRA medical)
Novel software can analyze a patient with suspected sarcopenia using a rapid neck-to-knee magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan.
The AMRA medical (Linköping, Sweden) Muscle Assessment Score (MAsS) Scan is designed to measure volumetric changes in muscle mass and the diffusion of fat infiltration into the muscle. The scanning protocol is based on symmetrical chemical shift imaging, also known as two-point Dixon imaging. Acquired images consist of fat and water image pairs, as reconstructed by the software. The images are automatically calibrated and corrected for variations caused by inhomogeneity in the magnetic field and coil sensitivity.
The resulting report contains the MAsS scan, anatomic and color-coded images, and precise body composition measurements with contextual insights based on AMRA's reference database. The platform-agnostic software works across all major 1.5 and 3T MR scanners, such that output across scanners is standardized and calibrated using the fat signal as an internal reference. The value of each pixel shows the percentage of fat in it; partial-volume effects do not affect quantification, and thin layers of fat (or even diffuse infiltration) contribute to fat quantification.
In addition, AMRA automates the classification and quantification of fat and muscle groups, with segmentation based on registration between the image data volume and manually segmented prototype volumes. Body fat is divided into subcutaneous, visceral, and ectopic compartments; muscle groups are automatically classified, and the volume of each individual muscle group is obtained. Additionally, the amount of fat in any user-defined region, (e.g. a muscle or an internal organ) can be calculated also for diffuse fat infiltration.
“The AMRA MAsS Scan will greatly benefit patients by allowing clinicians to assess sarcopenia and improve patient outcomes an objectively and accurately assess muscle quality and take action,” said Eric Converse, CEO of AMRA Medical. “The beauty of the report is that it is easy-to-understand, it creates a common language among clinicians with the muscle assessment score, and adds only minutes to an already prescribed MRI.”
Sarcopenia (from the Greek, meaning "poverty of flesh") is the degenerative loss of skeletal muscle mass. Sarcopenia is characterized first by muscle atrophy, along with a reduction in muscle tissue "quality," caused by such factors as replacement of muscle fibers with fat, an increase in fibrosis, changes in muscle metabolism, oxidative stress, and degeneration of the neuromuscular junction. Combined, these changes lead to progressive loss of muscle function and frailty. Sarcopenia can be thought of as a muscular analog of osteoporosis, also caused by inactivity and counteracted by exercise. The combination of osteoporosis and sarcopenia results in the significant frailty often seen in the elderly population.
Related Links:
AMRA medical
The AMRA medical (Linköping, Sweden) Muscle Assessment Score (MAsS) Scan is designed to measure volumetric changes in muscle mass and the diffusion of fat infiltration into the muscle. The scanning protocol is based on symmetrical chemical shift imaging, also known as two-point Dixon imaging. Acquired images consist of fat and water image pairs, as reconstructed by the software. The images are automatically calibrated and corrected for variations caused by inhomogeneity in the magnetic field and coil sensitivity.
The resulting report contains the MAsS scan, anatomic and color-coded images, and precise body composition measurements with contextual insights based on AMRA's reference database. The platform-agnostic software works across all major 1.5 and 3T MR scanners, such that output across scanners is standardized and calibrated using the fat signal as an internal reference. The value of each pixel shows the percentage of fat in it; partial-volume effects do not affect quantification, and thin layers of fat (or even diffuse infiltration) contribute to fat quantification.
In addition, AMRA automates the classification and quantification of fat and muscle groups, with segmentation based on registration between the image data volume and manually segmented prototype volumes. Body fat is divided into subcutaneous, visceral, and ectopic compartments; muscle groups are automatically classified, and the volume of each individual muscle group is obtained. Additionally, the amount of fat in any user-defined region, (e.g. a muscle or an internal organ) can be calculated also for diffuse fat infiltration.
“The AMRA MAsS Scan will greatly benefit patients by allowing clinicians to assess sarcopenia and improve patient outcomes an objectively and accurately assess muscle quality and take action,” said Eric Converse, CEO of AMRA Medical. “The beauty of the report is that it is easy-to-understand, it creates a common language among clinicians with the muscle assessment score, and adds only minutes to an already prescribed MRI.”
Sarcopenia (from the Greek, meaning "poverty of flesh") is the degenerative loss of skeletal muscle mass. Sarcopenia is characterized first by muscle atrophy, along with a reduction in muscle tissue "quality," caused by such factors as replacement of muscle fibers with fat, an increase in fibrosis, changes in muscle metabolism, oxidative stress, and degeneration of the neuromuscular junction. Combined, these changes lead to progressive loss of muscle function and frailty. Sarcopenia can be thought of as a muscular analog of osteoporosis, also caused by inactivity and counteracted by exercise. The combination of osteoporosis and sarcopenia results in the significant frailty often seen in the elderly population.
Related Links:
AMRA medical
Latest MRI News
- MRI Scans Reveal Signature Patterns of Brain Activity to Predict Recovery from TBI
- Novel Imaging Approach to Improve Treatment for Spinal Cord Injuries
- AI-Assisted Model Enhances MRI Heart Scans
- AI Model Outperforms Doctors at Identifying Patients Most At-Risk of Cardiac Arrest
- New MRI Technique Reveals Hidden Heart Issues
- Shorter MRI Exam Effectively Detects Cancer in Dense Breasts
- MRI to Replace Painful Spinal Tap for Faster MS Diagnosis
- MRI Scans Can Identify Cardiovascular Disease Ten Years in Advance
- Simple Brain Scan Diagnoses Parkinson's Disease Years Before It Becomes Untreatable
- Cutting-Edge MRI Technology to Revolutionize Diagnosis of Common Heart Problem
- New MRI Technique Reveals True Heart Age to Prevent Attacks and Strokes
- AI Tool Predicts Relapse of Pediatric Brain Cancer from Brain MRI Scans
- AI Tool Tracks Effectiveness of Multiple Sclerosis Treatments Using Brain MRI Scans
- Ultra-Powerful MRI Scans Enable Life-Changing Surgery in Treatment-Resistant Epileptic Patients
- AI-Powered MRI Technology Improves Parkinson’s Diagnoses
- Biparametric MRI Combined with AI Enhances Detection of Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer
Channels
Radiography
view channel
Routine Mammograms Could Predict Future Cardiovascular Disease in Women
Mammograms are widely used to screen for breast cancer, but they may also contain overlooked clues about cardiovascular health. Calcium deposits in the arteries of the breast signal stiffening blood vessels,... Read more
AI Detects Early Signs of Aging from Chest X-Rays
Chronological age does not always reflect how fast the body is truly aging, and current biological age tests often rely on DNA-based markers that may miss early organ-level decline. Detecting subtle, age-related... Read moreUltrasound
view channel
Wearable Ultrasound Imaging System to Enable Real-Time Disease Monitoring
Chronic conditions such as hypertension and heart failure require close monitoring, yet today’s ultrasound imaging is largely confined to hospitals and short, episodic scans. This reactive model limits... Read more
Ultrasound Technique Visualizes Deep Blood Vessels in 3D Without Contrast Agents
Producing clear 3D images of deep blood vessels has long been difficult without relying on contrast agents, CT scans, or MRI. Standard ultrasound typically provides only 2D cross-sections, limiting clinicians’... Read moreNuclear Medicine
view channel
Radiopharmaceutical Molecule Marker to Improve Choice of Bladder Cancer Therapies
Targeted cancer therapies only work when tumor cells express the specific molecular structures they are designed to attack. In urothelial carcinoma, a common form of bladder cancer, the cell surface protein... Read more
Cancer “Flashlight” Shows Who Can Benefit from Targeted Treatments
Targeted cancer therapies can be highly effective, but only when a patient’s tumor expresses the specific protein the treatment is designed to attack. Determining this usually requires biopsies or advanced... Read moreGeneral/Advanced Imaging
view channel
AI Tool Offers Prognosis for Patients with Head and Neck Cancer
Oropharyngeal cancer is a form of head and neck cancer that can spread through lymph nodes, significantly affecting survival and treatment decisions. Current therapies often involve combinations of surgery,... Read more
New 3D Imaging System Addresses MRI, CT and Ultrasound Limitations
Medical imaging is central to diagnosing and managing injuries, cancer, infections, and chronic diseases, yet existing tools each come with trade-offs. Ultrasound, X-ray, CT, and MRI can be costly, time-consuming,... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more
Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in medical diagnostics market is expanding with early disease detection being one of its key applications and image recognition becoming a compelling consumer proposition... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
GE HealthCare and NVIDIA Collaboration to Reimagine Diagnostic Imaging
GE HealthCare (Chicago, IL, USA) has entered into a collaboration with NVIDIA (Santa Clara, CA, USA), expanding the existing relationship between the two companies to focus on pioneering innovation in... Read more
Patient-Specific 3D-Printed Phantoms Transform CT Imaging
New research has highlighted how anatomically precise, patient-specific 3D-printed phantoms are proving to be scalable, cost-effective, and efficient tools in the development of new CT scan algorithms... Read more
Siemens and Sectra Collaborate on Enhancing Radiology Workflows
Siemens Healthineers (Forchheim, Germany) and Sectra (Linköping, Sweden) have entered into a collaboration aimed at enhancing radiologists' diagnostic capabilities and, in turn, improving patient care... Read more










 Guided Devices.jpg)










